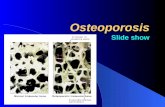
Penyakit Osteoporosis dan Pengobatan Osteoporosis Secara Medis
Osteoporosis
-
Upload
medicaldump -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
9.213 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Osteoporosis

OsteoporosisOsteoporosisOsteoporosisOsteoporosis

Learning objectives :Learning objectives : Burden of the disease.Burden of the disease. Screening and treatment Screening and treatment
guidelines.guidelines. Bisphosphonates.Bisphosphonates. Controversial topics : Controversial topics :
Association of bisphosphonates Association of bisphosphonates withwith ONJONJ Atypical femoral fracturesAtypical femoral fractures Atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation. Esophageal cancer.Esophageal cancer.

Burden of Disease Burden of Disease
1010 million people in US have Osteoporosismillion people in US have Osteoporosis
3333 million people in US have Osteopenia. million people in US have Osteopenia.
Bone health and osteoporosis: Department of health & human Bone health and osteoporosis: Department of health & human
services 2004.services 2004.

Burden of DiseaseBurden of Disease
> 2 million> 2 million fractures/year due to either.fractures/year due to either.
300,000300,000 HIP fractures. HIP fractures.
547,000547,000 vertebral fractures. vertebral fractures.
135,000135,000 pelvic factures.pelvic factures.
Bone health and osteoporosis: Department of health & Bone health and osteoporosis: Department of health &
human services 2004.human services 2004.

Burden of Disease :Burden of Disease :
Hip fracturesHip fractures : : 50 %50 % Permanent impaired mobility. Permanent impaired mobility.
25 %25 % Loose skills to live Loose skills to live independently.independently.
Increased all cause mortality : first Increased all cause mortality : first 3 months3 months after hip fracture. after hip fracture.
1.2010 position statement of the North American Menopause Society. Menopause 2010.1.2010 position statement of the North American Menopause Society. Menopause 2010.

Annual incidenceAnnual incidence

Osteoporosis Osteoporosis

Risk factors Risk factors

Who to screen Who to screen
Women > 65 years.Women > 65 years. Men > 70 years.Men > 70 years. Postmenopausal women /men >50 Postmenopausal women /men >50
years with clinical risk factors.years with clinical risk factors. H/o fracture at age > 50 years.H/o fracture at age > 50 years. Chronic steroid use.Chronic steroid use.


Who to treat ?Who to treat ?
Prior h/o hip/vertebral #Prior h/o hip/vertebral #
oror
T Score < -2.5T Score < -2.5
ororT Score -1 to -2.5 &10 yr risk (FRAX) :
HIP # > 3 % or major osteoporotic # > 20 %
T Score -1 to -2.5 &10 yr risk (FRAX) :
HIP # > 3 % or major osteoporotic # > 20 %
Postmenopausal women /men > 50 yrs
with

Calcium and vitamin Calcium and vitamin D D

Mainstay of Mainstay of treatmenttreatment : :
BisphosphonatesBisphosphonatesApproval in US for osteoporosisApproval in US for osteoporosis Alendronate : 1995Alendronate : 1995 Risedronate : 2000Risedronate : 2000 Ibandronate : 2005Ibandronate : 2005 Zoledronate : 2007.Zoledronate : 2007.

Bone marrow precursorsBone marrow precursors
OsteoblastsOsteoblastsOsteoclastOsteoclast
Lining cellsLining cells
Stimulators of Stimulators of Bone FormationBone Formation
FluorideFluoridePTH analogsPTH analogs
Sr Ranelate (?)Sr Ranelate (?)
Inhibitors ofInhibitors ofBone ResorptionBone Resorption Estrogen, SERMsEstrogen, SERMs
BisphosphonatesBisphosphonatesCalcitoninCalcitonin
Inhibitors ofRANKL
Cathepsin K
Therapeutic strategiesTherapeutic strategiesTherapeutic strategiesTherapeutic strategies

THE LANCETVol 348 • December 7, 1996
Clinical EvidenceClinical EvidenceClinical EvidenceClinical Evidence





Taking BisphosphonatesTaking Bisphosphonates

Contraindications Contraindications

Duration of treatmentDuration of treatment

Cost factorCost factor
Alendronate: $4 - Alendronate: $4 - $40/month $40/month
Risedronate : $60 - Risedronate : $60 - $120/month $120/month
Ibandronate (oral): Ibandronate (oral): $90 - $130/month $90 - $130/month
IV Ibandronate : IV Ibandronate : $1300/year $1300/year
IV Zoledronate : IV Zoledronate : $1300/year$1300/year

Hot topics Hot topics

Osteonecrosis of jaw Osteonecrosis of jaw

ONJ ONJ Osteoporosis :Osteoporosis :
Reporting rate 1/100,000 - 1/250.000.Reporting rate 1/100,000 - 1/250.000. True incidence may be higher.True incidence may be higher.
Malignancy/skeletal metastasis : Malignancy/skeletal metastasis : Estd. Incidence: btw 1- 10 %Estd. Incidence: btw 1- 10 %

Risk factorsRisk factors

RecommendationsRecommendations

Atypical fractures Atypical fractures

Atypical fracturesAtypical fractures
? Long term over suppression of ? Long term over suppression of bone turnover.bone turnover.
Incidence : 1 in 10,000.Incidence : 1 in 10,000. Associated median treatment Associated median treatment
duration : 7 years.duration : 7 years. Causality : long term bp/ atypical # Causality : long term bp/ atypical #
unproven.unproven. Further large scale studies needed.Further large scale studies needed.

RecommendationsRecommendations
Educate physician/patient about Prodromal pain.Educate physician/patient about Prodromal pain. Evaluate with urgent X-Ray.Evaluate with urgent X-Ray. If negative, may consider MRI.If negative, may consider MRI. Stop BP’s if atypical fracture confirmed.Stop BP’s if atypical fracture confirmed.
Shane et al. ASBMR task report. J Bone Miner Res. 2010Shane et al. ASBMR task report. J Bone Miner Res. 2010

Atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation FDA recommends physicians to not FDA recommends physicians to not
alter their prescribing patterns while it alter their prescribing patterns while it continues to monitor post marketing continues to monitor post marketing reports of AF in such patients.reports of AF in such patients.
In v/o above and absence of definitive In v/o above and absence of definitive data : Benefits of treatment outweigh data : Benefits of treatment outweigh risks.risks.

Esophageal cancer Esophageal cancer 23 cases reported in last 23 cases reported in last
2 decades. (Wysowski et 2 decades. (Wysowski et al)al)
31 cases from 31 cases from Europe/Japan.Europe/Japan.
Median time from use to Median time from use to diagnosis : 1-2 yr.diagnosis : 1-2 yr.
Time from exposure Time from exposure inconsistent w/ causal inconsistent w/ causal relation.relation.
Further studies needed.Further studies needed.

Renal safetyRenal safety
Safe for creatinine clearance > 30 -35 Safe for creatinine clearance > 30 -35 ml/min.ml/min.
Lack of experience < 30 ml/min.Lack of experience < 30 ml/min. No data for use in ESRD.No data for use in ESRD. Exact bone disease unknown unless Exact bone disease unknown unless
biopsy.biopsy. Expert opinion: half the dose could be Expert opinion: half the dose could be
used for 3 years in ESRD once bone used for 3 years in ESRD once bone biopsy confirms osteoporosis.biopsy confirms osteoporosis.

Take home points Take home points
Osteoporosis : significant burden of Osteoporosis : significant burden of disease.disease.
Main stay treatment : bisphosphonates.Main stay treatment : bisphosphonates. ? Duration of treatment : individualized.? Duration of treatment : individualized. More research needed to confirm More research needed to confirm
association with ONJ, Subtrochanteric association with ONJ, Subtrochanteric fracture.fracture.
Benefits of treatment outweigh risks in Benefits of treatment outweigh risks in osteoporosis.osteoporosis.