Physical characteristics of systemic circulation
-
Upload
aarti-sareen -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
1.967 -
download
5
description
Transcript of Physical characteristics of systemic circulation

Physical characteristics of
systemic circulation
Aarti SareenMSPT honours

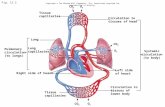
CIRCULATION: IS MOVEMENT OF BLOOD IN THE BODY. It is divided into the -systemic circulation and -pulmonary circulation.
SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION: The general circulation, carrying oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body tissue and returning venous blood to the right atruim is called systemic circulation. It supplies all the tissues of the body except lungs. Its is also called as greater circulation or peripheral circulation.


Various physical characteristics of systemic circulation:These either directly or indirectly affects the systemic circulation and are interrelated to
each other.1.Cross sectional area of the vessels.
2. Pressure in various portions.
3. Resistance provided by various structures.
4. Venous return
5. Blood flow
6. Vascular distensiblity.
7. Vascular compliance.

Cross sectional area:It is the diameter of the vessel.The velocity of blood flow in each segment of the circulation is inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area.
Total crossectional area (cm2)
Average velocity of blood flow
Aorta 4.5 40 cm/sec
Small arteries 72 (16times that of aorta)
1.4 cm/sec
Arterioles 400 0.5 mm/sec
Capillaries 4500 (1000 times that of aorta
0.3 mm/sec
Small veins 80 1-2 cm/sec
Inferior vena cava and superior vena cava
18 7-10 cm/sec

Left atruim 7-8/zero
Left ventricle 120/zero mmHg
Aorta and its larger branches 120/70 mmHg
Arterioles 60 mmHg
Metarterioles 40 mmHg
Capillaries 25 mmHg
Venules and larger veins 10 mmHg
Vena cava(superior and inferior) 2 mmHg
Pressure in various portions:Pressure means the force exerted by the blood against any unit area of the vessel walls. It is divided as-arterial pressure-venous pressure Pressure in major vessels are as follows:

ARTERIAL PRESSURE:
Arterial blood pressure is defined as the lateral pressure exerted by the contained column of blood on the walls of arteries. Generally the term pressure/blood pressure refers to arterial blood pressure.
It is further of 4 different types1. Systolic blood pressure2. Diastolic blood pressure3. Pulse pressure4. Mean arterial pressure

CENTRAL FACTORS(Factors pertained to heart)
PERIPHERAL FACTORS(Factors pertaining to blood vessels)
1. Cardiac output 1. Peripheral resistance
2. Heart rate 2. Blood volume
3. Venous return
4. Elasticity of blood vessels
5. Velocity of blood flow
6. Diameter of blood vessels
7. Viscosity of blood
DETERMINANTS OF ARTERIAL BLOOD PRESSURE/ FACTORS MAINTAINING ARTERIAL BLOOD PRESSUREE:

COMPONENT
DEFINATION CHARACTERISTIC FEACTURES
NORMAL VALUE (mmHg)
1. SYSTOLIC BLOOD PRESSURE (SBP)
It is the maximum pressure exerted during systole
-undergo considerable fluctuations - It indicates force with which the heart works and degree of pressure which arterial walls have to withstand.
Range100-140Average120
2. DIASTOLIC BLOOD PRESSURE(DBP)
It is the minimum pressure exerted during diastole
-undergoes much less fluctuations-it is measure of total peripheral resistance.
Range70-90Average80
3. PULSE PRESSURE (PP)
It is the difference of SBP and DBP i.ePP=SBP-DBP
-it determine the pulse volume
Average 40
4. MEAN BLOOD PRESSURE (MBP)
It is average pressure throughout cardiac cycle.
It is calculated asMBP=DBP+1/3 PP
Range95-100

Calculated as:Systolic blood pressure-diastolic blood
pressure= pulse pressureIt is dependent upon 3 factors Stroke volume (directly proportional) Amount of blood ejected from left ventricle
(directly proportional) Compliance of aorta (indirectly proportional)
Pulse pressure:Pulse Pressure is most easily defined as being the amount of pressure required to create the feeling of a pulse. the pressure difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures give you the amount of pressure change to create the pulse, which is the pulse pressure.

LOW PULSE PRESSURE:A pulse pressure is considered abnormally low if it is less
than 25% of the systolic value.e.g in Heart failure Aortic stenosis Shock Haemrhage
HIGH PULSE PRESSURE:A pulse pressure higher than 25%of systolic value is consider
high pulse pressure. It is temporary in case of exercise but constant high PP is in
Artherosclerosis Chronic aortic regurgitation Heart block Endocarditis
Pulse pressure ranges b/w 40-45

MEASUREMENT OF THE ARTERIAL PRESSURE:
1. Auscultatory method2. Stethoscope

NORMAL ARTERIAL BLOOD PRESSURE READINGS

1. Central venous pressure (CVP)
2. Peripheral venous pressure (PVP)
Blood from all systemic veins flow into right atrium, therefore right atrium pressure is called central venous pressure. Normally it is 1-6 mmHg.
It is the pressure in peripheral veins. Large veins offer considerable resistance to blood flow because they remain compressed at many points by the surrounding tissues. e.g abdominal veins by diff. organs and intra-abdominal pressure, arm veins by first rib and neck vein by atmospheric pressure. It is about 10 mmHg.
Venous pressure:is pressure exerted by the contained blood in the veins. It of 2 types:

Factors affecting venous return Venous pressure Position of the body: From lying to standing –
increase of the blood in veins – dilation of veins in the lower part of the body – decrease of venous return
Action of “muscular pump” Respiration movement. Gravity
VENOUS RETURN:The quality of blood flowing from veins into the right atrium per minute

Action of muscular pump:

Respiration movement. Negative pressure in the thoracic cavity that changes with respiratory movement – dilation of venae cave – increase of venous return

Gravity:in prolong standing-pooling of blood in legs-increase weight column of blood-increase pressure i.e 80mmHg

RESISTANCE OF VARIOUS STRUCTURES:Arterioles,metaarterioles and pre- capillary sphincters provide internal resistance to circulation where as skin and skeletal muscle provides peripheral resistance.

According to OHM’S law: F=ΔP/R
Where F= blood flow ΔP= pressure gradient R= vascular resistance
Relationship among pressure,flow and resistance:

Pressure gradient i.e p1-p2. Where p1 is pressure at proximal end of vessel & p2
pressure at distal end of vessel. Pressure gradient is directly proportional to blood flow.
Viscosity of blood: volume of blood flow is inversely proportional to viscosity of blood.
Diameter of blood vessels: volume of blood flow is directly proportional to the diameter of vessel.
Resistance to blood flow:Resistence= pressure gradiant/volume of blood flow
BLOOD FLOW:Blood flow means simply the quantity of blood thatpasses a given point in the circulation in a given period.Factors determining blood flow are:

When the pressure in blood vessels is increased, this dilates the blood vessels and therefore decreases their resistance.The result is increased blood flow not only because of increased pressure but also because of decreased resistanceThe most distensible by far of all the vessels are the veins. Even slight increases in venous pressure cause the veins to store 0.5 to 1.0 liter of extra blood. Therefore, the veins provide a reservoir function for storing large quantities of extra blood that can be called into use whenever required elsewhere in the circulation.
VASCULAR DISTENSIBILITY:

Anatomically, the walls of the arteries are far stronger than those of the veins. Consequently, the arteries,on average, are about eight times less distensible than the veins. That is,a given increase in pressure causes about eight times as much increase in blood in a vein as in an artery of comparable size.
Difference in Distensibility of the Arteries and the Veins

It is Important to know the total quantity of blood that can be stored in a given portion of the circulation for each millimeter of mercury pressure rise than to know the distensibilities of the individual vessels. This value is called the compliance or capacitance of the respective vascular bed; that is,
VASCULAR COMPLAINCE

Compliance and distensibility are quite different. highly distensible vessel that has a slight volume
mayhave far less compliance than a much less distensiblevessel that has a large volume because compliance isequal to distensibility times volume. The compliance of a systemic vein is about 24 timesthat of its corresponding artery because it is about 8times as distensible and it has a volume about 3 timesas great (8 ×3 = 24).

THANK YOU