OXYGEN THERAPY Dora M Alvarez MD 2001. Oxygen Delivery Systems A-a Gradient Oxygen Transport Oxygen...
-
Upload
lewis-mitchell -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
3
Transcript of OXYGEN THERAPY Dora M Alvarez MD 2001. Oxygen Delivery Systems A-a Gradient Oxygen Transport Oxygen...

OXYGEN THERAPYOXYGEN THERAPYDora M Alvarez MDDora M Alvarez MD
20012001

Oxygen Delivery SystemsA-a GradientOxygen TransportOxygen Deliver to Tissues

ABC of Critical CareABC of Critical Care
Basic Principle:The normal cellular function and survival
depends upon a continuous supply of oxygen.
Continuos monitoring is aimed to prevent tissue hypoxia by early detection and treatment of abnormalities leading to hypoxia

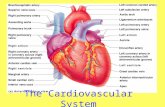
Inspired oxygen from the
environment moves across the
alveolar-capillary membrane into
the blood and is then transported
to the tissues.

INDICATORS OF OXYGENATIONINDICATORS OF OXYGENATION
Arterial Oxygen Tension (PaO2)Pulse Oximetry basic principles are:
– light absorption (different wavelengths)– Plephysmography

Mechanisms of HypoxiaMechanisms of Hypoxia
Pathophysiologic Mechanism leading to hypoxia– Hypoventilation– V/Q Mismatch– R to L shunt– Diffusion impairment– Reduced inspired oxygen tension

The alveolar-arterial oxygen (A-a)
(A-a) gradient is a useful measure of the efficiency of oxygenation.
It compares the diffusion of oxygen from the patient's alveoli to his or her pulmonary capillaries with diffusion in an idealized model of the lung without ventilation/perfusion inequalities or cyclical variations in ventilation or circulation.

A-a GradientA-a Gradient
Calculation of this value incorporates a measure of alveolar ventilation (alveolar CO2, approximated as arterial CO2), therefore it is unaffected by hyper- or hypoventilation

The A-a gradient can be calculated The A-a gradient can be calculated from the following formula:from the following formula:
A-a gradient = FiO2 x (pAtm-pH2O) - (paCO2/R) +
[paCO2 x FiO2 x (1-R)/R] - paO2,
where pAtm = 760 mmHg x exp( -altitude in
meters/7000 ) [3],
and pH2O = 47 mmHg x exp( (Temperature in
centigrade-37)/18.4 ) [4].

Arterial pCO2 in mmHg: 40
Arterial pO2 in mmHg: 90
Percent of inspired O2 (%): 21
(Fraction of inspired O2: 0.21 )
Respiratory quotient: 0.8
Patient's temperature in °F: 98.6 (or in °C: 37.0 )
Approximate elevation in feet: 0 (or in meters: 0 )
A-a gradient in mmHg: 10

• Normal A-a gradient values have not been well established, but • Tend to increase with age • Are slightly higher on 100 percent oxygen than on room air.

Oxygen DeliverOxygen Deliver
This delivery system sustains aerobic cellular metabolism throughout the body.

The Arterial Oxygen Content (CaO2)
The sum of the quantity of oxygen bound to hemoglobin
plus the amount of free oxygen dissolved in the blood,
according to the equation is
CaO2 = (1.34 x Hb concentration x SaO2) + (0.0031 x PaO2)
where:
PaO2 is the partial pressure of oxygen in the arterial blood
SaO2 is the arterial oxyhemoglobin saturation

Hb-Oxygen DisociationHb-Oxygen Disociation
.O2 Sat
PaO2
P50

CaO2 = (1.34 x Hb concentration x SaO2) + (0.0031 x PaO2)
= (1.34 x 15 x 0.98 % ) + (0.0031 x 90)
19.7 + 0.28
= ~ 20 mL of O2 /dL of blood
Arterial Oxygen ContentArterial Oxygen Content

Mixed Venous Oxygen Mixed Venous Oxygen Content Content
CaO2 = (1.34 x Hb concentration x SvO2) + (0.0031 x PvO2)where:
• PvO2 is the partial pressure of oxygen in the mixed venous blood
• SvO2 is the mixed venous oxyhemoglobin saturation
= (1.34 x 15 x 0.7 % ) + (0.0031 x 40)
14 + 0.124
= ~ 14.1 mL of O2 /dL of blood
The normal mixed venous oxygen content is ~ 15 mL O2/dL.

Oxygen DeliveryOxygen Delivery
Oxygen delivery (DO2) is the amount of oxygen transported from the lungs to the microcirculation. Oxygen delivery depends upon the cardiac output (Q) and CaO2:
DO2 (mL/min) = Q x CaO2 The normal oxygen delivery is approximately 1000 mL/min. If the calculation is done using cardiac index rather than cardiac output, then DO2 normalized
to body surface area is ~ 500 mL/min/m2.

Oxygen ConsumptionOxygen Consumption
Oxygen consumption (VO2)
Alternatively, oxygen consumption can be indirectly calculated from the Fick equation:
VO2 = Q x (CaO2 - CvO2) ~ 250 mL/min (1/4 of Oxygen deliver)

Oxygen Toxicity