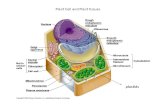
Plant Tissues...Plant Tissues A collection of cells performing a specific function is called tissue....
Transcript of Plant Tissues...Plant Tissues A collection of cells performing a specific function is called tissue....

Plant Tissues
A collection of cells performing a specific function is called tissue.
Plant tissues can be grouped into plant tissue systems each performing
specialized functions. A plant tissue system is defined as a functional
unit, connecting all organs of a plant. Plant tissue system is also
grouped into various tissues based on their functions. Let’s find out
more.
Types of Plant Tissues
Plant tissues can be broadly classified based on the ability of the cells
to divide into Merismatic tissue and Permanent tissue.

What is Dermal Tissue System?
Merismatic tissues consist of a group of cells that have the ability to
divide. These tissues are small, cuboidal, densely packed cells which
keep dividing to form new cells. These tissues are capable of
stretching, enlarging and differentiating into other types of tissues as
they mature. Meristematic tissues give rise to permanent tissues.
Merismatic tissues can be of three types depending on the region
where they are present: Apical meristems, lateral meristems, and
intercalary meristems.
Permanent tissues are derived from the merismatic tissues and have
lost their ability to divide. They have attained their mature form. They
are further classified into two types: Simple and complex permanent
tissues.
Browse more Topics under Anatomy Of Flowering Plants
● Tissue System
● Stem
● Leaf
● Inflorescence
● Secondary Growth

● Flower
● The Fruit
● The Seed
● Classification of Flowering Plants
● Anatomy of Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants
Permanent Tissues
The permanent tissues form the major portion of the plant.
Simple Permanent tissues ● Parenchyma– These tissues are found in the soft parts of a plant
such as the roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. The cells of this
tissue are loosely packed and contain large intercellular spaces
between them. Each cell has a vacuole at the center. The
functions of parenchyma tissues are storage, photosynthesis,
and to help the plant float on water.
● Collenchyma- Are similar to parenchyma cells with thicker cell
walls. They are meant to provide mechanical support to the
plant structure in parts such as petiole of the leaf.

● Sclerenchyma- The cells of this tissue are dead. They are rigid,
contain thick and lignified secondary walls. Their main
function is to provide strength and support to parts of the plant.
Complex Permanent Tissue
Unlike simple permanent cells which look the same and are made up
of one type of cells, complex permanent tissues are made up of more
than one type of cells. These different types of cells coordinate to
perform a function. Xylem and Phloem are complex permanent tissues
and are found in the vascular bundles in the plants.
Xylem- It consists of tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem
fibres. Tracheids and vessels are hollow tube-like structures that help
in conducting water and minerals. The xylem conducts only in one
direction i.e vertically. The xylem parenchyma is responsible for

storing the prepared food and assists in the conduction of water.
Xylem fibres are supportive in function.
Phloem- It consists of four of elements: sieve tubes, companion cells,
phloem fibres and the phloem parenchyma. Unlike the xylem, phloem
conducts in both directions. It is responsible for transporting food
from the leaves to the other parts of the plant. Phloem contains living
tissues except for fibres that are dead tissues.
Functions of plant tissues Plant tissues have different functions depending upon their structure and
location
● Help provide mechanical strength to organs.
● They help in providing the elasticity and flexibility to the
organs.
● They help the tissues to bend easily in various parts of a plant
like- leaf, stem, and branches without damaging the plant
● The xylem and phloem tissues help in transportation of
material throughout the plants
● They divide to produce new cells and help in the growth of the
plants.

● They help in various cellular metabolisms like photosynthesis,
regeneration, respiration, etc.
Anatomy of Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants
Solved Example for You
Q: Pick the odd one out.
(a) sieve tubes (b) companion cells
(c) phloem fibres (d) Tracheids
Sol. (d) Tracheids
The odd one out is option (d) tracheids as they are a part of xylem
tissue whereas the other three options are parts of phloem tissue.
Stem: Functions, Structure, and Types
The main functions of stems are to support and elevation of leaves,
fruits, and flowers. Stem arranges leaves in a way that it gets direct
sunlight to perform photosynthesis. Xylem and Phloem conduct water

across the plant. Stems stores food, water, and nutrients. Cells of a
stem, meristems, produce new living tissues. Underground stem,
Aerial stem, and subaerial stem are three different types of Stem. A
stem has many important functions it performs other than letting you
climb a tree. Let us take an in-depth look at the stem of plants.
A plant stem is one of the two main structural axes of a vascular plant.
It is the part of the plant that lies above the ground. Few stems are also
found underground and are considered to be stem modifications.
Functions of Stem
● It supports and holds leaves, flowers, and fruits.
● The stem allows the leaves to arrange in a way that they are
able to receive direct sunlight in order to efficiently perform
photosynthesis. The arrangement and position of leaves also
allow for gas exchange.
● The xylem and phloem present in the vascular bundles of stems
conduct water and minerals across the plant.
● Stems bear flowers and fruits in a position that facilitates the
processes of pollination, fertilization, and dispersion of seeds.

● Some stems undergo modification to store food and water.
Example: succulents.
● Few green stems contain chloroplasts and are capable of
carrying out photosynthesis as well.
● Some stems are modified to carry out vegetative propagation
which is a form of asexual reproduction seen in plants.
Browse more Topics under Anatomy Of Flowering Plants
● Plant Tissues
● Tissue System
● Leaf
● Inflorescence
● Secondary Growth
● Flower
● The Fruit
● The Seed
● Classification of Flowering Plants
● Anatomy of Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants
Structure of a Stem

The stem divides into nodes and internodes. The nodes give rise to the
leaves and hold the buds which grow into branches. The internodes
separate two nodes.
Internally, it contains three basic types of tissues: Dermal tissue,
Ground tissue, and Vascular tissue all of which are made of simple
cells.
● Epidermis: The epidermis is a single layer of cells that make up
the external tissue of the stem called dermal tissue. This tissue
covers the stem and protects the underlying tissue. Woody
plants have an extra layer of protection on top of the epidermis
known as bark. In some cases, the bears’ multi-cellular hairs
and a few stomata.

● Ground tissue divides into two- the central portion is known as
the pith and the cortex which lies between the vascular tissue
and the epidermis.
Learn more about the concept of the Tissue System here in detail.
The cortex can be further divided into three layers:
● Hypodermis: It is the outermost layer of the cortex. It is formed
of 4 to 5 cell thick layer of collenchymatous cells. These cells
are living and contain chloroplasts.
● General cortex: Lies below the hypodermis. It consists of
thin-walled parenchymatous cells with intercellular spaces.
Some of the cells have chloroplasts and are known as
chlorenchyma.
● Endodermis: The innermost layer of the cortex. It is made up of
a single row of compact barrel-shaped cells without
intercellular spaces. The cells of endodermis store starch grains
and so they are known as the starch sheath. Casparian strips are
distinctly visible in endodermal cells.
● The vascular tissue of the stem consists of the complex tissues
xylem and phloem which carry water and nutrients up and

down the length of the stem and are arranged in distinct strands
called vascular bundles. Cambium is a strip of thin-walled cells
that lie between the xylem and phloem in dicot plants.
Cambium is made up of merismatic cells and is responsible for
secondary growth. It is absent in monocots.
What are Plant Tissues?
Growth in a Stem
Growth in stems occurs in two ways:
● Primary growth occurs at the apical tips of the stem by virtue of
the rapidly dividing merismatic tissue in these regions of the
stem.
● Secondary growth is actually the increase in the thickness of
the stem by virtue of the lateral meristems. These are absent in
the herbaceous plants as they lack cambium which is
responsible for this type of growth.
Types of Stems

Based on their location with respect to the ground, there are three
types of stems:
● Underground stem
● Aerial stem
● Subaerial stem.
Understand Tissue System
Underground stems
These stems remain at the ground level and produce aerial shoots that
rise above the soil. Their roots are superficially present. These stems
are meant for storage of food and perennation. These stems are also
capable of vegetative propagation.

They are of different types as follows:
● Rhizome- is a thickened underground stem that has distinct
nodes and internodes and scaly leaves at the nodes. Example:
Ginger.
● Tuber- is a horizontal underground stem that becomes enlarged
at its growing tips due to the accumulation of stored food,
commonly starch. E.g. Potato.
● Bulb- It is a short underground stem with a fleshy base with
leafy scales. The stem is actually reduced to form a disc-like
structure. The nodes bear fleshy scales. On the upper side, the
disc bears a terminal bud surrounded by a number of leaves. E
.g. Onion.
● Corm- is a short, vertical, swollen underground stem of a plant
that serves as a food storage organ to enable the plant to
survive adverse conditions. E.g Colocasia
Know more about Secondary Growth
Subaerial Stems

These stems run parallel to the ground and give off roots at certain
intervals or nodes.
They are further divided into the following types:
● Runner- It grows parallel to the ground and has a creeping stem
with long internodes. On the lower surface, the nodes give out
adventitious roots at regular intervals. A runner develops from
the axils of lower leaves of the aerial stem
● Offset- These are shorter and thicker than the runner and are
often seen in aquatic plants
● Stolon- It is similar to a runner but arises from the lower part of
the main axis.

● Sucker- These stems are similar to the stolon but it grows
obliquely upwards and gives rise to a new plant
What is Inflorescence?
Aerial Stems
These stems are found above the ground and perform varied functions.
They are of the following types:
● Thorns- These stem modifications appear as hard, woody and
sharp outgrowths that protect the plant. example: roses
● Tendril – These types of stems are slender, twining strands that
enable a plant to seek support while climbing on other surfaces.

● Phylloclade- This type of stem is a green, flattened or
cylindrical one that resembles a leaf. A phylloclade is capable
of performing photosynthesis and we can find them in
xerophytes or in other plants that have little or no leaves.
● Cladode- This is a modification of the phylloclade where it
contains one or more internodes.
● Bulbil- These stems are actually modified axillary buds which
become fleshy and rounded due to the storage of food. They
become detached from the plant, fall o the ground and develop
into a new plant, thus help in vegetative propagation.
Solved Example for You
Q: What kind of a stem is a potato?
a. Tuber
b. Tendril
c. Bulbil
d. Rhizome
Sol: The correct option is (a) Tuber

A potato is an underground modification of a stem and it stores food
in the form of starch. This type of stem modification is called a tuber.
Leaf
A leaf is actually called ‘the kitchen of the plant’. This is because
they are the main organ responsible for photosynthesis, through which
the plant produces its energy a.k.a. it’s food. They obtain their green
color due to the presence of chlorophyll. Let us learn more about
them.
Leaf
A leaf is the green, flat lateral outgrowth in plants. They come in
different shapes, sizes, and colors, and are generally dorso-ventrally
flattened and thin. They are the main organ responsible for
photosynthesis as they contain chlorophyll.
Browse more Topics under Anatomy Of Flowering Plants
● Plant Tissues
● Tissue System
● Stem
● Inflorescence

● Secondary Growth
● Flower
● The Fruit
● The Seed
● Classification of Flowering Plants
● Anatomy of Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants
Parts of a Leaf
Leaves have two main parts: The leaf blade and the Stalk or the
petiole.
● The leaf blade: It is also called the lamina. It’s generally broad
and flat. It is in this layer that photosynthesis occurs. It contains
a prominent midrib at the center of the leaf blade which is the
main vein. From this midrib arise branches called veins. They
are of different types depending upon the type of edges, the
pattern of the veins and the number of blades per leaf.

● The petiole: It is the stalk-like structure which connects the leaf
blade to the stem. The petiole has tiny tubes, that connect the
veins on the leaf blade to the stem. Few of these enable water
transport to the leaf while the other carry food away from the
leaf to other parts of the plant.
Some plants also contain another part called stipules. These are small
flap-like structures that grow at the base of the petioles. They are
protective in some plants when they protect the growing petiole while
in others, they fall off once the petiole starts growing.
Do you know about SEED ?
Types of Leaves
Leaves can be classified based on many anatomic and morphologic
features:
Based on Blade
● Simple Leaf- the lamina or the leaf blade is undivided. Even if
there are small divisions, they do not reach the midrib and
divide the lamina.

● Compound Leaf- The leaf blade is divided from the midrib into
two or more parts. Sometimes these divided parts function as
separate leaves.
Based on Shape of the Blade
● Elliptical
● Lanceolate
● Linear
● Ovate
● Cordate
Want to know about Plant Tissues ?
Based on the presence or absence of the petiole (stalk)
● Petiolated- These leaves have a stalk or petiole which attaches
them to the stem.
● Sessile- These leaves do not have a petiole and are directly
attached to the stem.
Based on the serration on the edge of the leaf blade

● Smooth: This type of leaf margin is called ‘entire’ leaf margin
and is smooth all around
● Sinuate: Have smooth curves along the margins
● Dentate: They have teethed margins
● Serrate: Have saw-teeth shaped margins
● Lobed: the leaf blade is divided but the division doesn’t reach
the midrib
Based on the arrangement of veins
● Parallel: The veins on the leaf blade run parallel to each other
maintaining the same distance throughout.
● Palmate: The veins originate at a point and diverge from the
point similar to the palm of the hand
● Pinnate: There is a midrib which is present in the middle of the
leaf blade. From this midrib arise the lateral veins.
Based on their arrangement on the stem
● Alternate: Each leaf arises from a separate node on the stem at
different levels

● Opposite: Each node gives rise to two leaves, one on each side
placed oppositely.
● Whorled: In this arrangement, several leaves are present at the
same level around the stem giving it a whorled appearance.
● Rosulate: The leaves arrange themselves in a ring-like pattern
around the stem.
Structure of a leaf
(Source: Wikipedia)
Each leaf consists of the following layers.
● Epidermis: It is the outermost layer and secretes a waxy
substance called the cuticle. The cuticle helps retain water
inside the leaf cells. The epidermis houses the guard cells

which regulate the movement of water into and outside the cell.
Guard cells do so by controlling the size of the pores also
called stomata.
● Mesophyll: This forms the middle layer of the leaf. It is
differentiated into two layers depending on the type of cells
found: palisade and spongy mesophyll layers. It is in this layer
that the chloroplasts are found. Chloroplasts are cell organelles
that contain chlorophyll which is required for photosynthesis.
The vascular tissues of the leaf are contained in the irregularly
arranged spongy mesophyll cells.
● Vascular Tissue: The vascular tissue is actually found in the
veins of the leaf. The vascular tissues are composed of xylem
and phloem which are responsible for the transport of water
and food.
Learn more to understand the concept of Tissue here in detail.
Functions of a Leaf
● Photosynthesis: This is the most important function of a leaf.
They contain chloroplasts which have the pigment chlorophyll

that is responsible for helping in photosynthesis. The prepared
food is transported to the other parts of the plant via phloem
tissue.
● Helps the plant breathe: The epidermis of the leaf contains
guard cells that control and regulate the small pores on the
undersurface of the leaves. These pores are called stomata.
Stomata are responsible for regulating water in and out of the
cell. It is also responsible for the exchange of gases across the
epidermis.
● Storage of food: In some plants, the leaves are modified to
store food. These plants generally have succulent leaves as seen
in xerophytic plants.

Solved Example for You
Q: Which structure of the leaves helps in gaseous exchange?
a. Stomata
b. Petiole
c. Spongy mesophyll
d. Xylem
Sol: The correct option is (a) Stomata
Stomata are small pores that are found in the lower epidermal layer of
the leaf blade. They are regulated by the guard cells. The stomata help
in regulating water intake and output across the cells and help in
exchange of gases across them too.
Inflorescence
Flowers are the reproductive parts of a plant. They are bright in colour
and attractive to attract pollinators to it. Flowers can be present
solitarily or in bunches or clusters. Clustered flowers can be found
arranged on branches different from the other branches of the plant.

These clusters of flowers are known as an inflorescence and each
individual flowers in it are known as florets.
Parts of an Inflorescence
An inflorescence has the following parts:
a)Peduncle: It is the main supporting stalk of the inflorescence.
b)Pedicle: It is the stalk of the individual flowers. Some flowers are
sessile and do not have a stalk, they are directly attached to the
peduncle.
c)Bracts: These are small green petal-like structures that are found
near the peduncle. They are similar to the sepals in a flower.
d)Flower/Flowers: These rest atop the pedicle or the main stalk.

Learn more about Stem Structure here in detail.
Types of Inflorescence
It can be broadly classified based on the following:
1. Number and position of flowers
2. Sequence of flower development, and
3. The nature of inflorescence branching
They are commonly classified and studied under two categories:
Racemose and Cymose inflorescence.
Racemose Inflorescence
In this type, the axis of the inflorescence has unlimited growth. The
flowers are arranged in acropetal manner which means that the older
flowers are present at the base while the younger ones are present
towards the top. The individual flowers may be sessile or pedunculate.

(Source: Wikipedia)
The different types of the racemose inflorescence are:
● Raceme-Flowers with pedicel and are in an acropetal
arrangement. Example: mustard
● Spike- Flowers without pedicel and are in an acropetal
arrangement. Example: Barley
● Umbel- Pedicilate flowers in which the flowers originate from
the same place and reach the same level. Example Waxflowers
● Corymb- Unlike in the Umbel, the corymb consists of
pedicilate flowers where the length of pedicels of the lower
flowers is more than that of the upper ones such that all the

flowers come up to the same level. They have an umbrella
appearance when seen from the top. Example: Hawthorn
● Spadix- when a spike is covered sheath-like covering by a
spathe it becomes a spadix. Example: Banana
● Capitulum- It is actually a short spike where the flowers are
directly placed on the peduncle and giving it a flower-like
appearance. A smaller capitulum is called the head. Example:
Dandelion, sunflower.
Learn more about Tissue System here in detail.
Cymose Inflorescence
(Source: Wikipedia)

In a cymose inflorescence, the axis has limited growth and the flowers
are arranged in a basipetal manner which means that the older flowers
are found towards the top and the younger ones towards the base of
the axis.
The different types of the cymose inflorescence are:
● Monochasial/Uniparous– the main axis ends in a flower and
has one lateral branch. Example: Drosera
● Dichasial/Biparous– The main axis produces a flower at the tip
and produces two branches simultaneously at a lower level
both of which also end in flowers. This pattern of branching is
further repeated. Example: Dianthus
● Polychasial/ Multiparous– The main axis ends in a flower and
at the same time it produces a number of lateral flowers around.
The oldest flower lies in the centre and ends the main floral
axis. Example: Calotropis
● Cymose Capitulum– In this case, the peduncle is reduced to
form a disc-like structure. This disc bears sessile flowers with

the oldest in the centre and the younger ones towards the
periphery.
Solved Example for You
Q: Which of the following type of inflorescence has an axis with
limited growth?
(a) Drosera (b) Sunflower
(c) Mustard (d) Barley
Sol. (a) Drosera
Axis with limited growth is seen in the cymose type. Drosera is a
cymose inflorescence whereas the other three are racemose(have
unlimited growth of axis). Therefore, the correct answer is option a.
Secondary Growth
Do you know how the age of a tree is calculated? Well, we simply
count the annual rings that form in its trunk due to the wood growth.

This lateral expansion or growth of a tree is called Secondary Growth.
Lets us learn about it here.
Secondary Growth
Growth in plants occurs in two ways: primary and secondary.
● Primary growth causes the plant to grow in length, both below
and above the ground, due to the apical meristems that are
actively dividing into these regions.
● Secondary growth causes the plant to grow in width due to the
presence of lateral meristems or cambium layer which actively
divides to bring about this kind of growth.
We need to understand that secondary growth occurs in both stems as
well as roots.
Browse more Topics under Anatomy Of Flowering Plants
● Plant Tissues
● Tissue System
● Stem
● Leaf

● Inflorescence
● Flower
● The Fruit
● The Seed
● Classification of Flowering Plants
● Anatomy of Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants
Secondary growth in stems
(Source: BiologyDisscussion)
As mentioned earlier, secondary growth occurs due to the lateral
meristems that divide similar to the apical meristems.The cells of the
lateral meristems divide rapidly and grow outwards laterally rather
than apically as in case of primary growth. The lateral meristems that

cause secondary growth are known as cambium. This layer of
cambium is present in dicots but absent in monocots.
Two layers of Cambium
Cork Cambium: The cork cambium makes a tough, insulating layer of
cells called as cork. These cells have wax in them, which helps them
protect the stem from water loss. Cork is also a part of the bark.
Vascular Cambium: The vascular cambium produces vascular tissue
(xylem and phloem), which provide additional support for the shoot
system in along with transporting water and nutrients. The xylem and
phloem that arise from the vascular cambium replace the original
(primary) xylem and phloem, and so are called as secondary xylem
and secondary phloem. They add to the width of the plant. The
vascular cambium is only single layer in thickness and adds xylem on
the inside and phloem on the outside of it. In trees, the secondary
xylem forms the wood and the secondary phloem forms the bark.
In cases of monocots, who lack cambium, secondary growth is not
seen. The stems do not get as wide as in the dicots.
Secondary growth in roots

(Source: UCD)
Secondary growth in roots leads to increase in the thickness of the
root. This happens by the addition of vascular tissue.
Initiation of secondary growth takes place in the zone of maturation
soon after the cells stop elongating there. The vascular cambium
differentiates between the primary xylem and phloem in this zone. The
pericycle is a cylinder of parenchyma or sclerenchyma or cells that
lies just inside the endodermis and is the outer most part of the stele of
plants.The pericycle cells divide simultaneously with the procambium.
As a result, a cylinder of cambium is formed that encircles the primary
xylem. Similar to the stem, the xylem is formed on the inside and the
phloem towards the outside of the cambium.
Some roots form an outer protective layer called the periderm which
originates from the pericycle and replaces the epidermis. The

pericycle resumes its meristematic character and begins to divide
periclinally again. At this point, it is called the phellogen or the cork
cambium. This cork cambium forms cork cells towards the outside of
the plant. They are suberized which makes the cells impermeable to
water.
Solved Example for You
Q: Which part of the vascular cambium forms the bark in trees?
(a) Endodermis (b) Secondary phloem
(c) Pericycle (d) Secondary xylem
Sol. (b) Secondary phloem
It is the secondary phloem of the vascular cambium of dicot stems that
forms the bark of trees. The secondary phloem forms the wood.
Flower
Did you know the largest flower found on earth weighs fifteen pounds
and can grow up to three feet! It is called the Rafflesia Arnoldii. And

the smallest is the Wolffia and it is the size of a grain of rice. Flowers
are more than pretty things, they are responsible for the reproduction
of plants and are absolutely essential. Let us learn more about them.
Plants are majorly classified on basis of presence or absence of flower
into flowering and non- flowering plants. A flower is a characteristic
feature of flowering plants and is actually an extension of the shoot
meant for reproduction. Flowers are attractive and appear in different
colours and shapes to attract pollinators who help in pollen transfer.
Browse more Topics under Anatomy Of Flowering Plants
● Plant Tissues
● Tissue System
● Stem
● Leaf
● Inflorescence
● Secondary Growth
● The Fruit
● The Seed
● Classification of Flowering Plants

● Anatomy of Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants
Parts of a Flower
(Source: anmh.org)
Most flowers have four main parts: sepals, petals, stamens, and
carpels. The stamens are the male part whereas the carpels are the
female part of the flower. Most flowers are hermaphrodite where they
contain both male and female parts. Others may contain one of the two
parts and may be male or female.
Before getting into parts, understand the classification of Flowers
here.
● Peduncle: This is the stalk of the flower.

● Receptacle: It is that part of the flower to which the stalk is
attached to. It is small and found at the centre of the base of the
flower.
● Sepals: These are the small, leaf-like parts growing at the base
of the petals. They form the outermost whorl of the flower.
Collectively, sepals are known as the calyx. The main function
of the calyx and its sepals is to protect the flower before it
blossoms(in the bud stage).
● Petals: This layer lies just above the sepal layer. They are often
bright in colour as their main function is to attract pollinators
such as insects, butterflies etc to the flower. The petals are
collectively known as the corolla.
● Stamens: These are the male parts of a flower. Many stamens
are collectively known as the androecium. They are
structurally divided into two parts:
○ Filament: the part that is long and slender and
attached the anther to the flower.
○ Anthers: It is the head of the stamen and is responsible
for producing the pollen which is transferred to the

pistil or female parts of the same or another flower to
bring about fertilization.
(Source: Wikipedia)
● Pistil: This forms the female parts of a flower. A collection of
pistils is called the gynoecium.
Learn more about Inflorescence here.
Pistil consists of four parts

(Source: Britannica)
a. Style -is a long slender stalk that holds the stigma. Once the
pollen reaches the stigma, the style starts to become hollow and
forms a tube called the pollen tube which takes the pollen to the
ovaries to enable fertilization.
b. Stigma– This is found at the tip of the style. It forms the head
of the pistil. The stigma contains a sticky substance whose job
is to catch pollen grains from different pollinators or those
dispersed through the wind. They are responsible to begin the
process of fertilization.
c. Ovary – They form the base of the pistil. The ovary holds the
ovules.

d. Ovules– These are the egg cells of a flower. They are contained
in the ovary. In the event of a favorable pollination where a
compatible pollen reaches the stigma and eventually reaches
the ovary to fuse with the ovules, this fertilized product forms
the fruit and the ovules become the seeds of the fruit.
Introduction to Leaf Structure
Solved Example for You
Q: What forms the androecium in a flower?
a. Petals
b. Stamens
c. Sepals
d. Pistil
Sol: The correct option is (b) Stamens
The androecium is the male part of the flower. A collection of stamens
is an androecium.
The Fruit

Everybody likes fruits! Fruits are a characteristic of flowering plants.
Once pollination and fertilization occur, the ovary of the plant
becomes the fruit and the ovules become the seeds. They can be fleshy
or dry. Let’s learn more about them.
The main purpose of fruits is that they protect the seeds during
development. Since they are often colourful and emanate a delectable
odour, they help in attracting birds and other animals to eat seeds. This
way the seeds get dispersed to other areas for generating new plants.
Structure of a fruit
The fruit primarily contains two parts: the pericarp and the seed. The
pericarp layer is actually the outer wall of the ovary from which the
fruit developed. The pericarp has three layers:

Source: Google
● Exocarp or Epicarp: This is the outermost layer of the pericarp
that forms the skin.
● Mesocarp: It is the thick, fleshy and juicy middle layer of the
pericarp.
● Endocarp: It is the innermost layer of the fruit which often
develops into the pith.
Classification of Fruits
On basis of the number of ovaries and the number of flowers involved
in their formation, fruits are broadly classified into three categories:

● Simple Fruits
● Aggregate Fruits
● Multiple Fruits
Source: Backyard Nature(google)
Simple Fruits
● These fruits develop from a single ovary of one or more
carpels.
● These fruits are further divided into Dry fruits and Fleshy fruits
depending upon pericarp.
Dry Fruits

In these fruits, the pericarp is not succulent and the pericarp becomes
dry one the fruits mature. Dry fruits are of two types: Dehiscent and
Indehiscent.
a. Dehiscent fruits: These fruits dehisce or split open when they
mature. Types of dehiscent dry fruits are:
Source: Google
● Follicle- is a dry dehiscent fruit which arises from a single
carpal and on maturity splits only along one suture. E.g.
Larkspur

● Legume- is a dry dehiscent fruit which arises from a single
carpal and on maturity splits along its dorsal and ventral
sutures. E.g. Pea
● Capsule- made up of multiple carpals and splits in four ways.
E.g Eucalyptus
● Silique- is made up of two carpals that split on maturity. E. g
Mustard plant
b. Indehiscent fruits: These fruits do not split open on maturity. Types
of indehiscent dry fruits are:
Source: Google
● Akene- where the only seed is attached to the fruit at one point
only. E.g. sunflower

● Caryopsis- where the only seed is attached to the fruit at all
possible points. E.g. Maize
● Samara- is a one or two seeded which has seeds with wing-like
structures. E.g.Maple
● Schizocarp- is made up of multiple carpals which separate on
maturity to form multiple indehiscent fruits. E.g. Dill
● Nut- has thick pericarps and is a one-seeded fruit formed from
a compound ovary. It is hard in texture. E.g Chestnuts
Fleshy Fruits
In these fruits, the fruit wall or pericarp is thick and fleshy. They are
of the following types:

Source: Google
● Berry is made up of one or more carpals and contains one or
more seeds. The pericarp is soft, fleshy and juicy. E.g Banana,
grapes
● Drupe is derived from a single carpel and containing one seed.
Exocarp is present as a thin skin, the mesocarp is fleshy and the
endocarp becomes stony hard. E.g Mango
● Pome (accessory fruit) is an accessory fleshy fruit formed by a
group of carpels that are firmly united with each other and
surrounded by and united to the receptacle. E.g Apple
Aggregate Fruits
These fruits develop from multiple ovaries but of the same flower. So,
an aggregate fruit consists of a collection of simple fruits called
fruitlets. E.g Blackberries, strawberries.
Multiple Fruits

They are formed by all the flowers of an inflorescence which together
result in a single big fruit. Multiple fruits are called false or composite
fruits. E.g Mulberries, pineapple.
Solved Example for You
Q: Which of the following types of fruit has seeds with wing-like
structures?
(a) Akene (b) Capsule
(c) Samara (d) Caryopsis
Sol. (c) Samara
Samara is a simple dry indehiscent which is made up of one or two
seeds which have a wing-like structure.
The Seed
The seed in a plant is the part that develops from the ovules after
fertilization. They are enclosed in the fruit which develops from the
fertilized ovary. The seeds are formed as a result of sexual

reproduction and contain the young embryo which can develop into a
new plant. Let’s learn more.
Structure of a Seed
Seeds of different plants may vary in many ways, but the basic
anatomy remains the same. A typical seed consists of the following
parts:
Source: Google
● Tesla: It is the outer coat of the seed that protects the
embryonic plant.

● Micropyle: It is a tiny pore in the testa that lies on the opposite
of the tip of the radicle. It permits water to enter the embryo
before active germination.
● Hilum: Is a scar left by the stalk which attached the ovule to the
ovary wall before it became a seed.
● Cotyledon: In some plants, this contains high quantities of
starch and will provide a source of food for the developing
embryo prior to germination, in other plants this role is
performed by an endosperm. In monocotyledons, there is just
one cotyledon whereas in dicotyledons there are two.
Depending on the type of germination (epigeous or hypogeous)
the cotyledons may remain below ground or be pulled above
ground.
● Radicle: This is the embryonic root which will develop into the
primary root of the plant. It is usually the first part of the
embryo to push its way out of the seed during germination.
● Plumule: This is the embryonic shoot. It appears as a bud
which will give rise to the shoot and the remaining structures in
the plant.

● Endosperm: In many plants, a separate part for storage of
starch develops and this is called the endosperm. It is seen in
maize and wheat.
Learn more about Stem Structure here in detail.
Functions of Seeds
The seeds perform the following functions:
● They help in germination of the new plant.
● The seeds contain food reservoirs in the form of cotyledons and
endosperm.
● The seed coat is protective in nature which protects the embryo
inside.
Dispersion of Seeds
Dispersion is defined as the scattering or transport of seeds from one
place to another by means of a dispersing agent. It can occur by four
modes:

● Wind
● Water
● Animals
● Explosion
Dispersion by Wind
The seeds that are dispersed by wind are generally light and small
such that they can be easily carried away by the wind. Example:
cotton seeds
Source: Google(Tes.com)
Dispersion by Animals

These seeds have external structures such as spines or hooks such that
they can attach themselves to animals and get dispersed to other
places. These seeds are generally attractive and so are their fruits.
Example: Guava seeds, dates.
Dispersion by Water
These seeds have a structure, generally, hollow such that they can
easily float on water. Once they reach a place where the conditions are
suitable, they germinate. Example: Mangroves.
Source: Google

Dispersion due to Explosion/Expulsion
Some plants fling or throw their seeds out once the fruit has ripened.
This explosion occurs as a result of evaporation of water from the
pods. Once the pods dry out, they expel the seeds which are then
carried by wind or gravity to other places where they germinate.
Example: Viola

Source: Pinterest
Solved Example for You
Q: Which of the following parts does the seed develop from?
(a) Ovary (b) Embryo
(c) Embryo sac (d) Ovule
Sol. (d) Ovule
Once fertilization occurs, the ovary starts maturing and eventually
develops into the fruit and the ovules contained in them become the
seeds.
Classification of Flowering Plants
Plants are the primary food producers of the food chain. What are
different types of flowers? They can be classified in many different
ways: Based on presence or absence of seeds, Based on whether the
plants produce flowers or not, Based on the presence of stems, leaves,
and roots. The most accepted and popular classification of plants is

based on whether they are flowering plants (angiosperms) or
non-flowering plants (gymnosperms).
Lets us understand the classification of Angiosperms or flowering
plants.
Classification of Angiosperms
A large number of plants fall into this category and so there was a
requirement to classify angiosperms. There are three systems that
classify angiosperms:
● Artificial Systems based on superficial features.
● Natural systems based on form relationships.

● Phylogenetic systems based on evolutionary and genetic
relationships.
Artificial systems
These systems of classification were based on one or few
morphological characters. Many botanists used this system and
classified angiosperms into different classes. Few of these botanists
are
● Theophrastus- who is known as the father of botany and
apparently the first to provide a difference between dicots and
monocots.
● John Ray- His system was more advanced than the earlier
systems
● Carolus Linnaeus- Introduced the binomial system of naming
Natural Systems
These systems the plants were classified on the basis of their natural
affinities (i.e. the basic similarities in the morphology) rather than on a
character for determining the affinities. Compared to the artificial

systems, it was based on the proper utilization of all facts and figures
available in nature. In this system, the plants were grouped and placed
into different taxa like classes, orders, families, and genera. Michel
Adanson was the first scientist to reject all the artificial systems and
support the natural systems of classification. The main demerit of this
system was that the classification was not based on evolutionary
relationships. Different families had been placed in specific groups
which do not show any evolutionary relationships.
Learn more about the Anatomy of Fruits here.
Phylogenetic systems
These classification systems came up after Darwin’s theory of
evolution was proposed and widely accepted.
There were two popular systems:
Engler and Prantl: They arranged flowering plants according to
increasing complexity of their floral morphology. Their system
considered monocots as more primitive than dicots.

Hutchinson: He proposed the most widely used classification which is
also known as the ‘Hutchinson’s classification’.
The Hutchinson’s classification broadly divided angiosperms into:
● Dicotyledons
● Monocotyledons
Dicotyledons/ Dicotyledonous plants
These are flowering plants which have two cotyledons in their seeds.
Endosperm may or may not be present in the seed.

The following are the features of dicots:
Roots: They have a tap root system with smaller secondary roots
originating from it. Due to its tap root system, they can penetrate
deeper into the soil to find water and minerals required for its growth.
Leaves: They have reticulate venation also called net venation on their
leaves. They have a stalk that attaches the leaves to the stem. Learn
the structure and different types of Leaves here with video.
Vascular system: Cambium is present which helps in secondary
growth of the stem.
Stems: The stems are hollow and the plants are generally herbaceous
or woody.
Flowers: The parts of the flowers usually exist in numbers of fours or
fives. Learn more about the parts and structure of Flowers here in
detail.
Dicotyledons are further divided into- Lignosae and Herbaca.
Monocots/ Monocotyledonous Plants

These flowering plants have a single cotyledon in their seeds.
Endosperm is always present in the seed.
Roots: They have a fibrous root system.
Leaves: Their leaves have parallel venation and the leaves are sessile
i.e they do not have a stalk which attaches the leaf to the stem.
Vascular System: Cambium is absent and so there is no secondary
growth of the stem.
Flowers: the parts of the flowers exist in numbers of three.
The two divisions of Monocotyledons- Calciflorae, Corolliferae,
Glumiflorae.
Learn Anatomy of Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants in
more detail here.
Solved Example for You
Q: Which is the most accepted system of classification?

(a) Artificial systems (b) Natural system
(c) Hutchinson’s system (d) Englar and Prantl system
Sol. (c) Hutchinson’s system
Hutchinson’s
system is a phylogenetic system that classified plants. It was
systematic, and grouped plants based on evolution along with features.
Anatomy of Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants
Tulips and daisies are both beautiful flowering plants. However, they
do not fall into the same category of plants. Flowering plants are
actually classified into two categories based on their embryo, called
Monocotyledonous (monocot) plants and Dicotyledonous plants. Let
us find out more about these plants.
Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants

Plants can be broadly classified into flowering and non-flowering
plants. Flowering plants are called as angiosperms while non-
flowering plants are known as gymnosperms. Angiosperms are further
classified based on the nature of the embryo in the seed into
Monocotyledonous and Dicotyledonous plants.
Dicots are plants that have seeds with two cotyledons and so are
termed as dicotyledonous plants. Examples: Sunflower, Mango
Monocots are plants that have seeds with one cotyledon and so they
are called as monocotyledonous (monocot) plants. Example:
Sugarcane, Maize

Browse more Topics under Anatomy Of Flowering Plants
● Plant Tissues
● Tissue System
● Stem
● Leaf
● Inflorescence
● Secondary Growth
● Flower
● The Fruit
● The Seed
● Classification of Flowering Plants
Anatomy of Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants
Both sets of plants differ structural features: Stems, leaves, flowers,
and roots.
Dicotyledonous Plants

(Source: Plantlist)
Roots
● These plants have a tap root system
● They have two layers: the outermost epidermis which
sometimes forms root hairs, the inner endodermis or the cortex.
● The epidermis consists of loosely packed cells whereas the
endodermis has tightly packed cells.
● The central pith is inconspicuous.
Stems
● Stems are usually solid
● Cambium is present

● The number of xylem and phloem are two to four and they are
distinguished by a layer of parenchymatous cells called
conjunctive tissue.
● Vascular bundles in the stem are fewer and arranged in circles
or rings
● Pith is evident as is made up of palisade cells
● Bundle sheath absent around vascular bundles
● Pericycle is present
● Phloem parenchyma and phloem fibres are present
Leaves
● They have reticulate or net venation
● Leaves have a stalk
● The mesophyll that contains chloroplasts is composed of
spongy and parenchymatous cells
Flowers and seeds
● Flowers are usually pentamerous i.e the floral parts are present
in numbers of five

● Seeds germination either hypogeal or epigeal.
● They have two cotyledons
● The pollen grains have three furrows or pores.
Examples of dicotyledonous plants: Tomatoes, Cauliflower, beans,
apples, potatoes, etc
Monocotyledonous Plants
Roots
● They have an adventitious root system
● Pith is large and conspicuous
● The number of xylems is 6 or more

● Secondary growth is absent in monocots due to an absence of
cambium
Stem
● No cambium and so no secondary growth in stem
● Stem usually hollow
● Vascular bundles in the stem are scattered and numerous
● Phloem parenchyma is absent
● Pith is absent
● Vascular bundles are surrounded by a sclerenchymatous bundle
sheath
● Pericycle is absent
Leaves
● The leaves are sessile i.e it is directly attached to its base
(without stalk)
● They have parallel venation

● Mesophyll is not differentiated into spongy and palisade cells
Flowers and seeds
● Seed germination is hypogeal
● They have a single cotyledon
● Flowers are incomplete and trimerous(floral parts are in the
number of threes)
● The pollen grains have a single furrow or pore
Examples of monocotyledonous (monocot) plants: Maize, Corn,
Grass, Wheat
Understanding the anatomy of these plants is useful from the
horticultural and agricultural aspects. Choosing the right product for
the right kind of plant is important. A herbicide or pesticide designed
for a monocot might not help kill pests around a dicot. Due to the tap
root system that is found in dicots, they can penetrate deeper into the
soil compared to monocots who have a fibrous root system which
cannot penetrate that deep.

Learn more about the concept of Tissue System here in detail.
Solved Example for You
Q: Which of the following are features of dicot plants
(a) Taproot system (b) Fibrous root system
(c) Two cotyledons (d) both a and c
Sol. (d) both a and c
Dicot plants have a taproot system, and seeds contain two cotyledons.
The fibrous root system is found in monocots. So, the correct answer
is (d) both a and c
![Plant tissues [2015]](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/55c30ee7bb61ebd9738b4723/plant-tissues-2015.jpg)