P1b revision SJT
Click here to load reader
-
Upload
monkseaton-high-school -
Category
Education
-
view
781 -
download
3
description
Transcript of P1b revision SJT

All EM waves travel through space at speed of light (300 million m/s).
Wave speed= Frequency X Wavelength
(m/s) (Hz) (m)
X-rays and gamma rays are absorbed by dense material such as bone and metal but pass through soft tissue
X-rays and gamma rays damage living tissue when they pass through it.
Large doses can kill cells, small doses can cause cancer
Gamma rays •Have the shortest wavelengths • used to kill bacteria in food, sterilise surgical equipment and kill cancer cells.
Ultraviolet-UV Found naturally in sunlight. UV harms the skin and eyes, causes a sun tan, used in security markers
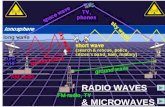
Radio waves are reflected by the IONOSPHERE.
Stronger in summer
Analogue signals vary continuously in amplitude or frequency Digital signals are on or off. Digital signal free of interference and carry more information. Carrier waves (radio, microwaves etc) carries digital/analogue signal
Infrared-IR •All objects emit IR. The hotter the object the more IR it emits •IR heat objects. •Uses: heaters, IR scanners, IR cameras, remote controls, optical fibres and communications
Optical Fibres •Visible light and IR carry signals •Carry more info than wires •More secure, signal stays in wire
Microwaves •Short waves •Can pass through atmosphere for satellite communications •Used in cooking, microwave ovens - heat water molecules
Radio waves •Have the longest wavelengths •Used in communications •Radio waves - smallest long waves - 300,000Hz+ •Carry radio, TV, mobile phone signals •Alternating voltage ariel receiver •Frequency of radio wave = alternating voltage of carrier wave •High frequency radio waves-
•Carry more information •Have a shorter range •Less diffraction
X-rays are used in hospitals to take radiographs.
The use of radio waves depends on the frequency of the waves
P1b, Physics

Marie Curie- Discovered Radioactivity. Worked with uranium. Died of cancer because of her work.
Unstable radioactive elements decay randomly and give off particles Isotope atoms of an element have different numbers of neutrons Detect radiation with Geiger Muller Tube (GM tube)
Alpha Radiation- Stopped by paper or a few cm of air Beta Radiation– Stopped by thin aluminium or about 1m of air Gamma radiation- Stopped by thick lead or concrete and has an unlimited range in air
Alpha particle Positive charge, deflected in magnetic and electric fields, Helium nucleus Beta particle Negative charge, deflected in magnetic and electric fields, electron emitted from nucleus Gamma particles No charge, not deflected in magnetic and electric fields, EM wave
Ionisation- Alpha and beta particles knock electrons out of atoms
Uses of radioactivity •Automatic thickness monitoring- uses beta •Radioactive tracers- uses gamma •Radioactive carbon/uranium dating •Carbon- wood •Uranium- rocks •Smoke detectors- uses alpha
•Light from distant galaxy is red-shifted to longer wavelengths •Edwin Hubble discovered that light from galaxies were red-shifted •Distant galaxies are moving away from us •Speed of distant galaxy is proportional to distance from us The universe is expanding
Big Bang (BB)Theory •Massive explosion from a small point •Background microwave radiation is radiation created just after the BB. •Created as high energy gamma radiation after BB As universe expanded, it stretched into longer and longer wavelengths.
The Earths atmosphere absorbs all electromagnetic waves, except visible light, radio waves and some UV radiation. Satellite detectors are used to make observations outside the visible and radio spectrum. Clear images are observed using telescopes on satellites detecting visible light.
Half life Time it takes for number of radioactive nuclei of the isotope to decay to half its initial value.
P1b Physics
A radioactive substance contains unstable nuclei. An unstable nucleus becomes stable by emitting radiation.
The most distant galaxies are about 13 million light years away.
•Space, time and matter created by the Big Bang •BIG BANG happened 13,000 million years ago
Isotopes Different types of atoms of the same chemical element, each having a different number of neutrons