Permeability: transporting drugs through (lipid) membranes 1 st Physical Chemistry Symposium,...
-
Upload
dylon-griest -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of Permeability: transporting drugs through (lipid) membranes 1 st Physical Chemistry Symposium,...

Permeability: transporting drugs through (lipid) membranes
1st Physical Chemistry Symposium, November 30, 2005
Paula Garcia

Efflux (or counter-transport)
Metabolic (in)stability: microflora
intestines
liver
Factors Determining Oral Bioavailability
Physicochemical factors:
Biochemical factors
Dissolution (solid to solution)
Aqueous Solubility
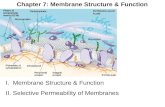
Membrane PermeabilityMembrane Permeability

Di, L., Kerns, E., Fan, O.J., Carter, G.T., Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 38, 223.
Permeation Mechanisms
Cellular
Barrier
Passive Diffusion
Active Transport EffluxParacellular
Endocytosis
PAMPA StructureMotifs
MWPolarity
Caco-2MDCK
Passive diffusion: major absorption pathway

Can any of these methods be adapted for high throughput measurements?
*2000, www.fda.gov.cder/guidance/index.html
In-vivo intestinal perfusion studies in humans or animals In-vitro permeation experiments using excised human or animal intestinal tissues In-vitro permeation experiments across a monolayer of cultured human intestinal
cells (e.g Caco-2 cells)
• Methods approved for the Biopharmaceutical Classification System*
Permeability Measurements
Rule of five - Lipinski
Lipophilicity H-bond capacity Molecular size Polar Surface Area (PSA) Quantum properties
• In-silico models based on:

• Because they are made from cultured cells, Caco-2 membranes express all mechanisms of transport;
• Therefore, if a drug goes through a Caco-2 membrane, it will probably be absorbed by the GI tract
Can Caco-2 assay be used for permeability screening?
Yes, but…
It takes several days to create membranes* and requires cell culture skills
* normally 21-25 days4-day culture was recently reported: Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 200, 41.
Drug
basolateral
apical
human colonic cell line
Caco-2 Permeability Assay

Protein
Phospholipid Head
Lipophilic Tail
Structure of the cell membrane
Permeability through lipid membranes ?!
Lipid membranes are quickly and easily made by robots; easily automated for high throughput permeability assays.
a) Artursson P., Book of Abstracts, PAMPA 2002 Conference, 2002, San Francisco; Mandagere A.K., Thompson T.N., J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 304.
Transcellular Absorption
80-95% of commercial drugs (a)80-95% of commercial drugs (a)

1998 - PAMPA was initially introduced by Kansy from Hoffmann-La Roche 2005 – 95 hits in Pubmed
Kansy, M.; Senner, F.; Gubernator, K., J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 1007.
Membrane: egg lecithin in hydrophobic filter
Good correlation between PAMPA flux
and % HIA
Active transport of polar compounds with
low Mw
PAMPA: Permeability through lipid membranes

Donor
Acceptor
Membrane(20% (W/V) phospholipid mixture in dodecane)
PAMPA: Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay
Dru
gPassive Diffusion- Pe (cm/s)

Donor
Acceptor(pH=7.4)
Membrane
GastroIntestinal Tract (GIT)
Double-Sink Conditions
SDS micelles
(pH= 5-8)
PAMPA: Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay
Dru
gPassive Diffusion- Pe (cm/s)
Unstirred Water Layer

PAMPA: workstation

phospholipidcocktail
sink (acceptor at top)
stirrer (donor at bottom)
PAMPA: Sandwich plates

Solubility-Diffusion Model / pH-Partition Theory
Passive diffusion: pKa, solubility and lipophilicity are important!
LogP

The effect of the pH on Permeability
O
O
N
N
O
O
HCl
-8.0
-7.0
-6.0
-5.0
-4.0
-3.0
-2.0
2.0 4.0 6.0 8.0 10.0
pH
log
Pe
Verapamil pKa=9.07Base
Ketoprofen
-6.5
-5.5
-4.5
-3.5
-2.5
2.0 4.0 6.0 8.0 10.0pH
log
Pe
pKa=3.98
O
O
HO
Acid
Faller, B., Wohnsland, F., J.Med.Chem., 2001, 44, 923; Ruell, J.A., Tsinaman, K.L., Avdeef, A., Eur.J.Pharm.Sci., 2003, 20, 39; Kerns, E.H., Di, L., Jupp, P., Pharm.Sci., 2004, 93, 6, 1440;

The effect of the pH on Permeability
Permeability of ionisable compounds is pH dependent!
-5.0
-4.5
-4.0
-3.5
-3.0
2.0 4.0 6.0 8.0 10.0pH
log
Pe
Carbamazepine
N
NH2O
unionisable

Unstirred Water Layer and Ionisation
pKaflux
pH where 50% of the resistance to transport comes from the UWL
and 50% from the membrane
UWL:
In GIT: 40 mIn BBB: no UWL
BBB
GIT
UWL can be reduced by stirring the donor solution

PAMPA Assay: DOUBLE-SINK and Stirring
Pe is UWL limited!
Compounds with a log P ≥ 2, follow the protocol with stirring.
Log P ≥ 2 Log P < 2

The Effect of lipophilicity on Permeability
Permeability improves with increase in lipophilicity

The Effect of lipophilicity on Permeability
Caco-2 Assay
Pe is UWL limitedParacellular transport

AstraZeneca database
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
-2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
cLogPC
aco
-2 (
nm
/s)
What is the Permeability hurdle, lipophilicity or solubility?
Caco-2 versus CLogP/D
y = -0.2183x 2 + 0.8639x + 0.4508R 2 = 0.5362
-0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
-1 0 1 2 3 4 5
cLogD7.4
log
Pap
p
Riley et al, Curr. Drug Metab., 2002, 3, 527
Organon database
Membrane Retention

The Effect of Solubility on Permeability: Co-Solvent PAMPA Assay (b)
Compound logP Solubility Solubility pH
pH 5 (mg/ml) pH 7.4 (mg/ml) H2O H2O: ACN (8:2)v/v
Antipyrine 5 2,1 1,2
0,56 > 197 > 194 6,2 2,1 1,6
7,4 2,3 1,6
Caffeine 5 2,6 0,8
-0,07 > 20000 > 20000 6,2 2,6 0,7
7,4 2,5 0
Theophylline 5 1,2 0,4
0 > 189 > 186 6,2 1,4 0,5
7,4 1,1 0,3
Verapamil.HCl 5 189 12
4,33 > 500 > 500 6,2 763 96
7,4 1707 739
Ketoprofen 5 264 123
3,16 > 259 > 262 6,2 20 14
7,4 4 3
Ketoconazole 5 496 68
4,34 43 11 6,2 und 1254
7,4 0 equ
Danazol 5 0 1754
3,9 0,09 0,06 6,2 0 819
7,4 64 419
Pe x 10-6 (cm/sec)
SOl (ketoconazole)ACN:H2O=53 (pH 5); 37(pH 7.4); SOl (danazol)ACN:H2O=1 (pH 5); 3(pH 7.4)

0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
1600
1800
AntipyrineCaffeineTheophyllineVerapamil.HClKetoprofenKetoconazoleDanazol
H2O
H2O
H2O:ACN (8:2 v/v)
The Effect of Solubility on Permeability-Co-Solvent PAMPA AssayP
ex1
0-6 (
cm/s
)
Pe is solubility limited(Low Sol., but high Pe)
(High Sol., high Pe)
(High Sol., Low Pe)
Membrane keeps its integrity
Sugano, K., Hamada, H., Machida, M., Ushio, H, Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 228, 181; Ruell, A.J., Tsinman, O., Avdeef, A., Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 561

The Effect of Solubility on Permeability-Co-Solvent PAMPA Assay (b)
Compound MWElogD (7.4)
Sol (pH 5) Sol (pH 7.4)
Pe x10-6 (cm/sec)
(µg/ml) (µg/ml) pH H2O H2O/ACN (8:2 v/v)
Cpd 1 539 4.6 55 7 5.0 1137.6 57.4
6.2 1875.1 331.3
7.4 0.0 916.7
Cpd 2 555 4.4 > 58 8.9 5.0 891.4 78
6.2 1361.1 364.5
7.4 0.0 862.5
Cpd 3 422 4,1 0.5 0.3 5.0 78.5 89.6
6.2 391.1 166.9
7.4 0.0 168.2
Cpd 4 529 5.2 < 0.1 0.2 5.0 0.0 879.5
6.2 0.0 173.3
7.4 0.0 216.4
Cpd 5 650 4.4 1 1.1 5.0 256.2 109.5
6.2 347.9 129.4
7.4 270.1 201.5
Cpd 6 543 6 0.5 0.7 5.0 0.0 0.0
6.2 98.0 4.89
7.4 918.0 143.9

PAMPA Assay in Organon
Ionisable compounds display Permeability- pH profile
a)- Kern, E. et al., Pharm. Sci., 2004, 93, 6, 1440;
Lipophilicity ↔ Permeability
• Reducing the UWL is important for lipophilic compounds.
• Highly lipophilic compounds display a high membrane retention.
b)- Bermejo, M. et al., Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 2004, 21, 429;
Low aqueous solubility might be a limiting factor in Permeability measurements:
• Use of co-solvent method allows to differentiate compounds from classes III and IV in the BCS system.
• 20% of ACN doesn’t interfere with the integrity of the membrane.
d) Avdeef, A., et al., Chem. Pharm. Bull., 2004, 52, 561; Sugano, K., et al., Int. J. Pharm., 2001, 181.

30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
-7,00 -6,50 -6,00 -5,50 -5,00 -4,50 -4,00 -3,50 -3,00 -2,50 -2,00
log PeMax (pH 5.0, 6.2, 7.4)
% H
IA
Theophiline
Caffeine
Antipyrine
Atenolol
Furosemide
Tertbutaline
Hydrocholorthiazide
Ranitidine
Dexamethasone
Metoprolol
PiroxicamCarbamazepin
Quinine
Ketoprofen TestosteronePropanolol
VerapamilDesipramine
Max-Pe PAMPA Model for Prediction of Human Intestinal Absorption
high permeabilitylow permeability
a)- Avdeef, A., Absorption and Drug Development, 2003, Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Interscience,b)- Avdeef, A. Curr. Top. Med. Chem., 2001, 1, 277.
Classification Pe
High >20x10-6 cm/s
Medium 10- 20x10-6 cm/s
Low <10x10-6 cm/s

Factors Determining Intestinal Drug Absorption
Fraction of drug absorbed (Fa) is governed by several processes:
Dose/Dissolution ratio,
Chemical degradation and/or metabolism in the lumen,
Complex binding in the lumen,
Intestinal Transit,
Effective Permeability across the Intestinal Mucosa (HJP)Effective Permeability across the Intestinal Mucosa (HJP)
Winimater, S., Bonham, N. M., Lernnernas, H., J. Med. Chem., 1998, 41, 4939.

PAMPA Model for prediction the Human Jejunal Permeability (HJP)(a)
Double–Sink (pH=5.0/7.4)
y = 0,4731x - 1,4404
R2 = 0,9408
-6,0
-5,5
-5,0
-4,5
-4,0
-3,5
-3,0
-2,5
-2,0
-8,5 -7,5 -6,5 -5,5 -4,5 -3,5 -2,5
log Pe 5.0/7.4
Lo
g P
eH
JP
Hydrochlorotiazide
Tertbutaline
Ranitidine
Atenolol
Furosemide
Antipirine
Metoprolol
Carbamazepine
Piroxicam
Propanolol
Ketoprofen
Naproxen
Verapamil
Desipramine
a)- Avdeef, A., Absorption and Drug Development, 2003, Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Interscience, b)- Karlsson, J. P., Artursson, P., Int. J. Pharm., 1991, 7, 55; Karlsson, J. P., Artursson, P., Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 1999, 9, 47.

Compound ClogP MW Nb Rot HBD HBA PSA In-Silico PAMPA Caco-2
(-2<X<5) (X<500) (X<12) (X<6) (X<11) (X<110) x10-6 x10-6
Progesterone
3,8 314 1 0 2 31,4 Good
1879 20
Nandrolone
2,7 274 0 1 2 38,1 Good
422 35
Hydrocortisone
1,7 362 2 3 5 78,3 Good
28 18
Cortisone
1,3 360 2 2 5 77,1 Good
26 34
Cpd 1
5,9 458 3 2 3 55,2 Moderate
1185 20
L-Dopa
-2,8 197 3 5 5 108,0 Moderate
0 0
Verapamil
4,5 455 14 0 6 61,8 Moderate
1188 15
Cpd 2
3.0 650 13 1 9 114,0 Bad
1600
Cpd 35.2 557 12 0 10 102,0 Bad
500
Permeability and Molecular Properties
Pe is a physicochemical process that depends on physicochemical properties of a molecule and its interactions with a membrane.

Caco-2 vs. PAMPA
BCS compounds
Kerns, E.H., Di, L., Petusky, S., J. Pharm. Sci., 2004, 93, 6,1440.
Absorptive Transport
Passive Diffusion Transport
Secretory transport
y = 0.6155x - 2.5577
R2 = 0.8032
-7.20
-6.70
-6.20
-5.70
-5.20
-4.70
-4.20
-3.70
-3.20
-7.00 -6.50 -6.00 -5.50 -5.00 -4.50 -4.00 -3.50 -3.00 -2.50 -2.00
Log Pe Max (pH 5.0, 6.2, 7.4)
Lo
g P
e C
ac
o-2
Theophiline
Antipyrine
Caffeine
Ranitidine
Hydrochlorotiazide
Furosemide
Carbamazepine
MetoprololKetoprofen
Naproxen
Quinine Desipramine
Propanolol
Verapamil

Comparison of PAMPA and Caco-2 Permeability Assay Characteristics
Characteristics PAMPA Caco-2Membrane composition Phospholipid in alkane Caco-2 cell monolayer
Permeability mechanism Passive diffusion Passive diffusion
Active transport
Active efflux
Paracellular
Metabolism No Yes
Max. throughput/instrument 690 cpd/week (3 plates/day in duplicate)
50 cps/week (2 plates/day in both A>B and B>A directions)
Resources Robot, plate washer, UV reader, 1 scientist
Cell culture lab., robot, HPLC or LC/MS, 1.5 scientist
Supplies ++ +++
Estimate cost/sample 1X 15-20X
• PAMPA is a good choice for Screening on Permeability.

Strategy for Combined Use of PAMPA and Caco-2
PAMPA
PAMPA + Caco-2
Caco-2
Passive Diffusion
MechanisticInformation
Passive, active, influx, efflux
and paracellular
Exploratory Discovery Pre-Development Development
Kern, E., (Wyeth Research), J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 6, 1440.

Acknowledgements
Medicinal Chemistry
• Maarten Honing
• Marcel Hermkens
• Michiel Scheffer
• Department of Medicinal Chemistry

30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
PSA
% H
IA
Piroxicam
Tertbutaline
Atenolol RAnitifine
Hydrochlorotiazide
Furosemide
PSA< 62, highly absorved
PSA> 62, poorly absorved
CortisoneDexamethasone
PSA Model for Prediction of Human Intestinal Absorption

Co-Solvent PAMPA Assay
Membrane keeps its integrity
Pex1
0-6 (c
m/s
)

Physicochemical properties of 309 NCEs with low and high bioavailability in rats
0
25
50
75
100
125
150
Bad* Moderate* Good
Monika prediction
nu
mb
er
of
co
mp
ou
nd
s
≤30%
>30%
Bad two or more properties out the preferred rangeModerate one property out the preferred rangeMost important properties are logP, Mw and rotatable bonds