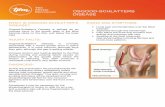
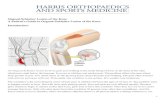
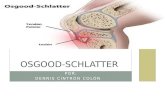
Osgood-Schlatter disease
-
Upload
maryam-al-qahtani -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
441 -
download
2
description
Transcript of Osgood-Schlatter disease

Limping Child
Maryam AL-
Qahtani




A 13-year-old footballer
Pain in both knees

A hard, bony protuberance can be felt at the level of the tuberositas tibiae in both legs.
Tibiae Tuberosity

Objectives:
What is the tuberositas? What is its function ?
What is the probable causes of the patient’s
complaints? Could there be a malignancy?
What diagnostic will you use ?
What treatment is indicated : operative,
conservative or observation?

A large tubercle or
rounded elevation(a
projection or
protuberance),
especially from the
surface of end of a bone
.
Tuberosit
as:

Tibial tuberosity
function:
Location :
At the superior end of the TIBIAL
anterior border
Function :
provides distal attachment for the
patellar ligament, which stretches
between the inferior margin of the
patella and the tibial tuberosity .

What is the probable
causes of the patient’s
complaints? Could there
be a malignancy?

Osgood-Schlatter disease is a painful
condition that usually affects the rapidly
growing knee. The bony knob just below the
kneecap, where the tendon attaches to the leg
bone (shinbone, or tibia), becomes painful.

occurs in young athletes because of too
much stress on the knee. This
disorder occurs more often in boys,
at (13 and 14 years of age).

The bony
knob just
below the
kneecap
becomes
infalmed and
painful.
Bony knob

Cause of the patient’s complain
NO malignancy involved in this case.

Diagnosis

History
The typical symptoms.
Physical examination
findings.
will check the knee for tenderness,
swelling, pain and redness

The typical symptoms.
Painful swelling over a bump on the lower leg bone (shinbone).
leg pain or knee pain , which gets worse with running, jumping, and
climbing stairs.
History:Diagnostics of choice

Diagnostics of choice
Extending the knee against resistance
Evaluation of range of motion of the hip to make sure that the knee pain
is not related
Pain on examination may be reproduced by
Squatting with the knee in full flexion
Straight-leg raising usually is painless

An x-ray can confirm
the diagnosis.
Radiographs
Plain radiographs are obtained to exclude other conditions (eg, tibialapophyseal fracture, tumors, osteomyelitis) in patients who have atypical features.

TreatmentIndicated : operative, conservative or
observation?

Tre
atm
en
t
Benign and a self-limiting
condition.
90% of patients treated with
conservative care were relieved
of all of their symptoms
approximately 1 year (or 6 to 18
months ) after onset of
symptoms.

Goal:
Control of pain and swelling.
Continuation of activity.
Physical therapy (to strengthen the quadriceps and
improve quadriceps and hamstring flexibility).

Treatment involves:
RICE.Rest, Ice, Compressing, and Elevating the area.
Medication .

RICE:
R = Rest the knee from the painful activity.

I = Ice the affected area for 20 minutes, 3 times a day.
C = Compress the painful area with an elastic bandage.
RICE

E = Elevate the leg.
A suitable
program can be
provided by a
physiotherapist
RICE

Summary:

Medication :
Analgesics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
(NSAIDs) may be given for pain relief and reduction of local
inflammation.
Most use :Acetaminophen or ibuprofen

Surgical Management
Excision of intra-tendon
ossicles.
Tibial sequestrectomy.

Quiz

I have Osgood-Schlatter disease .My Treatment Indicated :
operative
conservative
observation



What is most plain radiographs are obtained to exclude other conditions in patients who have atypical features of osgood-schlatter disease ?


Osgood-schlatter disease is a painful condition that usually affects the
rapidly growing knee.
Caused by small injuries due to repeated overuse.
The diagnosis of osgood-schlatter disease is made by clinical examination.
X-ray (plain radiographs )are obtained to exclude other conditions .
Treatment :conservative care.

References:
Osgood-Schlatter disease –up to data .
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001258.htm
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1993268-treatment.
http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/osgood-schlatter-disease/basics/causes/con-20021911
http://familydoctor.org/familydoctor/en/diseases-conditions/osgood-schlatter-disease/treatment.html

Goodbyes are not forever. Goodbyes are
not the end . They simply mean I will miss you, until we
meet again!