Nd (Neodymium) – YAG (Yttrium Aluminium Garnet) LASER Principle Characteristics
description
Transcript of Nd (Neodymium) – YAG (Yttrium Aluminium Garnet) LASER Principle Characteristics

Nd (Neodymium) – YAG (Yttrium Aluminium Garnet) LASER
PrinciplePrinciple CharacteristicsCharacteristics
Doped Insulator laser refers to yttrium aluminium garnet doped with neodymium.
The Nd ion has many energy levels and due to
optical pumping these ions are raised to excited levels. During the transition from the metastable state to E1,
the laser beam of wavelength 1.064μm is
emitted
Type : Doped Insulator Laser
Active Medium : Yttrium Aluminium Garnet
Active Centre : Neodymium
Pumping Method
: Optical Pumping
Pumping Source
: Xenon Flash Pump
Optical Resonator
: Ends of rods silver coatedTwo mirrors partially and totally reflecting
Power Output : 20 kWatts
Nature of Output
: Pulsed
Wavelength Emitted
: 1.064 μm

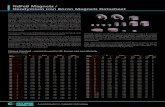
Nd (Neodymium) – YAG (Yttrium Aluminium Garnet) LASER
Power Supply
Capacitor
Resistor
Laser Rod
Flash Tube
M1– 100% reflector mirror
M2 – partial reflector mirror

E1, E2, E3 – Energy levels of NdE4 – Meta Stable StateE0 – ground State Energy Level
ApplicationsTransmission of signals over large distancesLong haul communication systemEndoscopic applicationsRemaote sensing
Energy Level Diagram of Nd– YAG LASER
Non radiative decay
Laser1.064μm
Non radiative decay
E3
E2
E0
E1
E4
Nd

Carbon Di Oxide LASER PrinciplePrinciple
The transition between the rotational and vibrational energy levels lends to the construction of a molecular gas laser. Nitrogen atoms are
raised to the excited state which in turn deliver energy to the CO2 atoms whose energy levels are close to it. Transition takes place between the
energy levels of CO2 atoms and the laser beam is emitted.
Type : Molecular gas laser
Active Medium : Mixture of CO2, N2, He or H2O vapour
Active Centre : CO2
Pumping Method : Electric Discharge Method
Optical Resonator : Gold mirror or Si mirror coated with Al
Power Output : 10 kW
Nature of Output : Continuous or pulsed
Wavelength Emitted : 9.6 μm or 10.6 μm

Symmetric 100 C - stationaryO - vibrates simultaneously along molecular axis
Bending 010,020
C & O vibrate perpendicular to molecular axis
Asymmetric Stretching
001, 002
C & O atoms vibrate in opposite directions along molecular axis


Applications• Bloodless surgery• Open air
communication
• Military field


Principle• The electron in the
conduction band combines with a hole in the valence band and the recombination produces radiant energy. This photon induces another electron in the CB to combine with a hole in the VB and thereby stimulate the emission of another photon.
Type : Homojunction Semiconductor laser
Active Medium : P – N junction
Active Centre : Recombination of electrons and holes
Pumping Method
: Direct Pumping
Optical Resonator
: Polished junction of diode
Power Output : 1 mW
Nature of Output
: Continuous or pulsed
Wavelength Emitted
: 8400 – 8600 Angstrom Units
HOMOJUNCTION SEMICONDUCTOR LASER (Ga-As Laser)



Applications• Compact & used in fibre optic communications• CD writer• Relieves pain• Laser printers


PrincipleTwo beams (object beam and reference beam) are superimposed on a
holographic plate to form an image called a hologram.

PrincipleA beam of light
(reading beam) having the same wavelength as that of the reference beam used for constructing the hologram, is made to fall over the hologram, which in turn gives rise to a 3-D image in the field of view.