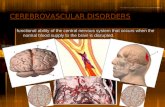
Neurology Cerebrovascular Accident Brunner’s Ch. 62 pg 1887.
-
Upload
kelley-georgia-lambert -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
1
Transcript of Neurology Cerebrovascular Accident Brunner’s Ch. 62 pg 1887.

Neurology
Cerebrovascular AccidentBrunner’s Ch. 62 pg 1887

Breaking down in tears
• I’m a nursing student who’s never seen a person die. When the time comes, I’m afraid I’ll lose it and upset the patient or family. How do you do this work all the time and not break down in tears?

Cerebrovascular accident
AKA• CVA• Stroke• Brain attack

CVA: Pathophysiology
• Disruption of blood flow to part of the brain
• Ischemia • Tissue Anoxia
• PaO2 & PaCO2 • Acidosis • Infarction • Edema • ICP

CVA: Etiology
• Ischemic– Thrombosis
• __?__ thrombosis• Arteriosclerosis• Common site
– Carotid artery
– Embolism• Atrial fib or HTN • Plaque breaking off and
becoming an emboli– d/t Long standing cardio-
vascular disease

CVA: Etiology
• Hemorrhage– Rupture of the cerebral
blood vessel– Commonly caused by
poor control of HTN

CVA: Etiology
• Hemorrhage– This type of CVA results
in:• Slow recovery• probability of
neurological deficits• No meds to reverse the
effects

CVA: Etiology
• Other causes– Syphilis– Trauma– Hypertension– Hypoxia– ***Anything the blood
flow

CVA: Risk FactorsChangeable• Smoking• Obesity• HTN• Sedentary life• Stress• fat diet• Na diet• Substance abuse• Oral contraceptives• Diabetes mellitus
Non-changeable• Age• Gender• Family history• Race

CVA: Risk Factors
Which is the most important risk factor for a stroke?A. SmokingB. WeightC. DietD. HTNE. StressF. Substance Abuse

CVA: Risk Factors
What is the number one cause of CVA in a younger patient?
A. SmokingB. WeightC. DietD. HTNE. StressF. Substance Abuse

CVA: Pathophysiology substance abuse
• Substance (PCP, crack) • Blood pressure • ICP • Subarachnoid &
intracerebral hemorrhage
• Interrupt blood flow • O2 & glucose • Depressed neurons

CVA: Pathophysiology
• ** Vessels involved determine the area of the brain involved
• ***Area affected determines the S&S

CVA: Clinical manifestations
S&S depend on:1. Location2. Size3. Amount

CVA: Clinical ManifestationsCommon clinical manifestations
• Syncope• Alt. LOC• Paresthesia• H/A• Aphasia• Seizures• Vision disturb• Difficulty walking• Labile emotion• Hemiparesis/hemiplegia

Left vs. Right Hemispheric CVALeft CVA Right CVA
Aphasia Language Intact
Dysarthria Speech Dysarthria
Right Homonyous hemianopsia
Sensation Left Homonyous hemianopsia
Normal awareness Perception Unilateral neglect
Right side paresis Movement Left side paresis

Left vs. Right Hemispheric CVA
Judgment intact
Depression
Slow & cautious
Behavior Judgment impaired
Denial
Impulsive behavior
Impaired analytical Cognition
Deficit new language info
Memory Deficit new spatial info

CVA: diagnostic findings
• LP– pressure– Blood
• CT / MRI– Bleeding– Infarction– Shift
• Angiography– Occlusion

CVA: Medical Management
Focus on Cause & Control• #1 cause =
– Hypertension– Medications

CVA: Rx - HTN
• Beta-blockers– Action
• Block sympathetic response
– Example• Propranolol
hydrochloride

CVA: Rx - HTN
• Central acting Anti-hypertensive– Action
• Cardiac output• Heart rate
– Example• Catapres

CVA: Rx - HTN
• Vasodilators– Action
• Relax smooth muscles– Example
• Apresoline– Emergency
• Hyperstat• Nipride

CVA: Medical Management
• Diet– Sodium
• – Fat
• – Potassium
• – Stimulants
• – Fluids
•

CVA: Medical Management
• Prevent clot formation– Meds / anticoagulants
• Coumadin– Antidote?
» Vit K
• Heparin• ASA

CVA: Medical Management
• Prevent clot formation– Non-Rx
• Ted hose• ROM• Isometric exercise

CVA: Medical Management
• Surgery– Endarterectomy
• Carotid stenosis– Craniotomy
• Evacuate clot

CVA: Medical Management
• Thrombolytic agents– Action
• Break down thrombi– S/E
• Hemorrhage– Streptokinase– Urokinase– Tissue-type prasminogen
activator (tPA)

CVA: Medical Management
• Thrombolytic agents – Tissue-type prasminogen
activator (tPA)• Take in 3 hrs of CVA

CVA: Medical Management
• Airway– Patent– reflex– O2– Suction– Mech vent

CVA: Medical Management
• Prevent Seizures– Precaution– Meds– stimuli

CVA: Medical Management• ICP
– O2• Mech vent
– Position• HOB
– Activity• Rest
– Meds• Diuretics• Glucocorticoids
– Monitor• BP• Systolic < 180• Diastolic < 100

CVA: Medical Management
• Nutrition– NGT

CVA: Medical Management
• Monitor for trouble– VS
• Rectal temp– NO
– I&O – Labs
• Na• K• Glucose• ABG’s • PT/PTT
– Pulse oximetry

CVA: Medical Management
Prevent complications• ROM• PT/SLP• Isometric exercise• Antacids
– Maalox– Tums
• Histamine antagonist– Tagamet– Zantac
• Pain– Codeine

CVA: NRS management
Alt. tissue perfusion• r/t ICP
– Monitor ICP– Avoid act that ICP

CVA: NRS managementRisk for injury• r/t seizures• r/t repeat CVA• r/t unilateral neglect• r/t falls
– Padded side rails– Call light– Assist w. amb.– Suction– BR assist – Items w/in reach– Clear path– H2O temps– Turn & position

CVA: NRS management
Alt. nutrition• r/t impaired swallowing• Motor deficits• Impaired judgment
– SLP– Swallow eval– HOB high fowlers– Straws – no– Thick liquids– Swallow twice– pocketing food
– Talk & eat – NO– Easy chew– Head position– Unaffected side of tongue– gag– choking– Small meals– High texture food

CVA: NRS management
Alt. Mobility• r/t neuro deficits
– Begin on admit– Turn q2hr– Pillows– P skin– ROM
– Splints• Hand & fingers• Arm• Legs
– Footboards– Built-up utensils– Raised toilet– W/in reach– Pt. to do exercises

CVA: NRS management
Impaired Communication
• r/t aphasia– SLP– Time– Anticipate– Call bell– Slow & clear– Face patient– Eye contact
– Yes/No ?– ID methods – Gestures– Visual aids

CVA: NRS management
Knowledge Deficit• r/t new diagnosis
– Orient– Explain– K.I.S.S.– Written, verbal & picture– Little at a time– Meds– Safety

CVA: NRS management
Self-Care Deficit• Eating
– Non-skid mats– Stabilizer plates– Plate guards– Wide grip utensils

CVA: NRS management
Self-Care Deficit• Bathing & Grooming
– Long handle sponge– Grab bars– Non-skid mats– Hand held showers– Electric razor– Shower seat

CVA: NRS management
Self-Care Deficit• Toileting
– Raised seat– Grab bars

CVA: NRS management
Self-Care Deficit• Dressing
– Velcro– Elastic shoelaces– Long-handle shoehorn

CVA: NRS management
Self-Care Deficit• Mobility
– Canes– Walkers– Wheelchair– Transfer devices

CVA: NRS management
• Risk of care-giver role strain– Support systems

CVA: NRS management
Unilateral neglect• Unaffected side
– Personal items– Approach– Door face
• Cue • Scan environment• Sling

CVA: NRS management
Impaired thought processes
• Family• KISS• SS&TTP• distractions• Repeat• Visual reminders
• Time• Simple complex• Positive feedback• Non-judgmental

Hemorrhagic Stroke
• Usually more severe with a longer recovery period than ischemic stroke
• Caused by bleeding into:– Brain– Ventricles– Subarachnoid space

Hemorrhagic Stroke
• Cerebral aneurysm– Dilitation, bulging or
ballooning out of part of the wall of a vein or artery in the brain
– When they enlarge and press upon cranial nerves or tissue
• Symptoms

Hemorrhagic Stroke
• Etiology– HTN– Arteriosclerosis– Meds

Hemorrhagic Stroke
Clinical Manifestations• Similar to ischemic • Unique S&S
– H/A– LOC– Nuchal rigidity

TIA: Transient Ischemic Attack
• Short reversible ischemic event
• Duration– < 24 hrs
• No permanent neuro deficit
• Warning!














![Brunner’s Gland Hamartoma of the Duodenum: A Literature …Brunner’s glands appear from the 13th to 14th weeks of embryonic develop-ment [2, 3]. Prevalence of Brunner’s glands](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/6147f9f3a830d0442101c8b3/brunneras-gland-hamartoma-of-the-duodenum-a-literature-brunneras-glands-appear.jpg)
