Paranasal Sinus Mucoceles - UTMB Health - Welcome to · PDF filePage 3 Introduction What is a...
Transcript of Paranasal Sinus Mucoceles - UTMB Health - Welcome to · PDF filePage 3 Introduction What is a...

Page 1
Paranasal Sinus Mucoceles
Ashley Agan, MSIV Faculty Advisor: Patricia A. maeso, MD
University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology
Grand Rounds Presentation November 22, 2010

Page 2
Outline
Introduction
Anatomy
Physiology
Pathophysiology
Symptoms
Treatment
Case Presentation

Page 3
Introduction
What is a mucocele? Mucoceles are epithelium-lined, mucus-containing sacs
that completely fill a paranasal sinus
Caused by obstruction of the sinus ostium or obstruction of a mucous secreting gland
– Benign
– Expansion can cause destruction of surrounding structures
– Infected mucopyocele

Page 4
Epidemiology • Rare in United States
• Can take as many as 10-15 years to produce symptoms
• Most commonly found in frontal and ethmoid sinuses
• Japan – increased incidence of maxillary sinus mucoceles • Radical surgery was common for sinusitis

Page 5
Prevalence
• 1978 Natvig and Larsen – 112 patients with mucoceles from 1947 to 1974
77% Frontal Sinus
14% Frontal/anterior ethmoid
5% Anterior ethmoid
1% Posterior ethmoid
3% Maxillary

Page 6
Anatomy Maxillary Sinus

Page 7
Anatomy Frontal Sinus

Page 8
Anatomy Frontal Sinus
– Funnel-shaped
– Vary in size and shape
– Generally have central septum
– Floor slopes inferiorly to the midline
– Primary ostium located on the floor close to the midline
Frontal Recess • Hourglass-like narrowing between frontal sinus and anterior middle meatus • Obstruction results in a loss of ventilation and mucus clearance from frontal sinus

Page 9
Anatomy
Sphenoid Sinus

Page 10
Physiology
• Sinuses are lined by ciliated respiratory epithelium
• Mucous blanket on surface
• Cilia propel mucus in specific pattern of flow – mucociliary clearance

Page 11
Maxillary Sinus
• Mucous flow originates in the antral floor
• Flow is directed centripetally toward primary ostium

Page 12
Frontal Sinus
• Mucous flows up medial wall, laterally across roof, and medially along floor
• Some mucous exits through primary ostium
• The rest is recirculated

Page 13
Appearance
• Macroscopically » Thick walled grayish cyst
• Histology » Pseudo-stratified columnar epithelial cells
» Few ciliated cells
» Sterile mucus and cholesterol crystals
» Hypertrophic goblet cells
» Fibrous thickening of submucosa

Page 14
Pathophysiology
• Obstruction of ostium or outflow tract or of mucus secreting gland
–Inflammation –Trauma/Surgery
–Fractures –Caldwell Luc Procedure
–Mass –Radiotherapy → scarring

Page 15
Caldwell Luc Procedure

Page 16
Pathophysiology
• Secretion of mucus continues → accumulation
• Pressure increases
– Bone devascularization
– Osteolysis

Page 17
Pathophysiology
• Inflammation – cytokines
– IL-1, -6
– TNF alpha
– PGE2
– Bone resorption by osteoclasts

Page 18
Clinical Features • Headache
• Facial pressure
• Facial swelling/deformity
• Dental Pain
• Nasal Obstruction
• Ophthalmic manifestations – Proptosis, Periorbital pain,
Impaired ocular mobility, Blurred/loss of vision, Diplopia
• Neurologic manifestations –Confusion –Meningitis –CSF leak

Page 19
Ophthalmic Manifestations
• Maxillary, Frontal, Anterior ethmoids –
– Proptosis, Periorbital pain, decreased ocular mobility
– Pressure on globe pushes it outwards
– Expansion on to extraocular muscles restricts movement

Page 20
Ophthalmic Manifestations • Sphenoid, posterior ethmoids –
– Blurred vision & decreased ocular mobility
– Expansion of sinus wall may compress optic nerve or compromise its blood supply → optic atrophy
– Direct spread of suppuration → optic neuritis
– Involvement of abducent or oculomotor nerve can cause palsy

Page 21
Complications
• Vision loss – Associated with sudden onset of visual loss by spread of
infection or inflammation to optic nerve → poor prognosis (permanent blindness)
– Gradual vision loss caused by ischemia → better prognosis (resolution of ophthalmic symptoms)

Page 22
Suspicious Historical Elements
• Facial trauma
• Surgery
• Allergic/inflammatory sinus disease

Page 23
Imaging
• CT scan
– Sinus walls bow radially outwards
– Thin or thick sinus walls
– Bony erosions
– Mucocele appears homogeneous and airless

Page 24
45 year old male with left maxillary sinus mucocele

Page 25
37 year old male with bilateral postoperative maxillary sinus mucoceles

Page 26
Imaging • MRI
– Protein and water concentrations vary
– Viscosity varies
– Not best imaging modality
– Good for differentiating mucocele from sinonasal tumors (particularly contrast enhanced)
» Mucoceles have thin peripheral linear enhancement
» Tumors have diffuse enhancement

Page 27

Page 28
Treatment
• Surgical removal or drainage is the only way to prevent intracranial and/or orbital complications
• Surgery » External
» Endoscopic
» Both

Page 29
External
• Indicated if orbital or intracranial involvement
• Good for fronto-ethmoidal mucoceles
• Several different variations
» Riedel
» Killian
» Lynch-Howarth
» Lothrop

Page 30
Riedel’s Procedure
• Removal of anterior wall and floor of frontal sinus
• Entire mucosal lining removed

Page 31
Lynch-Howarth
• Curved incision from inferomedial eyebrow, along upper third of nose
• Medial wall of orbit perforated

Page 32
Osteoplastic Flap
• Cut is made through eyebrows
• Scalp is lifted
• Frontal sinus obliterated with fat
• Bone replaced
• Better cosmesis

Page 33
Endoscopic Approach
• Endoscopic management with marsupialization
– Complete removal of the cyst lining is not required
– Recurrence rates are near 0%
– Goal is establishment of sinus drainage

Page 34
Recurrence
• Risk factors
– Surgery during acute infection
– Presence of multiple mucoceles
– Significant extension outside the sinus wall

Page 35
Surveillance
• Periodic nasal endoscopy in the office is recommended to assess patency of ostium
• Recurrences are few if adequate drainage is established
• It can take many years for mucoceles to recur

Page 36
Case Presentation • 50 yo female
• Referred for chronic sinus issues
• Chief complaint of significant left facial pain and pressure for the past 9 years
• PMH significant for allergic rhinitis and previous episodes of acute sinusitis
• PSH significant for Le Fort I Osteotomy with maxillary advancement procedure done as a child
» Dental cyst found on CT one year previously
» Patient lost job and was without insurance so was not evaluated by OMFS

Page 37
Case Presentation
• Physical Exam
– No polyps or masses
– Extraocular muscles intact
– Nasal mucosa showed no crusting, hypertrophy, or congestion

Page 38
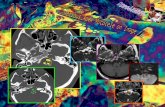
Case Presentation • Dental cyst found on CT one year previously
• Repeat CT
– CT scan read “expansile unilocular homogeneous lesion with thin sclerotic margins associated with the left posterior most tooth apex”

Page 39
Case Presentation
• Patient was seen by OMFS
• Curettage and lavage of the left maxillary sinus and I&D of abscess was performed
• Pain and pressure resolved but returned two weeks later

Page 40
Case Presentation
• CT was reviewed in conjunction with an assessment of the surgery notes
• Lesion was determined to be a mucocele abutting the floor of the maxillary sinus around her teeth

Page 41
Case Presentation

Page 42
Case Presentation
• FESS and antral puncture with marsupialization of the maxillary mucocele
• 1 month after surgery patient had no more complaints of facial pain or pressure

Page 43
Summary • Mucoceles are late complications of sinus ostium
obstruction or mucous gland obstruction
• Expansile lesions that are capable of bony destruction and compromise of surrounding structures
• Endoscopic sinus surgery is the first choice for treatment
• External approaches may be necessary

Page 44
Sources 1. Flint, PW, Cummings CW. "Chronic Frontal Sinus Disease." Cummings
Otolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery. Philadelpha, PA: Mosby Elsevier, 2010. Print.
2. Cagigal BP, Lezcano JB, Blanco RF, Cantera JMG, Cuellar LAS, Hernandez AV. “Frontal Sinus Mucocele with Intracranial and Intraorbital Extension.” Medicina Oral , Patología Oral y Cirugía Bucal 2006; 11:E527-30.
3. Malard O, Gayet-Delacroix M, Jegoux F, Faure A, Bordure P, de Montreuil CB. “Spontaneous Sphenoid sinus Mucocele Revealed by Meningitis and Brain Abscess in a 12-year-old Child.” American Journal of Neuroradiology 2004; 25:873-875.
4. Yap SK, Yap EY. “Frontal Sinus Mucoceles Causing Proptosis – Two Case Reports.” Annals Academy of Medicine Singapore 1998; 27:744-7.
5. Tseng CC, Ho CY, Kao SC. “Ophthalmic Manifestations of Paranasal Sinus Mucoceles.” Journal of Chinese Medical Association 2005; 68:260-4.

Page 45
Sources 6. Rontal ML. “State of the Art in Craniomaxillofacial Trauma: Frontal Sinus.”
Current Opinion in Otolaryngology & Head and Neck Surgery 2008;16:381-6.
7. Moeller CW, Welch KC. “Prevention and Management of Complications in Sphenoidotomy.” Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America 2010; 43:839-54.
8. Natvig K, Larsen TE. “Mucocele of the paranasal sinuses.” The Journal of Laryngology & Otology 1978; 92:1075-82.
9. East D. “Mucoceles of the Maxillary Antrum.” The Journal of Laryngology & Otology 1985; 99:49-56.
10. Kariya S, Okano M, Hattori H, Sugata Y, et al. “Expression of IL-12 and T helper cell 1 Cytokines in the Fluid of Paranasal Sinus Mucoceles.” American Journal of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Medicine and Surgery 2007;28:83-6.
11. Har-El G. “Endoscopic Management of 108 Sinus Mucoceles.” Laryngoscope 2001; 111:2131-4.