Pentose PO4 pathway, Fructose, galactose metabolism · For each mole of glucose 6 PO 4 metabolized...
Transcript of Pentose PO4 pathway, Fructose, galactose metabolism · For each mole of glucose 6 PO 4 metabolized...

Pentose PO4 pathway, Fructose, galactose metabolism

The Entner Doudoroff pathway begins with hexokinase producing Glucose 6 PO4 , but produce only one ATP. This pathway prevalent in anaerobes such as Pseudomonas, they doe not have a Phosphofructokinase.



For each mole of glucose 6 PO4 metabolized to ribulose 5 PO4, 2 moles of NADPH are produced. 6-Phosphogluconate dh is not only an oxidation step but it’s also a decarboxylation reaction.
The pentose phosphate pathway (also called the phosphogluconate pathway and the hexose monophosphate shunt) is a biochemical pathway parallel to glycolysis that generates NADPH and pentoses. While it does involve oxidation of glucose, its primary role is anabolic rather than catabolic. There are two distinct phases in the pathway. The first is the oxidative phase, in which NADPH is generated, and the second is the non-oxidative synthesis of 5-carbon sugars. For most organisms, the pentose phosphate pathway takes place in the cytosol.

The primary results of the pathway are: The generation of reducing equivalents, in the form of NADPH, used in reductive biosynthesis reactions within cells (e.g. fatty acid synthesis). Production of ribose-5-phosphate (R5P), used in the synthesis of nucleotides and nucleic acids. Production of erythrose-4-phosphate (E4P), used in the synthesis of aromatic amino acids.
Transketolase and transaldolase reactions are similar in that they transfer between carbon chains, transketolases 2 carbon units or transaldolases 3 carbon units.

Regulation; Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase is the rate-controlling enzyme of this pathway. It is allosterically stimulated by NADP+. The ratio of NADPH:NADP+ is normally about 100:1 in liver cytosol. This makes the cytosol a highly-reducing environment. An NADPH-utilizing pathway forms NADP+, which stimulates Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase to produce more NADPH. This step is also inhibited by acetyl CoA.

Epimerase interconverts the stereoisomers ribulose-‐5-‐phosphate and xylulose-‐5-‐phosphate. Isomerase converts the ketose ribulose-‐5-‐phosphate to the aldose ribose-‐5-‐phosphate. Both reac:ons involve deprotona:on to form an endiolate intermediate, followed by specific reprotona:on to yield the product. Both reac:ons are reversible.
Ribose-‐phosphate diphosphokinase (or phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase)
ATP AMP
PRPP

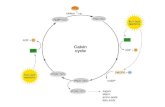
Role of NADPH and glutathione in protecting cells against highly reactive oxygen derivatives. Reduced glutathione (GSH) protects the cell by destroying hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl free radicals. Regeneration of GSH from its oxidized form (GSSG) requires the NADPH produced in the glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase reaction.


Muscle Metabolism of Fructose (Anaerobic Glycolysis) Large Amounts of Hexokinase!
O
HO
HOCH2
H
OH H
CH2OH
OHH
ATP ADP
O
HO
POCH2
H
OH H
CH2OH
OHHHexokinase
!-D-Fructose
Glycolysis
!-D-Fructose-6-P

Fructose is metabolized almost completely in the liver in humans, where it is directed toward replenishment of liver glycogen and triglyceride synthesis. Under one percent of ingested fructose is directly converted to plasma triglyceride. 29% - 54% of fructose is converted in liver to glucose, and about quarter of fructose is converted to lactate. 15% - 18% is converted to glycogen. Glucose and lactate are then used normally as energy to fuel cells all over the body.


Aldolase B also known as fructose-bisphosphate aldolase B or liver-type aldolase is one of three isoenzymes (A, B, and C) of the class I fructose 1,6-bp aldolase enzyme, and plays a key role in both glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. The generic fructose 1,6-bp aldolase enzyme catalyzes the reversible cleavage of fructose 1,6-BP into GAP & DHAP as well as the reversible cleavage of fructose 1-p into glyceraldehyde and DHAP. In mammals, aldolase B is preferentially expressed in the liver, while aldolase A is expressed in muscle and erythrocytes and aldolase C is expressed in the brain. Slight differences in isozyme structure result in different activities for the two substrate molecules: FBP and fructose 1-p. Aldolase B exhibits no preference and thus catalyzes both reactions, while aldolases A and C prefer F 1,6bp.

The synthesis of glycogen in the liver proceeds from gluconeogenic precursors. Fructose is initially converted to DHAP and glyceraldehyde by fructokinase and aldolase B. The resultant glyceraldehyde then undergoes phosphorylation to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. Increased conc of DHAP and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate in the liver drive the gluconeogenic pathway toward glucose-6-phosphate, glucose-1-phosphate and glycogen formation. It appears that fructose is a better substrate for glycogen synthesis than glucose and that glycogen replenishment takes precedence over triglyceride formation. Once liver glycogen is replenished, the intermediates of fructose metabolism are primarily directed toward triglyceride synthesis.

Fructose results in the insulin-independent induction of several important hepatic lipogenic enzymes including PK, NADP+-dependent malate dh, citrate lyase, acetyl CoA carboxylase, FA synthase, as well as pyruvate dh.
Fr-1-PO4 then undergoes hydrolysis by Fr-1-PO4 aldolase (aldolase B) to form DHAP and glyceraldehyde; DHAP can either be isomerized to glyceraldehyde 3-PO4 by TIM or undergo reduction to glycerol 3-PO4 by glycerol 3-PO4 dh. The glyceraldehyde produced may also be converted to glyceraldehyde 3-PO4 by glyceraldehyde kinase or converted to glycerol 3-phosphate by glyceraldehyde 3-PO4 dh. The metabolism of fructose at this point yields intermediates in gluconeogenic pathway leading to glycogen synthesis, or can be oxidized to pyruvate and reduced to lactate, or be decarboxylated to acetyl CoA in the mitochondria and directed toward the synthesis of free FA, resulting finally in TG synthesis.

Lactose, which is converted to galactose and glucose, is the primary carbohydrate source for developing mammals, and in humans it constitutes 40 percent of the energy consumed during the nursing period. Why lactose evolved as the unique carbohydrate of milk is unclear, especially since most individuals can meet their galactose need by biosynthesis from glucose. Whatever the rationale for lactose in milk, the occurrence of galactose in glyco-proteins, complex polysaccharides, and lipids, particularly in nervous tissue, has suggested specific functions. The organoleptic and physical properties of galactose and, more specifically, the simultaneous occurrence of calcium and lactose in milk, may be significant evolutionary determinants.