Oral Tumor Path
description
Transcript of Oral Tumor Path

ORAL TUMORS

SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA OF THE TONSIL
• Left tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma exhibits enlargement and ulceration of the tonsil. • Between the ages of 50 and 70.
• History of smoking and drinking alcohol.

CANCER METASTASIS

LYMPHOMA OF THE TONSIL
• Second most common type of tonsillar malignancy. • Submucosal mass in an asymmetrical enlargement of one
tonsil. • Multiple enlarged lymph nodes commonly are observed on
the same side of the neck.

Ludwig's Angina
• Inflammation of the submandibular space ( submaxillary space sublingual space via the fascial planes NOT the lymphatics.
• submandibular space is expanded by cellulitis or abscess formation, floor of the mouth becomes indurated tongue is forced upward and backward, airway obstruction.
• Does NOT to mature and form an abscess, it is more likely to produce a cellulitis or a phlegmon.
CLINICAL MANFESTATIONS• Bilateral • Drooling, • Trismus, • Pain, • Dysphagia, • Submandibular swelling • Airway obstruction caused by displacement of the tongue. • Tongue protrusion outside the mouth.
MANAGEMENT• life-threatening condition that requires tracheotomy.

KAPOSI’S SARCOMA
• Small, painless, flat area (lesion) or lump, ranging in colour from brown or brown-red to reddish purple.
• Affect other parts of the body, most commonly the lymph nodes, the lungs and the organs of the digestive system (the gut).
• Signs and symptoms of internal KS depend on the site of the lesion.
• Common in AIDS-related KS,
• lymphoedema and is caused by the KS cells blocking the lymph nodes and disrupting the normal circulation of lymph fluid around the body.

Pleomorphic AdenomaBenign Mixed Tumor
• Most common parotid gland tumor.
• 70-80% of all benign parotid tumors.
• Over 84% of pleomorphic adenomas occur in the parotid gland, 8% occur in the submandibular gland, and 6.4% occur in the minor salivary glands.
• middle aged women
• Sarcomatous transformation is seen in only 2-5% of cases and is usually associated with tumors that have been present for 10-15 years.
CLINICAL MANIFESTATION
• Painless slowly growing mass.
• Solitary and well demarcated.
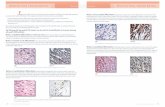
GROSS
• Heterogeneous secondary to hemorrhage, calcification, and necrosis.

Warthin's TumorBenign Papillary Cystadenoma Lymphomatosum
• Second most common benign tumor of the parotid gland.• It accounts for 2-10% of all parotid gland tumors. • More common in older white men and is the most likely
to be bilateral in 10% of the cases.