Notes: Muscle Types & Function. (1) Types of Muscle Skeletal Cardiac Smooth.
-
Upload
ralph-simon -
Category
Documents
-
view
227 -
download
0
Transcript of Notes: Muscle Types & Function. (1) Types of Muscle Skeletal Cardiac Smooth.

Notes: Muscle Types & Function

(1) Types of Muscle
• Skeletal
• Cardiac
• Smooth

Cardiac Muscle
Skeletal Muscle
Smooth Muscle

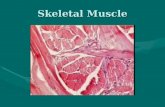
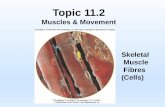
(2) Skeletal Muscle
• Physical Characteristics:– Long cells– Whole muscle has striations
• Type of Movement:– Voluntary– Allows overall body mobility– Contracts fast w/great force, tires fast also
• Location:– On top of bones & connecting them


(3) Cardiac Muscle
• Physical Characteristics:– Branched cells– Whole muscle has striations
• Types of Movement:– Involuntary– Steady, consistent movement– Heartbeat (rate gauged by nervous system)
• Location:– heart


(4) Smooth Muscle
• Physical Characteristics:– Long cells– Whole muscle NOT striated
• Type of Movement:– Involuntary– Slower, yet consistent movement– Forces fluids & solids through channels
• Location:– Digestive & excretive organs– Respiratory passageways


(5) Muscle Function
• Produce movement– Bones = attachment points– Internal organs (move nutrients, waste, etc.)
• Maintain posture– Unique to Bipedalism
• Stabilize joints– Allows for wider range of movement and use of
force
• Generate heat– During contraction