Nucleic Acids - WordPress.com · Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids Nucleotides have major metabolic...
Transcript of Nucleic Acids - WordPress.com · Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids Nucleotides have major metabolic...

Nucleic Acids
Structure, Function, and the Central Dogma

3.7 Nucleic Acids
Some nucleotides are subunits of nucleic acids
such as DNA and RNA
Some nucleotides have roles in metabolism

Nucleotides
Nucleotide
• A small organic molecule consisting of a sugar
with a five-carbon ring, a nitrogen-containing
base, and one or more phosphate groups
ATP
• A nucleotide with three phosphate groups
• Important in phosphate-group (energy) transfer

ATP

Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids
• Polymers of nucleotides in which the sugar of one
nucleotide is attached to the phosphate group of
the next
• RNA and DNA are nucleic acids

RNA
RNA (ribonucleic acid)
• Contains four kinds of nucleotide monomers,
including ATP
• Important in protein synthesis

DNA
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
• Two chains of nucleotides twisted together into a
double helix and held by hydrogen bonds
• Contains all inherited information necessary to
build an organism, coded in the order of
nucleotide bases

Four Nucleotides of DNA

Fig. 3-21, p. 48
adenine (A)
base with a
double ring
structure
thymine (T)
base with a
single ring
structure 3 phosphate
groups
sugar
(deoxyribose) guanine (G)
base with a
double ring
structure
cytosine (C)
base with a
single ring
structure

Fig. 3-22, p. 49
covalent
bonding in
sugar–
phosphate
backbone
hydrogen bonding
between bases

3.7 Key Concepts:
Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids
Nucleotides have major metabolic roles and are
building blocks of nucleic acids
Two kinds of nucleic acids, DNA and RNA,
interact as the cell’s system of storing, retrieving,
and translating information about building
proteins

DNA Structure and Function
Chapter 13

Impacts, Issues
Here Kitty, Kitty, Kitty, Kitty, Kitty
Clones made from adult cells have problems;
the cell’s DNA must be reprogrammed to
function like the DNA of an egg

13.2 The Discovery of DNA’s Structure
Watson and Crick’s discovery of DNA’s structure
was based on almost fifty years of research by
other scientists

DNA’s Building Blocks
Nucleotide
• A nucleic acid monomer consisting of a five-
carbon sugar (deoxyribose), three phosphate
groups, and one of four nitrogen-containing bases
DNA consists of four nucleotide building blocks
• Two pyrimidines: thymine and cytosine
• Two purines: adenine and guanine

Four Kinds of Nucleotides in DNA

Fig. 13-4a, p. 206
adenine (A)
deoxyadenosine triphosphate, a purine

Fig. 13-4b, p. 206
guanine (G)
deoxyguanosine triphosphate, a purine

Fig. 13-4c, p. 206
thymine (T)
deoxythymidine triphosphate, a pyrimidine

Fig. 13-4d, p. 206
cytosine (C)
deoxycytidine triphosphate, a pyrimidine

Chargaff’s Rules
The amounts of thymine and adenine in DNA
are the same, and the amounts of cytosine and
guanine are the same: A = T and G = C
The proportion of adenine and guanine differs
among species

Franklin, Watson and Crick
Rosalind Franklin’s research in x-ray
crystallography revealed the dimensions and
shape of the DNA molecule: an alpha helix
This was the final piece of information Watson
and Crick needed to build their model of DNA

Watson and Crick’s DNA Model
A DNA molecule consists of two nucleotide
chains (strands), running in opposite directions
and coiled into a double helix
Base pairs form on the inside of the helix, held
together by hydrogen bonds (A-T and G-C)

Patterns of Base Pairing
Bases in DNA strands can pair in only one way
• A always pairs with T; G always pairs with C
The sequence of bases is the genetic code
• Variation in base sequences gives life diversity

Structure of DNA

Fig. 13-5a, p. 207

DNA Double Helix
• Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin • James Watson and Francis Crick
Features: • two helical polynucleotides coiled around an axis • chains run in opposite directions • sugar-phosphate backbone on the outside, bases on the inside • bases nearly perpendicular to the axis • repeats every 34 Å • 10 bases per turn of the helix • diameter of the helix is 20 Å
Secondary Structure


Double helix stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
Which is more stable?

Axial view of DNA

A and B forms are both right-handed double helix. A-DNA has different characteristics from the more common B-DNA.

• left-handed • backbone phosphates zigzag
Z-DNA

Comparison Between A, B, and Z DNA:
A-DNA: right-handed, short and broad, 11 bp per turn
B-DNA: right-handed, longer, thinner, 10 bp per turn
Z-DNA: left-handed, longest, thinnest, 12 bp per turn

Major and minor grooves are lined with sequence-specific H-bonding.

Supercoiling
relaxed DNA
supercoiled DNA
Tertiary Structure

Consequences of double helical structure:
1. Facilitates accurate hereditary information transmission 2.Reversible melting
• melting: dissociation of the double helix • melting temperature (Tm) • hypochromism • annealing

Structure of Single-stranded DNA
Stem Loop

NUCLEIC ACIDS: STRUCTURE
RNA

Secondary Structure
transfer RNA (tRNA) : Brings amino acids to
ribosomes during translation

Transfer RNA
Extensive H-bonding creates four double helical domains, three capped by loops, one by a stem
Only one tRNA structure (alone) is known
Many non-canonical base pairs found in tRNA

ribosomal RNA (rRNA) : Makes up the ribosomes, together with ribosomal proteins.
Ribosomes synthesize proteins
All ribosomes contain large and small subunits
rRNA molecules make up about 2/3 of ribosome
Secondary structure features seem to be conserved, whereas sequence is not
There must be common designs and functions that must be conserved

messenger RNA (mRNA) : Encodes amino acid sequence of a polypeptide

small nuclear RNA (snRNA) :With proteins, forms complexes that are used in RNA processing in eukaryotes. (Not found in prokaryotes.)

13.2 Key Concepts
Discovery of DNA’s Structure
A DNA molecule consists of two long chains of
nucleotides coiled into a double helix
Four kinds of nucleotides make up the chains,
which are held together along their length by
hydrogen bonds

13.3 DNA Replication and Repair
A cell copies its DNA before mitosis or meiosis I
DNA repair mechanisms and proofreading
correct most replication errors

Semiconservative DNA Replication
Each strand of a DNA double helix is a template
for synthesis of a complementary strand of DNA
One template builds DNA continuously; the other
builds DNA discontinuously, in segments
Each new DNA molecule consist of one old
strand and one new strand

Enzymes of DNA Replication
DNA helicase
• Breaks hydrogen bonds between DNA strands
DNA polymerase
• Joins free nucleotides into a new strand of DNA
DNA ligase
• Joins DNA segments on discontinuous strand

DNA Replication

Stepped Art Fig. 13-6, p. 208
D DNA ligase seals any gaps that remain
between bases of the ―new‖ DNA, so a
continuous strand forms. The base sequence
of each half-old, half-new DNA molecule is
identical to that of the parent DNA molecule.
C Each of the two parent strands serves
as a template for assembly of a new DNA
strand from free nucleotides, according to
base-pairing rules (G to C, T to A). Thus, the
two new DNA strands are complementary
in sequence to the parental strands.
B As replication starts, the two
strands of DNA are unwound. In
cells, the unwinding occurs simul-
taneously at many sites along the
length of each double helix.
A A DNA molecule is double-stranded.
The two strands of DNA stay zippered up
together because they are complementary:
their nucleotides match up according to
base-pairing rules (G to C, T to A).

Semiconservative Replication of DNA

Discontinuous Synthesis of DNA

Fig. 13-8a, p. 209
A Each DNA strand has two
ends: one with a 5’ carbon,
and one with a 3’ carbon.
DNA polymerase can add
nucleotides only at the 3’
carbon. In other words, DNA
synthesis proceeds only in
the 5’ to 3’ direction.

Fig. 13-8b, p. 209
The parent DNA
double helix
unwinds in this
direction.
Only one new
DNA strand
is assembled
continuously.
5’
The other new
DNA strand is
assembled in
many pieces.
3’
3’
Gaps are
sealed by
DNA ligase. 5’ 3’
3’ 5’
B Because DNA synthesis proceeds only in the 5’ to 3’ direction, only
one of the two new DNA strands can be assembled in a single piece.
The other new DNA strand forms in short segments, which are called
Okazaki fragments after the two scientists who discovered them. DNA
ligase joins the fragments into a continuous strand of DNA.

DNA replication requires unwinding of the DNA helix.
expose single-stranded templates DNA gyrase – acts to overcome torsional stress imposed upon unwinding helicases – catalyze unwinding of double helix
-disrupts H-bonding of the two strands
SSB (single-stranded DNA-binding proteins) – binds to the unwound strands, preventing re-annealing


DNA Polymerase = enzymes that replicate DNA
All DNA Polymerases share the following: 1.Incoming base selected in the active site (base-complementarity) 2.Chain growth 5’ 3’ direction (antiparallel to template)
3.Cannot initiate DNA synthesis de novo (requires primer)
First DNA Polymerase discovered – E.coli DNA Polymerase I (by Arthur Kornberg and colleagues)
Roger D. Kornberg
2006 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
Arthur Kornberg
1959 Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine
http://www.nobelprize.org








Checking for Mistakes
DNA repair mechanisms
• DNA polymerases proofread DNA sequences
during DNA replication and repair damaged DNA
When proofreading and repair mechanisms fail,
an error becomes a mutation – a permanent
change in the DNA sequence

13.3 Key Concepts
How Cells Duplicate Their DNA
Before a cell begins mitosis or meiosis, enzymes
and other proteins replicate its chromosome(s)
Newly forming DNA strands are monitored for
errors
Uncorrected errors may become mutations

From DNA to Protein
Chapter 14

Impacts, Issues:
Ricin and your Ribosomes
Ricin is toxic because it inactivates ribosomes,
the organelles which assemble amino acids into
proteins, critical to life processes

14.1 DNA, RNA, and Gene Expression
What is genetic information and how does a cell
use it?

The Nature of Genetic Information
Each strand of DNA consists of a chain of four
kinds of nucleotides: A, T, G and C
The sequence of the four bases in the strand is
the genetic information

Converting a Gene to an RNA
Transcription
• Enzymes use the nucleotide sequence of a gene
to synthesize a complementary strand of RNA
DNA is transcribed to RNA
• Most RNA is single stranded
• RNA uses uracil in place of thymine
• RNA uses ribose in place of deoxyribose

Ribonucleotides and Nucleotides

Ribonucleotides and Nucleotides

DNA and RNA

Fig. 14-3, p. 217
DNA RNA adenine A
NH 2 deoxyribonucleic acid ribonucleic acid
adenine A
NH 2
N C N C C N nucleotide
base HC
C N HC
N N N C CH N C CH
sugar–
phosphate
backbone
guanine G
O guanine G
O
N C N C C NH C NH HC HC
N N NH 2 N NH 2
C C N C C
cytosine C NH 2
cytosine C NH 2
C C HC N HC N
HC C O HC C O N N
thymine T O base pair uracil U O
C C CH 3 C NH HC NH
HC C O HC C O N N
DNA has one function: It
permanently stores a cell’s
genetic information, which
is passed to offspring.
RNAs have various
functions. Some serve
as disposable copies of
DNA’s genetic message;
others are catalytic.
Nucleotide
bases of DNA
Nucleotide
bases of RNA

RNA in Protein Synthesis
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
• Contains information transcribed from DNA
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
• Main component of ribosomes, where polypeptide
chains are built
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
• Delivers amino acids to ribosomes

Converting mRNA to Protein
Translation
• The information carried by mRNA is decoded
into a sequence of amino acids, resulting in a
polypeptide chain that folds into a protein
mRNA is translated to protein
• rRNA and tRNA translate the sequence of base
triplets in mRNA into a sequence of amino acids

Gene Expression
A cell’s DNA sequence (genes) contains all the
information needed to make the molecules of life
Gene expression
• A multistep process including transcription and
translation, by which genetic information encoded
by a gene is converted into a structural or
functional part of a cell or body

14.1 Key Concepts
DNA to RNA to Protein
Proteins consist of polypeptide chains
The chains are sequences of amino acids that
correspond to sequences of nucleotide bases in
DNA called genes
The path leading from genes to proteins has two
steps: transcription and translation

14.2 Transcription: DNA to RNA
RNA polymerase assembles RNA by linking
RNA nucleotides into a chain, in the order
dictated by the base sequence of a gene
A new RNA strand is complementary in
sequence to the DNA strand from which it was
transcribed

DNA Replication and Transcription
DNA replication and transcription both
synthesize new molecules by base-pairing
In transcription, a strand of mRNA is assembled
on a DNA template using RNA nucleotides
• Uracil (U) nucleotides pair with A nucleotides
• RNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the
transcript

Base-Pairing in
DNA Synthesis and Transcription

Fig. 14-4, p. 218
Stepped Art
DNA template
New DNA strand
DNA template
RNA transcript

Process of Transcription has four stages:
1. Binding of RNA polymerase at promoter sites 2. Initiation of polymerization 3. Chain elongation 4. Chain termination

Transcription (RNA Synthesis)
RNA Polymerases
Template (DNA)
Activated precursors (NTP)
Divalent metal ion (Mg2+ or Mn2+)
Mechanism is similar to DNA Synthesis

Reece R. Analysis of Genes and Genomes.2004. p47.
Limitations of RNAP II:
1. It can’t recognize its target promoter and gene. (BLIND)
2. It is unable to regulate mRNA production in response to developmental and environmental signals. (INSENSITIVE)

Start of Transcription
Promoter Sites Where RNA Polymerase can indirectly bind

TATA box – a DNA sequence (5’—TATAA—3’) found in the promoter region of most eukaryotic genes.
Abeles F, et al. Biochemistry. 1992. p391.
Preinitiation Complex (PIC)
Transcription Factors (TF):
Hampsey M. Molecular Genetics of RNAP. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews. 1998. p7.
TFIID binds to TATA; promotes TFIIB binding
TFIIA stabilizes TBP binding
TFIIB promotes TFIIF-pol II binding
TFIIF targets pol II to promoter
TFIIE stimulates TFIIH kinase and ATPase
actiivities
TFII H helicase, ATPase, CTD kinase activities







Termination of Transcription
Terminator Sequence
Encodes the termination signal
In E. coli – base paired hair pin (rich in GC) followed by UUU…
1. Intrinsic termination = termination sites
causes the RNAP to pause
causes the RNA strand to detach from the DNA template

Termination of Transcription
2. Rho termination = Rho protein, ρ

Transcription
Many RNA polymerases can transcribe a gene
at the same time

Fig. 14-6, p. 219
RNA transcripts DNA molecule

14.2 Key Concepts
DNA to RNA: Transcription
During transcription, one strand of a DNA double
helix is a template for assembling a single,
complementary strand of RNA (a transcript)
Each transcript is an RNA copy of a gene

14.3 RNA and the Genetic Code
Base triplets in an mRNA are words in a protein-
building message
Two other classes of RNA (rRNA and tRNA)
translate those words into a polypeptide chain

prokaryotes: transcription and translation happen in cytoplasm
eukaryotes: transcription (nucleus); translation (ribosome in cytoplasm)

In eukaryotes, mRNA is modified after transcription
Capping, methylation
Poly-(A) tail
splicing
capping: guanylyl residue
capping and methylation ensure stability of the mRNA template; resistance to exonuclease activity

Post-Transcriptional Modifications
In eukaryotes, RNA is modified before it leaves
the nucleus as a mature mRNA
Introns
• Nucleotide sequences that are removed from a
new RNA
Exons
• Sequences that stay in the RNA

Alternative Splicing
Alternative splicing
• Allows one gene to encode different proteins
• Some exons are removed from RNA and others
are spliced together in various combinations
After splicing, transcripts are finished with a
modified guanine “cap” at the 5' end and a poly-
A tail at the 3' end

Post-Transcriptional Modifications

Fig. 14-7, p. 220
gene
exon intron exon intron exon
DNA
transcription into RNA
cap poly-A tail
RNA 5’ 3’
snipped out snipped out
mRNA

gene
exon intron exon intron exon
DNA
Fig. 14-7, p. 220
Stepped Art
transcription into RNA
cap poly-A tail
RNA 5’ 3’
snipped out snipped out
mRNA

mRNA – The Messenger
mRNA carries protein-building information to
ribosomes and tRNA for translation
Codon
• A sequence of three mRNA nucleotides that
codes for a specific amino acid
• The order of codons in mRNA determines the
order of amino acids in a polypeptide chain

Properties of mRNA
1. In translation, mRNA is read in groups of bases called “codons”
2. One codon is made up of 3 nucleotides from 5’ to 3’ of mRNA
3. There are 64 possible codons
4. Each codon stands for a specific amino acid, corresponding to the genetic code
5. However, one amino acid has many possible codons. This property is termed degeneracy
6. 3 of the 64 codons are terminator codons, which signal the end of translation

Genetic Information
From DNA to mRNA to amino acid sequence

Genetic Code
Genetic code
• Consists of 64 mRNA codons (triplets)
• Some amino acids can be coded by more than
one codon
Some codons signal the start or end of a gene
• AUG (methionine) is a start codon
• UAA, UAG, and UGA are stop codons

Codons of the Genetic Code


Encoded sequences.
(a) Write the sequence of the mRNA molecule synthesized from a DNA template strand having the sequence
(b) What amino acid sequence is encoded by the following base sequence of an mRNA molecule? Assume that the reading frame starts at the 5 end.
Practice

Answers
(a) 5’ -UAACGGUACGAU-3’ .
(b) Met-Pro-Ser-Asp-Trp-Met.

rRNA and tRNA – The Translators
tRNAs deliver amino acids to ribosomes
• tRNA has an anticodon complementary to an
mRNA codon, and a binding site for the amino
acid specified by that codon
Ribosomes, which link amino acids into
polypeptide chains, consist of two subunits of
rRNA and proteins

Ribosomes

tRNA


14.3 Key Concepts
RNA
Messenger RNA carries DNA’s protein-building instructions
Its nucleotide sequence is read three bases at a time
Sixty-four mRNA base triplets—codons—represent the genetic code
Two other types of RNA interact with mRNA during translation of that code

14.4 Translation: RNA to Protein
Translation converts genetic information carried
by an mRNA into a new polypeptide chain
The order of the codons in the mRNA
determines the order of the amino acids in the
polypeptide chain

Translation
Translation occurs in the cytoplasm of cells
Translation occurs in three stages
• Initiation
• Elongation
• Termination

Initiation
An initiation complex is formed
• A small ribosomal subunit binds to mRNA
• The anticodon of initiator tRNA base-pairs with
the start codon (AUG) of mRNA
• A large ribosomal subunit joins the small
ribosomal subunit

Elongation
The ribosome assembles a polypeptide chain as
it moves along the mRNA
• Initiator tRNA carries methionine, the first amino
acid of the chain
• The ribosome joins each amino acid to the
polypeptide chain with a peptide bond

Termination
When the ribosome encounters a stop codon,
polypeptide synthesis ends
• Release factors bind to the ribosome
• Enzymes detach the mRNA and polypeptide
chain from the ribosome

Polysomes
Many ribosomes may
simultaneously
translate the same
mRNA, forming
polysomes

Initiation
A A mature mRNA
leaves the nucleus and
enters cytoplasm, which
has many free amino
acids, tRNAs, and
ribosomal subunits. initiator
tRNA
small
ribosomal
subunit
mRNA
Fig. 14-12 (a-b), p. 222
Stepped Art
An initiator tRNA binds
to a small ribosomal
subunit and the
mRNA.
large
ribosomal
subunit
B A large ribosomal
subunit joins, and
the cluster is now
called an initiation
complex.
Translation in
Eukaryotes

Translation in Eukaryotes

Fig. 14-12c, p. 223
Elongation
C An initiator tRNA
carries the amino acid
methionine, so the first
amino acid of the new
polypeptide chain will be
methionine. A second
tRNA binds the second
codon of the mRNA (here,
that codon is GUG, so the
tRNA that binds carries
the amino acid valine).
A peptide bond
forms between
the first two
amino acids
(here, methionine
and valine).

Fig. 14-12d, p. 223
D The first tRNA is
released and the
ribosome moves to the
next codon in the mRNA.
A third tRNA binds to the
third codon of the mRNA
(here, that codon is UUA,
so the tRNA carries the
amino acid leucine).
A peptide bond
forms between the
second and third
amino acids
(here, valine
and leucine).

Fig. 14-12e, p. 223
E The second tRNA
is released and the
ribosome moves to the
next codon. A fourth
tRNA binds the fourth
mRNA codon (here, that
codon is GGG, so the
tRNA carries the amino
acid glycine).
A peptide bond
forms between the
third and fourth
amino acids (here,
leucine and
glycine).

Fig. 14-12f, p. 223
Termination
F Steps d and e are repeated over and
over until the ribosome encounters a stop
codon in the mRNA. The mRNA transcript
and the new polypeptide chain are
released from the ribosome. The two
ribosomal subunits separate from each
other. Translation is now complete. Either
the chain will join the pool of proteins in
the cytoplasm or it will enter rough ER of
the endomembrane system (Section 4.9).

14.4 Key Concepts
RNA to Protein: Translation
Translation is an energy-intensive process by
which a sequence of codons in mRNA is
converted to a sequence of amino acids in a
polypeptide chain

14.5 Mutated Genes
and Their Protein Products
If the nucleotide sequence of a gene changes, it
may result in an altered gene product, with
harmful effects
Mutations
• Small-scale changes in the nucleotide sequence
of a cell’s DNA that alter the genetic code

Common Mutations
Base-pair-substitution
• May result in a premature stop codon or a
different amino acid in a protein product
• Example: sickle-cell anemia
Deletion or insertion
• Can cause the reading frame of mRNA codons to
shift, changing the genetic message
• Example: Huntington’s disease

Common Mutations

Fig. 14-13, p. 224
part of DNA
A Part of the DNA,
mRNA, and amino acid
sequence of the beta
chain of a normal
hemoglobin molecule.
mRNA transcribed
from DNA
resulting amino acid sequence
THREONINE PROLINE GLUTAMATE GLUTAMATE LYSINE
base substitution
in DNA
B A base-pair
substitution in DNA
replaces a thymine
with an adenine. When
the altered mRNA is
translated, valine
replaces glutamate as
the sixth amino acid of
the new polypeptide
chain. Hemoglobin with
this chain is HbS—sickle
hemoglobin (Section
3.6).
altered mRNA
altered amino acid sequence
THREONINE PROLINE VALINE GLUTAMATE LYSINE
deletion in DNA
C Deletion of the
same thymine causes a
frameshift. The reading
frame for the rest of the
mRNA shifts, and a
different protein product
forms. This mutation
results in a defective
hemoglobin molecule. The
outcome is thalassemia, a
type of anemia.
altered mRNA
altered amino acid sequence
THREONINE PROLINE GLYCINE ARGININE

What Causes Mutations?
Transposable elements
• Segments of DNA that can insert themselves
anywhere in a chromosomes
Spontaneous mutations
• Uncorrected errors in DNA replication
Harmful environmental agents
• Ionizing radiation, UV radiation, chemicals

Agents of Mutations 1. Physical Agents
a) UV Light b) Ionizing Radiation
2. Chemical Agents Some chemical agents can be
classified further into a) Alkylating b) Intercalating c) Deaminating
3. Viral

UV Light Causes Pyrimidine Dimerization
Replication and gene expression are blocked

Mutations Caused by Radiation
Ionizing radiation damages chromosomes,
nonionizing (UV) radiation forms thymine dimers


Chemical mutagens
• 5-bromouracil and 2-aminopurine can be
incorporated into DNA

Deaminating agents
Ex: Nitrous acid (HNO2) Converts adenine to hypoxanthine, cytosine to uracil, and guanine
to xanthine
Causes A-T to G-C transitions

Alkylating agents

Intercalating agents


Acridines Intercalate in DNA, leading to insertion or deletion
The reading frame during translation is changed

DNA Repair
Direct repair Photolyase cleave pyrimidine dimers
Base excision repair E. coli enzyme AlkA removes modified bases such as 3-
methyladenine (glycosylase activity is present)
Nucleotide excision repair Excision of pyrimidine dimers (need different enzymes
for detection, excision, and repair synthesis)

Inherited Mutations
Mutations in somatic cells of sexually
reproducing species are not inherited
Mutations in a germ cell or gamete may be
inherited, with evolutionary consequences

14.5 Key Concepts
Mutations
Small-scale, permanent changes in the
nucleotide sequence of DNA may result from
replication errors, the activity of transposable
elements, or exposure to environmental hazards
Such mutation can change a gene’s product

Summary:
Protein Synthesis in Eukaryotic Cells

Fig. 14-16, p. 226
Transcription Assembly of RNA on unwound
regions of DNA molecule
mRNA rRNA tRNA mRNA
processing
proteins
mature mRNA transcripts
ribosomal subunits
mature tRNA
Convergence
of RNAs Translation cytoplasmic
pools of
amino
acids,
ribosomal
subunits, and
tRNAs
At an intact
ribosome,
synthesis of a
polypeptide
chain at the
binding sites
for mRNA and
tRNAs
Protein

13.4 Using DNA to
Duplicate Existing Mammals
Reproductive cloning is a reproductive
intervention that results in an exact genetic copy
of an adult individual

Cloning
Clones
• Exact copies of a molecule, cell, or individual
• Occur in nature by asexual reproduction or
embryo splitting (identical twins)
Reproductive cloning technologies produce an
exact copy (clone) of an individual

Reproductive Cloning Technologies
Somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT)
• Nuclear DNA of an adult is transferred to an
enucleated egg
• Egg cytoplasm reprograms differentiated (adult)
DNA to act like undifferentiated (egg) DNA
• The hybrid cell develops into an embryo that is
genetically identical to the donor individual

Somatic Cell Nuclear
Transfer (SCNT)

Fig. 13-9a, p. 210
A A cow egg is held in place by
suction through a hollow glass
tube called a micropipette. The
polar body (Section 10.5) and
chromosomes are identified by
a purple stain.

Fig. 13-9b, p. 210
B A micropipette punctures the
egg and sucks out the polar body
and all of the chromosomes. All
that remains inside the egg’s
plasma membrane is cytoplasm.

Fig. 13-9c, p. 210
C A new micropipette prepares to
enter the egg at the puncture site.
The pipette contains a cell grown
from the skin of a donor animal.
skin cell

Fig. 13-9d, p. 210
D The micropipette enters the
egg and delivers the skin cell to
a region between the cytoplasm
and the plasma membrane.

Fig. 13-9e, p. 210
E After the pipette is withdrawn,
the donor’s skin cell is visible next
to the cytoplasm of the egg. The
transfer is complete.

Fig. 13-9f, p. 210
F The egg is exposed to an electric
current. This treatment causes the
foreign cell to fuse with and empty
its nucleus into the cytoplasm of the
egg. The egg begins to divide, and an
embryo forms. After a few days, the
embryo may be transplanted into a
surrogate mother.

A Clone Produced by SCNT

Therapeutic Cloning
Therapeutic cloning uses SCNT to produce
human embryos for research purposes
Researchers harvest undifferentiated (stem)
cells from the cloned human embryos

13.4 Key Concepts
Cloning Animals
Knowledge about the structure and function of
DNA is the basis of several methods of making
clones, which are identical copies of organisms

13.5 Fame and Glory
In science, as in other professions, public
recognition does not always include everyone
who contributed to a discovery
Rosalind Franklin was first to discover the
molecular structure of DNA, but did not share in
the Nobel prize which was given to Watson,
Crick, and Wilkins

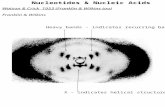
Rosalind Franklin’s
X-Ray Diffraction Image
Franklin died of cancer at age 37, possibly
related to extensive exposure to x-rays

13.5 Key Concepts
The Franklin Footnote
Science proceeds as a joint effort; many
scientists contributed to the discovery of DNA’s
structure