Objectives: 1. Identify two forces that result from electric charges 2. Explain why objects attract...
-
Upload
mustafa-nicolls -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of Objectives: 1. Identify two forces that result from electric charges 2. Explain why objects attract...
- Slide 1
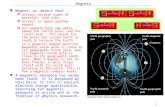
Slide 2 Objectives: 1. Identify two forces that result from electric charges 2. Explain why objects attract and repel each other. 3. Communicate how positively charged object can be used to determine the charge on another object. 4. Infer how electric charges behave in everyday situations Slide 3 Review concerning Charge and Force Recall that matter is made of atoms which contain electrons, protons and neutrons. PROTONS - ELECTRONS NEUTRONS + charge charge NO charge Slide 4 What do charged particles create? The positive and negative electric charges in objects can produce a force between the objects. If charges are opposite, they will cause objects to attract to each other. If charges are alike the will cause objects to repel or push away from each other. Slide 5 + Opposites attract Slide 6 - - Like charges will repel each other Slide 7 ELECTRIC FIELD An electric field is a region surrounding a charged object. Strongest part of field is closest to the charged area Weakest part of field Is the area farthest away from the charged object Slide 8 Perhaps you have experienced this. When you drive close to a power line you may get some static on a car radio. What causes this? Because there is an electric current flowing through the power line there is an electric field around the line. This electric field can cause interference on your radio. Power line Slide 9 ELECTRICITY AND YOU Your body uses electric signals to communicate with the brain. If you touch something hot, the - charge inside the nerve cell changes sending a signal along the nerve cell to the spinal cord, to your hand, telling it to drop the object. Slide 10 11.2 STATIC ELECTRICITY Objectives: 1. Identify three ways static charge can build up 2. Explain what causes lightning. 3. Compare electric conductors and insulators 4. Infer why lightning can be dangerous Slide 11 Has this ever happened to you? Slide 12 How does the person who shocked you become charged with electricity? First of all, you must understand that of the three Particles that make up an atom, ONLY THE e CAN MOVE. When the person who shocked you rubbed their feet on the carpet electrons from the carpet were moved to the person. This build up of electrons jumped from their finger to your ear. Static build-up is when electrons become overloaded on an object. Static means stationary or not moving. Slide 13 In this example the person (object) became charged by FRICTION Can you think of other examples of causing static build-up (charging) by friction? Slide 14 CONDUCTION Charging by conduction occurs when electrons are transferred from one material to another by direct contact -- - - - --- - ------ When the leaves of the electro- scope become loaded with electrons they repel and separate. electroscope -a device which detects an electrical charge Slide 15 INDUCTION Charging by induction occurs when charges are rearranged without direct contact, the charged object simple comes close to another object. -- - - --- -- - --- - --- ----- electroscope What has become charged? The leaves of the electroscope - - - - - Slide 16 HOW DOES IT HAPPEN ? Slide 17 +_+_+_+_+_+_+ _+_+_+_+_+_+_ +_+_+_+_+_+_+ When clouds are swirled around and blown together by turbulence in the upper atmosphere, there is a great deal of friction between the water molecules. This friction causes electrons to be jarred loose and eventually there is a build-up of electrons within an area of the cloud. This is called static build-up. When this happens, lightning can occur in several ways: Slide 18 +++++++++ +++++++++ +++++++++ +++++++++ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ +_ _ _+ _ _ + + _ _ _ _ + _ _ _ _ _ + _ _ _ + _ _ _ _ + _ _ _ _ One end of the cloud has more + charges. The other end of the cloud has more charges. What happens now? + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _+ _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ The + - attraction between the ends of the clouds causes a static discharge(lightning) resulting in a cloud which now has evenly distributed + & - charges. Lightning within a single cloud is called St. Elmos Fire The most common form of lightning Slide 19 + + + _ + + _ + + _ _ + + + + _ _ _ + _ _ + _ _ _ + + _ _ _ _ + + + _ + + _ + + _ _ + + + + _ _ _ + _ _ + _ _ _ + + _ _ _ _ What will happen here? A charged cloud + _ A second charged cloud + _ Where is the + - attraction? When the negative end of one cloud comes close to the positive end on another cloud you will see lightning from one cloud to another. Slide 20 + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ + _ +_ + + + _ + + _ + + _ _ + + + + _ _ _ + _ _ + _ _ _ + + _ _ _ _ + _ How does one cloud charge another? A charged cloudA neutral cloud + _ + + + _ + _ + + + + + + _ _ _ + _ _ _ + When a charged object comes close to another object, the second object becomes charged by __________________. INDUCTION What makes this happen? Like charges repel so when the end with a large number of electrons (-) comes close to the other cloud the electrons in the neutral cloud are repelled to the other end of the cloud causing it to have charged ends. + _ Slide 21 How does lightning strike things on the ground? + + + _ + + _ + + + _ + _ _ _ + _ _ _ _ A neutral tree with + & - scattered equally throughout A charged cloud What happens? + + + + _ + + _ + + _ _ _ _ _ + When the cloud gets close to the tree the tree becomes charged by induction. When the + / - attraction becomes great enough there is a static discharge of electrons to the tree. Slide 22 + + + _ + + _ + + + _ + _ _ _ + _ _ _ _ A charged cloud Why is it unsafe to seek shelter under a tree during a storm? + + + _ + + + + + _ ++ + ________ + _ + _ + _ Lightning will try to find the fastest way to the ground. The people under the tree become charged by induction just like the tree does. As lightning takes its path to the ground, it will come out of the tree and to the boys then to the ground. Slide 23 Dont make someone cry. Slide 24 Slide 25 CONDUCTORS - A material through which electric charges flow easily. Examples include most metals such as gold, silver, copper, aluminum and mercury. Non metals such as water and acid are also good conductors. NOTE: Pure water does not conduct electricity, it must have some type of electrolyte or substance in it. Since the water you use at home is not pure water, it is a good conductor, it is wise to be careful when handling appliances around wet areas. Slide 26 INSULATORS: Materials through which electric charges cannot move easily. Examples include wood, ceramic, rubber, glass and plastic. Note: you may have noticed that most wire to electrical appliances are coated with rubber or plastic. wire insulation In an insulator, the atoms are not arranged in a manner which will allow the electrons to move freely. Therefore, insulators are not capable of carrying electrical energy. Slide 27 SCIENCE AND YOU Do your clothes ever stick together when you take them of the dryer? Does your hair follow the comb or brush instead of lying flat? While drying, some clothes pick up a negative charge while others keep a positive charge. Using your knowledge about charges what happens? Using your knowledge about charges, explain what you think happens to your hair.