Peptic Ulcer Disease Ppt April 2005
description
Transcript of Peptic Ulcer Disease Ppt April 2005

Peptic Ulcer DiseasePeptic Ulcer Disease

Peptic Ulcer DiseasePeptic Ulcer Disease
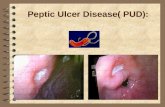
Condition characterized by Condition characterized by – Erosion of GI mucosa resulting from the Erosion of GI mucosa resulting from the
digestive action of HCl and pepsin digestive action of HCl and pepsin– Any portion of GI tract that comes in Any portion of GI tract that comes in
contact with gastric secretions is contact with gastric secretions is susceptible to ulcer development susceptible to ulcer development including lower esophagus, stomach, & including lower esophagus, stomach, & duodenumduodenum
– Includes Includes gastricgastric and and duodenaduodenal ulcersl ulcers

TypesTypes
Acute Acute – Superficial erosionSuperficial erosion– Minimal inflammationMinimal inflammation– Resolves quickly when cause is identified Resolves quickly when cause is identified
& removed& removed ChronicChronic
– Muscular wall erosion with formation of Muscular wall erosion with formation of fibrous tissue fibrous tissue
– Present continuously for many months or Present continuously for many months or intermittentlyintermittently
– 4 times more common than acute ulcers4 times more common than acute ulcers

Peptic UlcersPeptic Ulcers

Peptic Ulcer Disease Peptic Ulcer Disease Etiology and Etiology and PathophysiologyPathophysiology
Peptic Ulcer Disease Peptic Ulcer Disease Etiology and Etiology and PathophysiologyPathophysiology Develop only in presence of acid Develop only in presence of acid
environmentenvironment Excess of gastric acid not Excess of gastric acid not
necessary for ulcer developmentnecessary for ulcer development Person with a Person with a gastricgastric ulcer has ulcer has
normal to less than normal gastric normal to less than normal gastric acidity compared with person acidity compared with person with a with a duodenalduodenal ulcer ulcer

Peptic Ulcer Disease Peptic Ulcer Disease Etiology and Etiology and PathophysiologyPathophysiology
Peptic Ulcer Disease Peptic Ulcer Disease Etiology and Etiology and PathophysiologyPathophysiology Some acid does seem to be essential Some acid does seem to be essential
for a gastric ulcer to occurfor a gastric ulcer to occur Under specific circumstances the Under specific circumstances the
mucosal barrier can be broken and mucosal barrier can be broken and HCL freely enters the mucosa & injury HCL freely enters the mucosa & injury to tissues occursto tissues occurs
This results in cellular destruction & This results in cellular destruction & inflammationinflammation
Histamine is released Histamine is released – Vasodilation, Vasodilation, ↑ capillary permeability ↑ capillary permeability – Further secretion of acid and pepsinFurther secretion of acid and pepsin

Peptic UlcersPeptic Ulcers
Agents known to to destroy the Agents known to to destroy the mucosal barrier include:mucosal barrier include:
H. Pylori H. Pylori - causes chronic - causes chronic inflammation making mucosa inflammation making mucosa more vulnerable to noxious more vulnerable to noxious agentsagents
drugsdrugs (aspirin, NSAIDs, (aspirin, NSAIDs, corticosteroids) – cause abnormal corticosteroids) – cause abnormal permeabilitypermeability

Gastric UlcersGastric Ulcers
Commonly found on lesser Commonly found on lesser curvature in close proximity to curvature in close proximity to antral junctionantral junction
Less common than duodenal Less common than duodenal ulcersulcers
Prevalent in women, older adults, Prevalent in women, older adults, persons from lower persons from lower socioeconomic classsocioeconomic class

Gastric UlcersGastric Ulcers
Characterized by a normal to low Characterized by a normal to low secretion of gastric acidsecretion of gastric acid
Back diffusion of acid is greater Back diffusion of acid is greater (chronic)(chronic)
The ability of the gastric acid to The ability of the gastric acid to penetrate the mucosal barrier is penetrate the mucosal barrier is more important than the amount more important than the amount of gastric acid producedof gastric acid produced

Gastric UlcersGastric Ulcers
Critical pathologic process is amount of Critical pathologic process is amount of acid able to penetrate mucosal barrier acid able to penetrate mucosal barrier
H. pyloriH. pylori is present in 50% to 70% is present in 50% to 70%
H. pyloriH. pylori is thought to be more is thought to be more destructive when noxious agents are destructive when noxious agents are used e.g.. drugs or smokingused e.g.. drugs or smoking

Gastric UlcersGastric Ulcers
Drugs can cause acute and chronic Drugs can cause acute and chronic gastric ulcersgastric ulcers– Aspirin, corticosteroids, and NSAIDsAspirin, corticosteroids, and NSAIDs– Other known causative factors are:Other known causative factors are:
Chronic alcohol abuse, chronic Chronic alcohol abuse, chronic gastritisgastritis
Cigarette smoking is positively linked Cigarette smoking is positively linked with gastric ulcerswith gastric ulcers
Ingestion of hot, spicy foods may be a Ingestion of hot, spicy foods may be a cause but no evidence to support thiscause but no evidence to support this

Duodenal UlcersDuodenal Ulcers
Occur at any age and in anyoneOccur at any age and in anyone Incidence is high Incidence is high between ages of between ages of
35 to 45 years35 to 45 years Affect more men than women Affect more men than women
Account for 80% of all peptic Account for 80% of all peptic ulcersulcers

Duodenal UlcersDuodenal Ulcers
Associated with ↑ HCl acid Associated with ↑ HCl acid secretionsecretion
H. pyloriH. pylori is found in 90-95% of is found in 90-95% of patientspatients– Direct relationship has not been Direct relationship has not been
provenproven

Duodenal UlcersDuodenal Ulcers
Diseases with ↑ risk of duodenal Diseases with ↑ risk of duodenal ulcers -ulcers -COPD, cirrhosis of liver, chronic COPD, cirrhosis of liver, chronic
pancreatitis, hyperparathyroidism, pancreatitis, hyperparathyroidism, chronic renal failurechronic renal failure
Treatments used for these Treatments used for these conditions may promote ulcer conditions may promote ulcer developmentdevelopment

Duodenal UlcerDuodenal Ulcer

Psychological Stress Psychological Stress UlcersUlcers Acute ulcers that develop Acute ulcers that develop
following a major physiologic following a major physiologic insult such as trauma or surgery insult such as trauma or surgery
A form of erosive gastritis A form of erosive gastritis

Psychological Stress Psychological Stress UlcersUlcers Gastric mucosa of body of Gastric mucosa of body of
stomach undergoes a period of stomach undergoes a period of transient ischaemia in association transient ischaemia in association withwith– HypotensionHypotension– Severe injurySevere injury– Extensive burnsExtensive burns– Complicated surgery Complicated surgery

Peptic Ulcer PainPeptic Ulcer Pain
GastricGastric Burning or gaseousBurning or gaseous Can occur when Can occur when
stomach empty or stomach empty or immediately after immediately after foodfood
Located high in Located high in epigastriumepigastrium
Not necessarily Not necessarily relieved by foodrelieved by food
DuodenalDuodenal Burning or cramp-Burning or cramp-
likelike Occurs 2-4 hrs after Occurs 2-4 hrs after
mealsmeals Located in mid-Located in mid-
epigastriumepigastrium Usually relieved by Usually relieved by
food or antacidsfood or antacids

Peptic Ulcer DiseasePeptic Ulcer DiseaseComplicationsComplications
3 major complications3 major complications– HemorrhageHemorrhage– PerforationPerforation– Gastric outlet obstruction Gastric outlet obstruction
Initially treated conservativelyInitially treated conservatively May require surgery at any time May require surgery at any time
during course of therapy during course of therapy

Peptic Ulcer DiseasePeptic Ulcer DiseaseHemorrhage Hemorrhage
Most common complication of Most common complication of peptic ulcer disease peptic ulcer disease
Develops from erosion of Develops from erosion of – Granulation tissue found at base of Granulation tissue found at base of
ulcer during healingulcer during healing– Ulcer through a major blood vesselUlcer through a major blood vessel

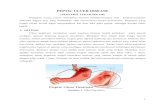
Peptic Ulcer DiseasePeptic Ulcer DiseasePerforationPerforation Most lethal complication of peptic ulcerMost lethal complication of peptic ulcer
Commonly seen in large penetrating Commonly seen in large penetrating duodenal ulcers that have not healed duodenal ulcers that have not healed and are located on posterior mucosal and are located on posterior mucosal wallwall
Perforated gastric ulcers often located Perforated gastric ulcers often located on lesser curvature of stomachon lesser curvature of stomach

Peptic Ulcer DiseasePeptic Ulcer DiseasePerforationPerforation
Fig. 40-15