New NSCLC biomarkers in clinical research: …...New NSCLC biomarkers in clinical research:...
Transcript of New NSCLC biomarkers in clinical research: …...New NSCLC biomarkers in clinical research:...

New NSCLC biomarkers in clinical research: detection of MET skipping mutation, EGFR T790M, and other important biomarkers Fernando López-Ríos Laboratorio de Dianas Terapéuticas Hospital Universitario HM Sanchinarro Madrid, Spain

Contents
• Background
• MET mutations causing exon 14 skipping
• Liquid biopsies
• Conclusions

Contents
• Background
• MET mutations causing exon 14 skipping
• Liquid biopsies
• Conclusions

NSCLC: emerging biomarkers in clinical research
NCCN guidelines version 8.2017 NSCLC. Available from: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/PDF/nscl.pdf. Accessed: September 2017.
Genetic alteration (i.e. driver event)
Available targeted agents with activity against driver event in lung cancer
High-level MET amplification or MET exon 14 skipping mutation
Crizotinib
RET rearrangements Cabozantinib
Vandetanib
HER2 mutations Trastuzumab (category 2B) Afatinib (category 2B)
Emerging targeted agents for patients with genetic alterations
HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; MET, MET proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase; NCCN, National Comprehensive Cancer Network; NSCLC, non-small-cell lung cancer; RET, RET proto-oncogene.

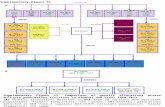
NSCLC: emerging biomarkers in clinical research
AC, adenocarcinoma; ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase; cfDNA, cell-free plasma DNA; ctDNA, circulating tumour-DNA; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; FISH, fluorescent in situ hybridization; H&E, haematoxylin and eosin; IHC, immunohistochemistry; NGS, next-generation sequencing; NOS, not otherwise specified; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; ROS1, ROS1 proto-oncogene receptor tyrosine kinase.
Adapted from Conde E, et al. Clin Transl Oncol. 2013;15:503-8, following the 2016 revised molecular testing guideline for selection of lung cancer patients
(CAP, IASLC, AMP, draft statements 2016).
ALK translocation
ROS1 translocation
EGFR mutation
FISH or
IHC If positive
FISH IHC NSCLC-NOS
H&E P40
TTF1
H&E
AC
Multiplexed genetic sequencing
panels
H&E Multiplexed genetic
sequencing panels
Progressed EGFR
positive
T790M testing
If negative
IHC
PD-L1 expression
x 10 (DNA)
If EGFR/ALK/ROS1
negative
x10 (DNA) x12 (RNA)
+ x 12 (RNA)
PD-L1 expression
x 1 x 1 x 1
5% (real-time
PCR)
30% (NGS)
x 1
Biomarkers Diagnosis Lap B1 Lap B2
x 1
IHC
x 2 x 2 x 1
720
ctDNA
ctDNA
x 1
• Expert consensus opinion: in some clinical settings in which tissue is limited and/or insufficient for molecular testing, physicians may in future consider to use a cfDNA assay for EGFR
• Expert consensus opinion: physicians may use cfDNA methods to identify for EGFR T790M mutations in lung AC patients with progression or acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs
• Testing of the tumour sample will be in future recommended is recommended if the plasma result is negative

Contents
• Background
• MET mutations causing exon 14 skipping
• Liquid biopsies
• Conclusions

• NSCLC (2.6%, 2.7%, 3%, 5.3%)
• Sarcomatoid variant, with AC morphology (5%, 22%, 32%)
• “Always” with MET overexpression (IHC)
• MET amplification in ~ 15–21%
• Concurrent amplifications – MDM2 (~ 35%) – CDK4 (~ 20%)
MET mutations causing exon 14 skipping
AKT, AKT serine/threonine kinase 1; BRAF, B-Raf proto-oncogene; CDK4, cyclin-dependent kinase 4 gene; ERBB2, erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2; HRAS, HRas proto-oncogene; KRAS, Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homologue; MAP2K1, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1; MDM2, murine double minute gene; NRAS, NRAS proto-oncogene; PIK3CA, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha.
Awad MM, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:721-30. Mengoli MC, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2016:22;3697-8.
Saffroy R, et al. Oncotarget. 2017;8:42428-37. Liu X, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:794-802.
Schrock AB, et al. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11:1493-502. Tong JH, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:3048-56.
Distribution of genotypes among 933 patients with non-squamous NSCLC
MET exon 14 (3.0%)
PIK3CA (2.9%) ERBB2 (2.5%)
NRAS (1%) RET (1%)
ROS1 (1%) AKT (< 1%)
HRAS (< 1%) MAP2K1 (< 1%)
BRAF (3.8%) ALK (3.9%)
EGFR (19%)
KRAS (34%)
No oncogenic mutation identified
(30%)

MET mutations causing exon 14 skipping
Cortot AB, et al. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017;109. Schrock AB, et al. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11:1493-502.
METex14 alterations, n (%)
Base substitution splice donor 149 (49.1) Indel splice acceptor 100 (32.9) Indel splice donor 42 (13.8) Base substitution splice acceptor 4 (1.3) Base substitution noncoding adjacent spice acceptor 4 (1.3) Indel noncoding adjacent spice acceptor 3 (1.0) Whole exon 14 deletion 2 (0.7)
g.116412042 G>A g.116412042 G>C g.116412042 G>T g.116412043 G>A g.116412043 G>T g.116412043 G>C g.116412044 T>A g.116412044 T>C
Mutation at the splice donor site (~ 48%)
g.116412019 del25 g.116412026 del24 g.116412036 del12 g.116412040 del14
Deletion at the splice donor site (~ 11%)
g.1164122042 c.3028
g.116411840 del49 g.116411857 del28 g.116411874 del26 g.116411880 del20 g.116411887 del28 g. 16411893 del30 g.116411897 del27
Deletion at the splice acceptor site (~ 41%)
g.116411902 c.2888 141 bases
…TTAAGATCTGG… ….CAGAAGGTATA… Exon 14
Amino acid sequence
Splice donor site
Regulatory sites:
Exam
ple
of M
ET
alte
ratio
ns
PKC phospho site (S985)
DLGSELVRYDARVHTPHLDRLVSARSVSPTTEMVSNESVDYRATFPE
47 AA
963 1009 Caspase site (D1002) CBL docking site (Y1003)
Splice acceptor site
CBL, cobalamin.

MET mutations causing exon 14 skipping
HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; PKC, protein kinase C. Cortot AB, et al. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017;109.

Fusion drivers (n = 23)
MET mutations causing exon 14 skipping
Data courtesy of López-Ríos, F.
RNA panel
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures

• Female, 72 years old
• Lung AC, stage IV
Case 1. MET mutations enriched in pan-negative lung adenocarcinomas
Data courtesy of López-Ríos, F.

Case 1. MET mutations enriched in pan-negative lung adenocarcinomas
• Oncomine™ focus assay • CNV: MET (x5,09 copies); confirmed with FISH (ratio 5:40) • MET exon 14 deletion [“skipping” exon 14 MET, MET(Ex13) –
MET(Ex15)]; confirmed with RT-PCR
CNV, copy number variation; NF1, neurofibromin 1; RIT1, Ras-like in all tissues; RT-PCR, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Collisson EA, et al. Nature. 2014;511:543-50. Data courtesy of López-Ríos, F.
FISH MET+
IHC MET+

• Oncomine™ focus assay • No CNV; confirmed with FISH (MET) • MET exon 14 deletion [“skipping” exon 14 MET, MET(Ex13) – MET(Ex15)];
confirmed with RT-PCR
FISH MET− IHC MET+
Case 2. MET mutations not always MET-amplified
Data courtesy of López-Ríos, F.

Contents
• Background
• MET mutations causing exon 14 skipping
• Liquid biopsies
• Conclusions

Liquid biopsies: analytical options
AF, allele frequency.
Available technologies for genotyping of plasma cfDNA PCR assays NGS assays
Characteristic Allele-specific PCR Emulsion PCR
Amplicon-based targeted NGS
Capture-based targeted NGS
Variants potentially detected
Known recurring mutations
Known recurring mutations
Any exonic mutations, copy number gains
Exonic mutations intromic gene fusions, copy number gains
Quantitation Semiquantitative (against standard curve)
Absolute or relative quantitation, wide dynamic range
Quantitation of relative AF, but vulnerable to PCR amplification bias
Quantitation of relative AF
Speed and complexity
Rapid, relatively easy to interpret
Rapid, relatively easy to interpret
Potentially rapid, less complex bioinformatics
Potentially slower more complex bioinformatics

Liquid biopsies: sensitivity and specificity
a 24/38 samples were tested using local tissue assays and 14/38 samples were tested via central assays. b Comprehensive exon 19 deletion data not available. ARMS, amplification refractory mutation system; ddPCR Droplet Digital polymerase chain reaction; dPCR, digital polymerase chain reaction.
Performance of four different plasma assays, using a tissuea test result as a non-reference standard, for detection of EGFR mutations from ctDNA in a set of 38 plasma samples from the AURA clinical trial
qPCR ARMS-PCR ddPCRTM BEAMingdPCR Exon 19 deletion Sensitivity, % (n/N) 86 (24/28) 82 (23/28) –b 93 (26/28)
Specificity, % (n/N) 100 (10/10) 100 (10/10) –b 100 (10/10)
Concordance, % 89 87 –b 95
L858R Sensitivity, % (n/N) 90 (9/10) 78 (7/9) 90 (9/10) 100 (10/10)
Specificity, % (n/N) 100 (28/28) 100 (28/28) 100 (28/28) 93 (26/28)
Concordance, % 97 95 97 95
T790M Sensitivity, % (n/N) 41 (7/17) 29 (5/17) 71 (12/17) 71 (12/17)
Specificity, % (n/N) 100 (6/6) 100 (6/6) 83 (5/6) 67 (4/6)
Concordance, % 57 48 74 70

Liquid biopsies: sensitivity and specificity
NPV, negative predictive value; PPV, positive predictive value.
Concordance, sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of tissue and cfDNA tests (n = 238) by EGFR mutation type
Overall EGFR mutation-positive
Exon 19 deletion L858R G719x L861Q
Concordance, % 87.8 94.5 93.3 99.6 100.0
Sensitivity, % 75.0 82.5 62.2 50.0 100.0
Specificity, % 96.5 98.3 99.0 100.0 100.0
PPV, % 93.5 94.0 92.0 100.0 100.0
NPV, % 85.1 94.7 93.4 99.6 100.0
Tissue-positive patients, n 96 57 37 2 1
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures

An example of our results
Promising technology for future use for liquid biopsies: NGS
LOD, log odds ratio; TP53, tumour protein 53.
Assay Genes Selected SNV hotspots Oncomine™ lung cfDNA assay
ALK, BRAF, EGFR, ERBB2, KRAS, MAP2K1, MET, NRAS, PIK3CA, ROS1, and TP53
> 150 hotspots including EGFR: T790M, C797S, L848R, exon 19 del KRAS: G12X, G13X, Q61X BRAF: V600E ALK: exon 21-25 PIK3CA: E545K, H1047R, E542K
Position Allele Frequency LOD chr7:55242470 EGFR p.L747_P753S 32.33% 0.05%
chr7:55249071 EGFR p.T790M 15.87% 0.10%
chr7:55249092 EGFR p.C797S 15.29% 0.10%
LOD (20 ng) ≤ 0.1%
Oncomine™ Lung cfDNA Assay
Data courtesy of López-Ríos, F. For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures

Case 3. Importance of broad profiling
Controls Position Control type Control status Flags Accepted by A01:A02:A03 Mutant control Valid
B01:B02:B03 Negative control Valid
Specimens
Position Sample ID Test
result Mutation
result Flags Accepted by
D01:D02:D03 Mutation detected
Exon 19 deletion
Run name: 07-FEB-2014 15:16 EGFR P1
IHC TTF1+
2014 Lung AC • Male, 70 years old • IHC TTF1+/P40− • EGFR exon 19 deletion
(real-time PCR) • No ALK fusion • Treated with 3rd-generation TKIs
2016 Soft-tissue metastasis • 52 genes NGS panel • EGFR exon 19 deletion
confirmation • No ALK fusion • T790M mutation • C797S mutation
Data courtesy of López-Ríos, F. For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures

Case
Case
Tumour FFPE (NGS assay)
Plasma Assay 1: NGS plasma panel
Plasma Assay 2: PCR plasma
T790M T790M T790M
EGFR exon 19 deletion EGFR exon 19 deletion EGFR exon 19 deletion
C797S C797S Not included in panel
Case 3. Importance of broad profiling
Data courtesy of López-Ríos, F. For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures

SNV, single-nucleotide variants; TNA, total nucleic acid.
Enhanced content • Amplicons: 58 • Total genes: 12 • Key hotspot mutations in 11 genes • Increase in hotspot SNVs and indels • Fusions (49) – ALK, RET, ROS1 – 1% LOD • CNV – MET • MET exon 14 skipping single library (DNA and RNA) SNV • LOD down to 0.1% with 20 ng input
ALK BRAF EGFR ERBB2
KRAS MAP2K1 MET NRAS
PIK3CA RET ROS1 TP53
Oncomine™ Lung cfTNA Assay
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Promising technology for future use for liquid biopsies: NGS total NA

Oncomine™ Lung cfTNA Assay: early experience • Analysis of plasma samples from patients diagnosed with NSCLC and previously
characterized by NGS (OncomineTM Focus Assay) or FISH analysis (FFPE samples). • Oncomine Lung cfTNA Assay Controls (n=4) run in parallel according to manufacturer’s
instructions.
1) Run performance OK: the assay works!
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures

Oncomine™ Lung cfTNA Assay: early experience 2) Analysis:
• A real sample…
FFPE tumor sample (FISH analysis)
Plasma sample (Oncomine™ Lung cfTNA Assay)
ALK positive
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures

Contents
• Background
• MET mutations causing exon 14 skipping
• Liquid biopsies
• Conclusions

Conclusions
• Broad profiling is recommended in NSCLC
• MET mutations causing exon 14 skipping is an emerging biomarker that can be detected with targeted NGS
• Using NGS in liquid biopsies allows for the detection of mutations, CNV, and rearrangements


Thermo Fisher Scientific and its affiliates are not endorsing, recommending, or promoting any use or application of Thermo Fisher Scientific products presented by third parties during this seminar. Information and materials presented or provided by third parties are provided as-is and without warranty of any kind, including regarding intellectual property rights and reported results. Parties presenting images, text and material represent they have the rights to do so.