Physical Science The Structure of Matter. What are compounds? When two or more elements are...
-
Upload
crystal-lawson -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of Physical Science The Structure of Matter. What are compounds? When two or more elements are...

Physical ScienceThe Structure of Matter

What are compounds?
• When two or more elements are chemically combined
• Ex)NaCl (sodium chloride) salt

Chemical bonds
• Chemical bond- the attractive force that holds atoms or ions together
• Chemical bonds distinguish mixtures from compounds
• Mixtures can be separated by physical means because they lack chemical bonds!

Compounds always have the same chemical formula
• A chemical formula shows the types and numbers of atoms or ions making up the simplest unit of the compound.
• Compounds are always made of the same elements in the same proportion.
• Ex) H2O

• Chemical structure-the arrangement of atoms in a substance
• Bond length – the average distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms
• Bond angle- the angle formed by two bonds to the same atom
(tells how they are oriented in space)


Models of Compounds
• Ball and stick
• Structural formulas
• Space-filling models

How does structure affect property?
• Compounds with network structures are strong solids with rigid structures
• Quartz SiO2• Very high melting and boiling points due to strong
bonds.

Compounds made up of networks bonded ions
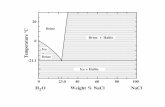
Table salt and sodium chloride in the form of regularly shaped crystals. Sodium chloride of crystals are cubed shaped.
Strong attractions between the oppositely charged ions caused the table salt and the other similar compounds to have high melting points and boiling points

Each grain of table salt is composed of a tightly packed network of Na+ ions and CI- ions
What is an Ion?

Compounds made of molecules
• Ex) sugar is made up of molecules
• C H O joined by bonds
• Molecules of sugar form crystals when bonded
• Weaker bonds
• Lower melting and boiling points then network ion compounds

Hydrogen bonds
• Attractions between water molecules
• Hydrogen bonds are relatively weak
• Low melting and boiling points

What holds bonded atoms together?
• Recall Three types of bonds discussed
Ionic, Covalent, Hydrogen
• Bonded atoms have stable electron configurations
• Valence electrons determine reactivity!
• They want to fill their outermost energy level, to be happy
• H2

Ionic Bonds
• Formed between oppositely charged ions.
• Cations-positively charged (metals)
• Anions-negatively charged (nonmetals)
Ionic bonds form by the transfer of electrons
Table salt= Sodium Chloride= Na+ and Cl-
together they form NaCl a neutral compound (no charge)

• Ionic compounds are in the form of networks, not molecules
• This affects melting and boiling points
• When melted or dissolved in water, ionic compounds conduct electricity!
• Ions are able to move about-thereby transferring electricity

Metallic Bonds
• Metals conduct electricity when they are solid, Ex) Copper Cu
• They are malleable, can be flattened into thin sheets
• They are ductile, can be drawn into fine wire

• Metallic bond- a bond formed by the attraction between positively charged metal ions and the electrons around them
• Atoms are packed together very tightly due to the attractions among neighboring metallic atoms
• Electrons are then free to move freely between atoms

• This explains the ability of metals to conduct electricity in the solid form
• Metals are flexible b/c atoms can slide past each other without breaking their bonds!

Covalent Bonds
• Covalent bond- a bond formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons
• Compounds made of molecules (water and sugar) have covalent bonds
• Most have low melting points
• Cl2


• Nonpolar covalent bond- when electrons are shared equally Ex) Cl2
• Polar covalent bond- an unequal sharing of electrons between two different atoms
• Ex) NH3 and H20

Molecular Models
•

Interpreting Molecular Models
• Can have single
• Double
• Or
• Triple bonds
• Each line ( bond) represents the sharing of two electrons
• Dots represent electrons that are not involved in bonding

• Multiple bonds are stronger than single bonds
• It takes more energy to multiple bonds than single bonds
• Multiple bonds are shorter than single bonds

Electronegativity
• Electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons

•

•
• If the atoms are equally electronegative, both have the same tendency to attract the bonding pair of electrons, and so it will be found on average half way between the two atoms. To get a bond like this, A and B would usually have to be the same atom. You will find this sort of bond in, for example, H2 or Cl2
molecules.

• Summary• No electronegativity difference between
two atoms leads to a pure non-polar covalent bond.
• A small electronegativity difference leads to a polar covalent bond.
• A large electronegativity difference leads to an ionic bond.

Polyatomic Ions
• An ion made of two or more atoms
• Polyatomic ions have both ionic and covalent bonds
• Parenthesis group the atoms of polyatomic ions
• Subscripts outside the ( ) show that the number applies to the entire ion

Writing Polyatomic Ions• Charges +2, -1, +1, -2 etc…
– Are written as super scripts Ca+
– Subscripts show how many ions are present
– If outside the ( ) Ex) (NH4)2 SO4
– Instead of N2 H8 SO4
– There are two ammonium ions per each sulfate ion
• Subcripts show how many atoms of each element are present if there are no ( )s
– Ex) N =1atom H4= 4 atoms CO3= 1 C & 3 O

Polyatomic Ion Names
• Some polyatomic anion names relate to their oxygen content
• Most names end with –ite or –ate
• Ion charge is the same, but # of O varies
• -ate has one more oxygen
• -ite has one less oxygen

Compound Names and Formulas
• Naming Ionic Compounds– Names of cations include the elements of which
they are composed– Na+ is the sodium ion– Ca2+ is the calcium ion
• Group 1 elements = +1
• Group 2 elements = +2

• Naming Anions
• Have altered element names
• Replace ending with –ide
• F- is Floride ion
• O 2- is Oxide ion
• Refer to chart 5 pg 160

Transition Metal Cations
• Refer to chart 6 pg 160

Determining the charge of a transition metal cation
• All compounds have a total neutral charge of zero. (+ = -)
• Fe2 O3• Know oxide ion is –2
3 O would have a charge of –6 ( 3x –2)= -6
• Charges must = 0 so +6 must be the + charge for 2 Fe to have a +6 charge, the Fe must have a 3+
charge

Naming Covalent Compounds
• Refer to table 7 page 162 know prefixes!– N2 04 is dinitrogen tetraoxide