Ovarian cysts
description
Transcript of Ovarian cysts

Ovarian cysts
• DR. Gehan Mohamed

ovarian cyst
• Definition: it is a fluid-filled sac arising from the ovary.
• Most types of ovarian cysts are harmless (specially the physiologic types )and go away without any treatment

Epidemiology of Ovarian Cysts?
• Many types.
• Different causes.
• Most are asymptomatic.
• Some types can cause serious health problems.

What are the Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts?
• It depend on its type• 1- physiologic cysts : usually Asymptomatic due to their small size
and usually resolve spontanously• 2- symptomatic : ovarian cysts produce A- Pain is caused by : - large size - bleeding - bursting of a cyst, which irritates the abdominal tissues. - Pain can also be caused when a cyst is twisted (called torsion),
which can block the flow of blood to the cyst.B- infertility as with endometriotic cyst, polycystic ovarian syndrome

Torsion of ovarian cyst occurs when the cyst twists on its' vascular stalk, disrupting its' blood supply causing necrosis in the cyst,ovary.

Classification of ovarian cysts
• A – physiologic ovarian cysts
• B- pathologic ovarian cysts

Physiologic ovarian cysts

A- Physiologic ovarian cysts• Types : a- follicicular cyst b- corpus luteum cyst• 95% of ovarian cysts disappear
spontaneously, usually after the next menstrual flow.

What Causes physiologic Ovarian Cysts?• The normal function of the ovaries is to produce an egg
each month.
• during ovulation The mature follicle ruptures so an egg is released and A corpus luteum forms from the empty follicle, and if pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum dissolves.
• Sometimes, however, this process does not conclude appropriately, causing the most common type of ovarian cyst -- functional ovarian cysts.
•

1
Corpus luteum
Graafian follicle
Primary follicles
Growth and Development of Ovarian Follicles


Non neoplastic physiologic ovarian cysts•1- follicular cyst :The most common type, which results from the growth of a follicle. It forms when the follicle grows larger than normal during the menstrual cycle and does not open to release the egg. Usually, follicular cysts resolve spontaneously over the course of days to months. •Cysts can contain blood (hemorrhagic cysts) from injury or leakage of tiny blood vessels into the egg sac.
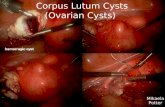
•2- corpus luteum cyst:• corpus luteum is an area of tissue within the ovary that occurs after an egg has been released from a follicle.• If a pregnancy doesn't occur, the corpus luteum usually breaks down and disappears. It may, however, fill with fluid or blood and persist as a cyst on the ovary.
•

Follicular cyst

Follicular cyst

Follicular cyst wall lined by granulosa cells.

Corpus luteum cyst with irregular outline.

Corpus luteum cyst has irregular wavy wall

B- Pathologic ovarian cysts:
• Non NeoplasticNon Neoplastic
a- endometriotic cyst
b- Inflammatory cyst(tubo ovarian abscess)
c- polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
Neoplastic a-Epithelial Tumor e.g mucinous cyst
adenoma b-Sex cord Tumor e.g granulosa cell tumor c-Germ cell Tumor e.g dermoid cyst d- cystic Metastatic
tumor

Neoplastic ovarian cysts

Difference between Benign & Malignant ovarian cysts
Benign ovarian cystsBenign ovarian cysts Malignant ovarian cystsMalignant ovarian cysts
UnilateralUnilateral Bilateral Bilateral
CysticCystic Cystic +Solid componentCystic +Solid component
UnilocularUnilocular MultilocularMultilocular
Stable over timeStable over time GrowGrow
Not associated with Not associated with ascitesascites
Ascites i.e there is fluid Ascites i.e there is fluid in the peritoneal cavity.in the peritoneal cavity. This fluid is formed due to the cancer cells secrete fluid or cause the normal lining of peritonum to produce fluid

Multilocular cyst

Multilocular cyst with solid tissue

Ascites : accumlation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity

• 1- Dermoid cyst or cystic teratoma : Occasionally,the germ cells in the ovary develop abnormally to form other body tissues such as hair or teeth.These common neoplasms contain a variety of elements of dermal origin, including teeth, hair, sebaceous glands, and hormone-producing thyroid cells.

Dermoid ovarian cyst showing hair

Dermoid cyst lined by stratified squamous epithelium with sebacous glands in the dermis

Cystadenoma of ovary is an ovarian cysts that develop from cells on the outer surface of the ovaries.

Non neoplastic pathologic ovarian cysts• 1-Endometriosis is a condition in which endometrial cells
that normally grow inside the uterus ,instead grow outside of the uterus as in ovary, lung ,brain.
• The mechanism by which endometriotic tissue reach other sites either by :
a- retrograde menstruation b- metaplasia in ovarian tissue c- endometrium travel through blood streamd- surgical implantation of endometrium in scar of
cesarian section.•

Effect of endometriotic cyst
• Cyst may grow and bleed with every menstrual cycle, forming a brown-colored cystic area referred to as a chocolate cyst or endometrioma



2- tubo-ovarian abscesses :Infections of the pelvic organs can involve the ovaries and Fallopian tubes .
- Inflammation of ovary called oophritis.- Inflammation of fallopian tube called salpingitis. In severe cases, pus-filled cystic spaces may be present
on or around the ovary or tubes .

3- Polycystic ovarian syndrome(POS) • Classic syndrome originally described by Stein
and Levanthal.
• It is a Syndrome, not a disease because there are multiple potential etiologies with variable clinical expression
• Definition: PCOS is a serious reproductive endocrine disorder characterized by ovulatory dysfunction and hyperandrogenism.

Pathogenesis of POS
• 1- Increased GnRH from hypothalamus lead to Excessive LH secretion relative to FSH by pituitary gland.
• 2- LH stimulates ovarian thecal cells for excess androgen production .
• This excess androgen prevent negative feed back done by estrogen and progesterone on hypothalamus to decrease
• release of LH.• 3- so excess LH lead to excess androgen and appearance of
musculnization criteria.• 4- also excess insulin stimulate excess androgen secretion from
adrenal gland.

hypothalamus
pituitary
ovary
GnRH
LH
androgens
Androgens block inhibitory effect of progesterone
X

Polycystic ovarian syndrome consists of :
1-Hyperandrogenism leading to symptoms of androgen excess as increased muscle mass,acne deepening voice , Hirsutism, acne, male pattern balding, alopecia.
2- Polycystic ovaries due to exces Intraovarian androgen results in excessive growth of small ovarian follicles may reach 12 or more follicles in each ovary measuring 2 to 9 mm in diameter, inhibition of Follicular maturation , thecal and stromal hyperplasia.

Polycystic ovarian syndrome consists of (cont.):
3- anovulation leads to : a-infertility• b- Menstrual irregularity due to deficient progesterone secretion with Chronic estrogen stimulation of the endometrium. the menstrual irregularity is in the form of :• infrequent periods ( > 35 day cycle)• dysfunctional uterine bleeding• occasionally regular periods . c- Increased risk for endometrial hyperplasia and/or endometrial Carcinoma.4-Excess insulin production and insulin resistance.

Androgenic manifestations in POS in form of hirsutism,acne

Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
cysts that form from follicles. These cysts cause the
ovaries to enlarge and create a thick outer covering, which may prevent
ovulation from occurring, and are often the cause of fertility problems.

P O L Y C Y S T I C O V A R I A N S Y N D R O M EP O L Y C Y S T I C O V A R I A N S Y N D R O M EP O L Y C Y S T I C O V A R I A N S Y N D R O M E
N o rm al o variesvo lu m e < 8 cm 3
sc atte red fo llic le sm ild ly e n la rg ed g e n era lly > 8 cm 3
p erip h era l d is trib u tio n o f fo llic le s
in creas ed s tro m a
P o lyc ys tic o varies

biochemical abnormality in polycystic ovary syndrome
total / free testosterone androstenedione LH or LH:FSH ratio. hyperinsulinemia