Obstetric Brachial Plexus Palsy
-
Upload
gajanan-pandit -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
683 -
download
10
description
Transcript of Obstetric Brachial Plexus Palsy

Obstretic brachial plexus palsyObstretic brachial plexus palsy
Dr. Gajanan Pandit
Mumbai Port Trust Hospital

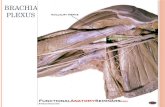
AnatomyAnatomy

Anatomy VariationsAnatomy Variations
Pre Fixedrun from C4-C8
stretching injury
-Erb’s palsy
Post fixedrun from C6-T2
abduction injury
-Kumpke’s palsy

DefinitionDefinition
An injury to all or to a portion of a child’s brachial plexus nerve network occurring at the time of delivery.

ClassificationClassification
Pre/PostganglionicSupra/InfraclavicularNature of injury Level of injury

Risk factorsRisk factors
Cephalopelvic disproportion A large or a macrosomic baby Delivery-Premature/Breech/Instrumental Shoulder dystocia Primigravida Prolonged labour Congenital anomalies

Shoulder dystociaShoulder dystocia

TypesTypes
Erb-Duchenne Palsy (60%)Klumpke’s Palsy (5%)
+ Horner syndrome (1%)Mixed (35%)

Erb-Duchenne PalsyErb-Duchenne Palsy
William Smellie, a British obstetrician is credited with the first medical description of obstetric brachial plexus palsy.
1861- Benjamin Amand Duchenne coined term ‘obstetric palsy of the brachial plexus’
1874 - Wilhelm Heinrich Erb concluded his thesis on adult brachial plexus injuries

Risk FactorsRisk Factors
MaternalFoetalIntrapartum events Neonatal

Mechanism of injuryMechanism of injury
Bending or stretching of the neck in a direction away from the side of injury

Clinical presentationClinical presentation
waiter’s /porter's/policeman’s tip position

Affected nerves Affected nerves
Dorsal scapular, suprascapular, lateral pectoral, long thoracic, musculocutaneous, radial, median and phrenic nerves.

Sensory deficits Sensory deficits
Radial side of the deltoid, forearm and hand

Muscle weakness Muscle weakness
External rotators and abductors of the shoulder/arm.
Flexors of the forearm. Extensors of the fingers (C7). Diaphragm descent (C4).

Muscle weaknessMuscle weakness
• Moro, biceps and radial reflexes are absent on the affected extremity however,
• grasp reflex remains intact.

Klumpke’s Palsy Klumpke’s Palsy
1885 -Augusta Dejerine-Klumpke neurologist and neuroanatomist diagnosed total brachial plexus radicular paralysis with oculopupillary involvement in a patient

Risk FactorsRisk Factors
MaternalFoetalIntrapartum events Neonatal

Mechanism of injuryMechanism of injury
Pulling up of the arm above the head, so that stretch on the C8 and T1 roots

Affected nervesAffected nerves
Inferior trunk ( C8,T1)Radial nerve, ulna nerve, the
thoracodorsal nerve, median nerve and the medial pectoral nerve.

Sensory deficitsSensory deficits
Ulnar side of the forearm and hand

Muscle weaknessMuscle weakness
Pronators of the forearm Flexors of the wrist joint.

Horner syndromeHorner syndrome
Bernard-Horner syndrome and oculo-sympathetic palsy
Injury to cervical sympathetic ganglions. Enophthalmos, partial ptosis, swelling of
the lower eyelid, miosis , unhydrosis and heterochromia.
Loss of ciliospinal reflex.

ComplicationsComplications
Fracture of the clavicle Fracture of the humerus Subluxation of the cervical spine Cervical cord injury Facial nerve palsy Phrenic nerve palsy

Nerve InjuryNerve Injury
Avulsion :- Rupture :-Stretching :-Scarring :- Neuropraxia Axonotmesis Nerotonmesis

ManagementManagement
X-rays to exclude fractures and examination for phrenic nerve paresis are important.
Other investigations - Electromyography, NAP, SEP, Nerve conduction studies, CT myography and MRI.

ManagementManagement
Most cases of OBPI resolve spontaneously in ~ 4 months to 2 year4 months to 2 year after delivery.
To prevent contractures, physiotherapy using wrist splits after 7days immobilization.
Surgery if movement doesn’t return after 3 months and electrophysiology indicate a poor prognosis.

Opponens Pollicis
Flexor Pollicis LongusAdductor Pollicis
Pectoralis Major (lower)
Biceps
Flexor Pollicis Brevis
Extensor Digitorum SuperficialisExtensor Digitorum Profundus
Pronator Quadratus
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus & Brevis
Frexor Carpi Radialis
Triceps
Extensor indices
Extensor DigitorumFlexor Carpi Ulnaris
Extensor Digiti MininiExtensor Carpi Ulnaris
Extensor Pollicis LongusAbductor Pollicis LongusExtensor Pollicis Longus
BrachialisPronator Teres
Pectoralis Minor
DeltoidSerratus Anterior
Rhomboid Major & MinorSupinator
C5SupraspinatusInfraspinatus
Pectoralis Major (upper)
T1 C8 C7 C6
LumbricalsBrevis
Abductor PollicisInterossei

NeurrorhaphyNeurrorhaphy

NeurolysisNeurolysis

NeuromaNeuroma

NeurotizationNeurotization

Botox InjectionBotox Injection

Nerve ConduitNerve Conduit

Tendon TransferTendon Transfer

Modified ‘Quad’Modified ‘Quad’

Tendon TransferTendon Transfer

Nerve DecompressionNerve Decompression

Bony ProceduresBony Procedures

Triangle TiltTriangle Tilt

Post op.Post op.

Thank you…..Thank you…..