Nature Of Disease
-
Upload
cwoot -
Category
Technology
-
view
3.278 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Nature Of Disease

Nature of disease

I. Nature of DiseaseA. Infectious vs notB. Koch's postulates (p. 1072)- anthrax was 1st
one tied to disease1. Pathogen found in host in every case of illness2. pathogen isolated & grown in pure culture3. placing new cultured organism in healthy host causes
disease4. pathogen re-isolated from new host and is the same
as originalExceptions: some won’t grow on artificial media-need
alternate host (ex: finally could study leprosy in armadillos)

Spread of DiseaseC. Spread of Disease
1. Reservoirs -(John Snow- classic epidemiological case study)Ex: (1) Living O’
(animals, human)-some can be just carriers and not be sick themselves-like typhoid Mary (2) Soil (3) Water

2. Transmission (p. 1073)a. direct contact- skin,
blood in a cutb. object- food, a toy,
shared needlec. air- cough, sneeze,
wind born sporesd. vector – mosquito,
tick

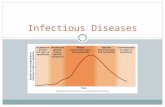
Spread of disease3. Symptoms
Bacteria produce toxins, leading to fever, cell metabolic disruptions, heart problems, nervous system disrupted, cell destroyed.
Viruses destroy or change cell or disrupt metabolism
4. Patterns of diseasea. endemic= constantly in a particular area or population
b. pandemic= worldwide
c. epidemic = a lot of cases in a short period of time

5. Treatments - antibiotics vs resistance (p. 1077)
medicines overused and resistant strains have developed
antibiotic only kills off the weaker ones those that don’t have a mutation that lets them survive
next generation is only made from the strong ones those with the right gene mutation
now all are is resistant and harder to kill

ArticleD. Lyme disease (see article) E. Sara Josephine Baker and Typhoid Mary (see
article)F. The Black Plague- a reading (see article)

IV. Defenses against Disease (p. 1078)A. Lymphatic system
1. 3 basic functionsa. maintain homeostasis of fluid levelsb. absorb fats from digestive tractc. **defense against disease
2. Lymph and lymph nodesa. Lymph = fluid from intercellular spacesb. lymph nodes: they filter the lymph, hold
lymphocytes (WBC) until needed3. Organs involved:
1. Tonsils = filter air as enters throat and filter lymph
2. Spleen = filter bacteria and destroy old RBC in blood and store extra blood
3. Thymus = lymphocytes(WBC) mature here
4. bone marrow = make blood components
5. Appendix = trap bacteria

C. Innate (nonspecific) immune system(p.1084) - see sheet for details
1. Skin and secretions like sweat & lysozyme (enzyme in tears)
2. Phagocytes= white blood cells
3. interferon =interferes with viral repro. and alerts other cells
4. Complement =proteins in blood to mark foreign antigen for destruction, making the cell leak
5. Histamine and heat (p.1082)-see flow chart

D. Adaptive immune system (p.1085) see sheet
1. Antigen vs. antibody antigen= foreign or self protein on outside of cells that
protein recognition molecule reacts to/recognizes antibody= produced by the body to inactivate particular
antigens
2. Adaptive vs cellular immunity (see p. 1085-6)
Adaptive (humoral) immunity= produces antibodies and B memory cells
cellular immunity= destroys already infected cells and makes T memory cells

E. Immune system diseases1. Auto immunity - diseases which attack own tissues
Ex: Multiple sclerosis (MS)- effects myelin sheath around the nerve cells
Grave’s disease - effects thyroid rheumatic fever- antibodies attack heart Lupus- effects multiple organs, or just the skin
2. Immunodeficiency= SCID - no ability to make antibodies
(Boy in Bubble)

F. Vaccines and natural immunity 1. Active immunity- long term
2 ways: (1) Natural: get actual pathogen, get sick and go thru adaptive response * keep memory B cells in “library” and make
antibodies FAST if exposed to the pathogen again-
destroy before get sick (2) Vaccine: has weak or inactivated
pathogen, then body will go thru adaptive response as
usual it is not really harmful & never get sick *DO make antibodies and keep memory B
cells so when exposed to real organism, can make antibodies fast as above

2. Passive immunity- temporary
a. Donor- antibodies from a recovered person or source like horse serum
b. Monoclonal antibodies= bacteria produced (genetically engineered)
c. Maternal= antibody crosses placenta and is in milk - give baby some protection until own immune system starts working

G. Scientistsa. Jenner: smallpox vaccineb. Pasteur: rabies vaccine and pasteurizationc. Salk & Sabin: polio vaccined. Lister: aseptic procedures for surgerye. Tonegawa: how antibodies are madef. Koch: methodology for linking O’ to diseaseg. Snow: cholera epidemic-linked to source-1st
epidemiologisth. Fleming: penicillium mold –took 1st step to the
antibiotic penicillini. Margulis: endosymbiotic theory

A. HIV and AIDS1. Defined=Acquired Immune Deficiency syndrome2. Cause: HIV destroys T-Helper cells and prevents rest of
adaptive immunity from happening3. Risk groups
• a. sharing needles• b. sex with effected partners• c. contaminated blood contact (hemophiliacs; health care workers)• d. certain nations are risky to visit (Haiti, Zambia)-more risk of
contraction
4. Opportunistic infections- what actually kills the AIDS victim

5. AIDS Symptoms
a. swollen glandsb. raised blotchesc. large, fast weight lossd. night sweatse. unexplained fever/coughf. frequent infections/illness,
especially rarer conditions normally fought off • Candida albacans (mouth
fungus) • Kaposi’s sarcoma (a cancer) • toxoplasmosis (brain infection) • Pneumonia

AIDS in the world – What do you know? More than 25 million people have died of AIDS
since 1981. Africa has 12 million AIDS orphans. At the end of 2007, women accounted for 50%
of all adults living with HIV worldwide, and for 61% in sub-Saharan Africa.
Young people (under 25 years old) account for half of all new HIV infections worldwide.
http://www.unaids.org/en/KnowledgeCentre/HIVData/EpiUpdate/EpiUpdArchive/2007/http://rehydrate.org/resources/cartograms.htm