Pelvic Fractures and Associated Injuries
description
Transcript of Pelvic Fractures and Associated Injuries

Pelvic Fractures and
Associated InjuriesDr Huw Williams MB BCh MCEM

1o Survey A
B
C
D
E
2o Survey
3o Survey
Pelvic Injuries in Trauma

1o Survey A
B
C
D
E
2o Survey
3o Survey
Pelvic Injuries in Trauma

Pelvic Anatomy

1. Sacrum
2. Innominate bones
3. Ligamentous complex
Pelvic Anatomy

Pelvic # in approx. 9% of all major traumas
All age mortality rate = 5-to-16%
Age > 65 years mortality rate = 20%
Some mortality quotes up to 45% ?
Pelvic Fractures in Trauma

Pelvic # in approx. 9% of all major traumas
All age mortality rate = 5-to-16%
Age > 65 years mortality rate = 20%
Some mortality quotes up to 45% ?
What does this mean?
? isolated pelvic injury (without an abdominal injury)
Pelvic #s = increased risk of death
Pelvic Fractures in Trauma

Where can we bleed from?

Where can we bleed from?
1. Pelvic venous plexus
2. Pelvic arterial injury
3. Fracture bone surfaces
4. Any visceral injury
Remember: extra-pelvic injuries

Where can we bleed from?
1. Pelvic venous plexus
2. Pelvic arterial injury
3. Fracture bone surfaces
4. Any visceral injury
Remember: extra-pelvic injuries

How much blood can we lose into our pelvis ?
1 litre ?
2 litres ?
3 litres ?
4 litres ?
5 litres ?

How much blood can we lose into our pelvis ?
‘Haemorrhage from pelvic fracture is essentially bleeding into a free space, potentially capable of accommodating the patient’s entire blood volume without gaining sufficient pressure-dependent tamponade’
(Suzuki et al., 2008)

Mechanism of Injury and Classification
Three mechanisms
i. AP Compression Injury
ii. Lateral Compression Injury
iii. A Shear Force Injury

Mechanism of Injury and Classification
Three mechanisms four patterns
i. AP Compression Injury
ii. Lateral Compression Injury
iii. A Shear Force Injury
iv. A Combination

How:
RTC (car vs. peadestrian / motor-cycle crash)
direct crush injury
fall (>12ft)
i. AP Compression Injury

How:
RTC (car vs. peadestrian / motor-cycle crash)
direct crush injury
fall (>12ft)
What Happens:
symphysis pubis brakes
tearing of posterior ligamentous complex
(may rupture venous plexus / internal iliac artery)
AP Compression (‘open book pelvis’)Frequency = 15 to 20 %
i. AP Compression Injury

How:
RTC (motor-cycle crash)
Direct compression / crush
ii. Lateral Compression Injury

How:
RTC (motor-cycle crash)
Direct compression / crush
What Happens:
internal rotation of hemi-pelvis
fractures around pubis
genitourinary system injury
(life threatening haemorrhage is less common)
Lateral Compression (‘closed pelvis’)Frequency = 60 to 70 %
ii. Lateral Compression Injury

How:
falling from a height onto one limb
RTC
iii. Shear Force Injury

How:
falling from a height onto one limb
RTC
What Happens:
high-energy applied in a vertical plane
major instability of pelvisVertical Shear
Frequency = 5 to 15%
iii. Shear Force Injury

Tile Classification
Young Classification
Ross Classification
iv. Combination

iv. Combinationi. AP Compression Injury
? major haemorrhage of the venous plexus / internal iliac artery
ii. Lateral Compression
injury to bladder/urethra/other / ↓ pelvic volume therefore ? ↓ haemorrhage
iii. A Shear Force
high-energy / major instability

Assessing the Pelvis‘Springing the Pelvis’

‘Springing the Pelvis’
Assessing the Pelvis

Direct Peritoneal Lavage
Assessing the Pelvis

Direct Peritoneal Lavage
Assessing the Pelvis

PR for ? high-riding prostate
Assessing the Pelvis

PR for ? high-riding prostate
Assessing the Pelvis

Inspect flanks, scrotum, peri-anal area ?blood at meatus / ?swelling / ?bruising / ?deep laceration
Major disruption
Leg length discrepancy
Distending Abdomen
Signs
Assessing the Pelvis

Tachycardia
Hypotension
Abdominal Pain
Pelvic Pain
Symptoms
Assessing the Pelvis

Plain film PXR BONE
eFAST BLOOD
CT BONE / BLOOD
Angiography / CT angiography BLOOD
Imaging
Assessing the Pelvis

AP Compression Injury
Lat. Compression Injury
A Shear Force Injury
A Combination
Normal
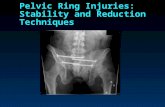
PELVIC X-RAY PLAIN FILM

AP Compression Injury
Lat. Compression Injury
A Shear Force Injury
A Combination
Normal
PELVIC X-RAY PLAIN FILM

AP Compression Injury
Lat. Compression Injury
A Shear Force Injury
A Combination
Normal
PELVIC X-RAY PLAIN FILM

AP Compression Injury
Lat. Compression Injury
A Shear Force Injury
A Combination
Normal
PELVIC X-RAY PLAIN FILM

AP Compression Injury
Lat. Compression Injury
A Shear Force Injury
A Combination
Normal
PELVIC X-RAY PLAIN FILM

AP Compression Injury
Lat. Compression Injury
A Shear Force Injury
A Combination
Normal
PELVIC X-RAY PLAIN FILM

AP Compression Injury
Lat. Compression Injury
A Shear Force Injury
A Combination
Normal
PELVIC X-RAY PLAIN FILM

AP Compression Injury
Lat. Compression Injury
A Shear Force Injury
A Combination
Normal
PELVIC X-RAY PLAIN FILM

AP Compression Injury
Lat. Compression Injury
A Shear Force Injury
A Combination
Normal
PELVIC X-RAY PLAIN FILM

AP Compression Injury
Lat. Compression Injury
A Shear Force Injury
A Combination
Normal
PELVIC X-RAY PLAIN FILM

AP Compression Injury
Lat. Compression Injury
A Shear Force Injury
A Combination
Normal
PELVIC X-RAY PLAIN FILM

AP Compression Injury
Lat. Compression Injury
A Shear Force Injury
A Combination
Normal
PELVIC X-RAY PLAIN FILM

-VE FAST
FOCUSED ABDOMINAL SONOGRAPHY IN TRAUMA

+VE FAST
FOCUSED ABDOMINAL SONOGRAPHY IN TRAUMA

Plain film CT Scan CT 3D reconstruction
CT

Plain film CT Scan CT 3D reconstruction
CT

CT


Angiography / CT Angiography

Managing the Pelvis in the EDSheet
Pelvic binders / splints
? Bend knees & tie ankles (internal rotation)
Scoops (not boards)
Large IV lines / ?permissive hypotensive
resuscitation / ? haemorrhage protocol

Definitive Management of the Pelvis
Surgery stem bleeding / fix pelvis / pack pelvis
Angiography plus iatrogenic embolization

Conclusion
Assume there is not a isolated pelvic injury
Assume the worst
Early intervention / minimal pelvis movement once splinted

Thankyou
Any Questions?

1. Grotz MR, Allami MK, Harwood P, et al. Open pelvic fractures: epidemiology, current concepts of management and outcome. Injury 2005; 36:1.
2. Giannoudis PV, Grotz MR, Papakostidis C, Dinopoulos H. Operative treatment of displaced fractures of the acetabulum. A meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2005; 87:2.
3. Dente CJ, Feliciano DV, Rozycki GS, et al. The outcome of open pelvic fractures in the modern era. Am J Surg 2005; 190:830.4. Hauschild O, Strohm PC, Culemann U, et al. Mortality in patients with pelvic fractures: results from the German pelvic injury
register. J Trauma 2008; 64:449.5. Cannada LK, Taylor RM, Reddix R, et al. The Jones-Powell Classification of open pelvic fractures:. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 2013;
74:901.6. Giannoudis PV, Grotz MR, Tzioupis C, et al. Prevalence of pelvic fractures, associated injuries, and mortality: the United Kingdom
perspective. J Trauma 2007; 63:875.7. Dechert TA, Duane TM, Frykberg BP, et al. Elderly patients with pelvic fracture: interventions and outcomes. Am Surg 2009;
75:291.8. Sathy AK, Starr AJ, Smith WR, et al. The effect of pelvic fracture on mortality after trauma: an analysis of 63,000 trauma patients. J
Bone Joint Surg Am 2009; 91:2803.9. Schulman JE, O'Toole RV, Castillo RC, et al. Pelvic ring fractures are an independent risk factor for death after blunt trauma. J
Trauma 2010; 68:930.10.Demetriades D, Karaiskakis M, Toutouzas K, et al. Pelvic fractures: epidemiology and predictors of associated abdominal injuries
and outcomes. J Am Coll Surg 2002; 195:1.
References