myweb.fsu.edumyweb.fsu.edu/ls10f/Embryology Unit II Review.docx · Web viewEmbryology: Cavities...
Transcript of myweb.fsu.edumyweb.fsu.edu/ls10f/Embryology Unit II Review.docx · Web viewEmbryology: Cavities...
Embryology: Cavitieso Formation of Body Cavities
Clefts appear in lateral plate mesoderm Parietal (Somatic) Visceral (Splanchnic) Space between parietal and visceral = primitive body cavity
Entire gut is suspended by dorsal mesentery connecting the parietal and visceral layer
Separation of Pericardial & Peritoneal Cavities Septum transversum
o Thick plate of mesoderm that incompletely divides the primitive body cavity
Between thorax and abdomeno Still communication between two cavities via
pericardioperitoneal canalso Liver will grow hereo Forms central tendon of diaphragm
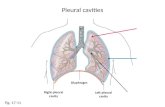
Separation of Pericardial & Pleural Cavities Lung buds
o Grow into pericardioperitoneal cavitieso Bud off foregut
Pleuropericardial foldso Separate off pleural cavities from pericardial cavityo Forms the fibrous pericardium
Phrenic nerve will sit on fibrous pericardium Diaphragm
Septum transversum forms central tendon to heart Pleuroperitoneal folds close the pericardioperitoneal canals
o Complete closure of pleural and peritoneal cavities Mesentery of esophagus form crura of diaphragm
o The crura of the diaphragm (singular: crus) are tendinous structures that extend inferiorly from the diaphragm to attach to the vertebral column.
Muscular part formed by myoblasts from C3-C5 somites C3,C4,&C5 spinal nerves invade the diaphragm Clinical Correlation
o Diaphragmatic hernias Failure of one pleuroperitoneal membrane closing 90% on posterior left side because liver is on right side
o Respiratory system Respiratory diverticulum (lung bud)
Outgrowth from floor of foreguto All epithelium in respiratory tree is from endodermo Surrounding tissue is splanchnic (visceral) mesoderm
Opening into the diverticulum is the laryngeal orifice Tracheoesophageal ridges grow inward to separate esophagus from
tracheao Clinical correlation
Tracheoesophageal fistulas 90% will be fistula between distal esophagus
and trachea with a blind proximal esophagus Mostly caused by excess amniotic fluid
(polyhydramnios) Tissues from pharyngeal slits IV&VI form larynx
Respiratory system Lung buds elongate to form trachea and bifurcates into primary bronchi Primary bronchi divide
o Right – 3 secondary bronchio Left – 2 secondary bronchio Further division form tertiary bronchi
Lungs expand into pericardioperitoneal canals and eventually fill the pleural cavities
Maturation of lungso Further division of bronchi through 7 monthso Cuboidal cells change
Type I alveolar – squamous for gas exchange Type II alveolar – secrete surfactant
Clinical correlationo Respiratory distress syndrome
Insufficient surfactant production
Treated by intratracheal surfactant
Alveolar cells establish close ties with capillarieso Stages
Pseudoglandular: 5-15 weeks Canalicular: 16-26 weeks Terminal sac: 26-weeks to birth Alveolar Period: childhood
Embryology: Cardiovascularo Cardiogenic Field
Splanchnic layer of lateral plate mesoderm surrounding head of embryo
Cardiac myoblasts Blood islands
o Unite to dorm U-shaped endocardial tube surrounded by cardiac myoblasts
Intraembryonic cavity over the tube will form the pericardial cavityo Cephalocaudal Folding
Endocardial tube is brought into neck region of embryo Pericardial cavity accompanies movement
o Lateral folding Two parts of the endocardial tube are brought together in the midline to form a
single heart tube Two pericardial cavities also join into a single cavity Heart tube suspended from dorsal body wall by dorsal mesocardium 3 layers of heart tube
o Endocardiumo Myocardiumo Epicardium
o Cardiac Loop Cephalic end bends ventrally, caudally, and to the right
Bulbus cordis and ventricle Caudal end bends dorsally, cranially, and to the left
Atrium Divisions
Bulbus Cordiso Primitive right ventricleo Conus cordis
Outflow tract of the ventricleso Truncus arteriosus
Aorta and pulmonary trunk Ventricle
o Primitive left ventricle Atrium
o Primitive right & left atriao Sinus venosus located here
o Venous Drainage Sinus venosus blood return
Vitelline veinso From yolk sac
Umbilical vein o From placenta
Cardinal veins
o From embryoo Sinus venosus
Entrance of sinus into atrium shifts to the right Right vitelline vein becomes inferior vena cava Right common cardinal becomes superior vena cava Left sinus horn becomes coronary sinus Right sinus horn becomes smooth part of right atrium
o Atrial septation Septum primum
Ostium (opening) primumo First free opening that disappears
Ostium secundumo Forms by cell death
Septum secundum Covers over ostium secundum Never completely divides
o Opening is foramen ovale Upper part of septum primum disappears
Rest becomes the valve of the foramen ovaleo Atrial Development
Right atrium Absorbs right sinus horn forming the smooth part of the right atrium
with the openings of the superior and inferior vena cavas Left atrium
Atrium absorbs proximal part of the pulmonary vein forming the smooth part of left atrium with 4 openings
Primitive atria become auricles in adult Clinical Correlation
Atrial septal defectso Left-to-right shunt is acyanotico Right-to-left shunt is cyanotic
o Division of the Atrioventricular Canal Endocardial cushions (mesenchyme) divide common atrioventricular canal into
right and left canals AV valves form by selective degeneration of surrounding myocardium
o Ventricular Septation Right and left sides grow. In the process a muscular interventricular septum is
created Membranous part of septum is made from conotruncal septum to finally
separate the two ventricleso Conotruncal Septum
Pair of opposing ridges form in both truncus arteriosus and conus arteriosus Conotruncal septa
Spiral around each other and fuse dividing the common truncus and conus into the aorta and pulmonary trunk
Septum fuses with the muscular IV septum forming membranous part of interventricular septum
Neural crest cells from the pharyngeal arches contribute to the endocardial cushions of conotruncal septum
Clinical Correlation Ventricular septal defects
o Types Membranous
Conotruncal septa Muscular
Ventricular growth Tetralogy of Fallot
o Four defects Pulmonary stenosis VSD Overriding aorta
Aorta overrides pulmonary trunk Right ventricular hypertrophy
o Cyanotico Major Arteries
Aortic arches Arch of aorta Carotids Pulmonary arteries
Dorsal aorta Descending aorta
Vitelline Celiac trunk Superior and inferior mesenteric arteries
Umbilical arteries Medial umbilical ligaments
o Major veins Umbilical vein (left)
Ligamentum teres hepatis Vitelline veins
Hepatic portal system Cardinal veins
Superior and inferior vena cavao Changes at birth
Three shunts Ductus venosus
o Shunt in liver that bypasses liver and go right into the inferior vena cava to enter right atrium
o Goes through right atrium and through the foramen ovale and straight into the left atrium
o Blood entering right atrium goes to right ventricle which is pumped into the ductus arteriosus and into the aortic arch. Some goes to the lungs
o First breath decreases pulmonary resistance Foramen Ovale
o Clamping of the maternal blood causes an increase in pressure in the left atrium to close the foramen ovale
Lungs are able to give oxygenated blood to left atrium Ductus arteriosus
o Increase left pressure causes reverse flow through the ductus arteriosus
o Oxygenated blood inhibits prostaglandin production and causes muscle contraction
o Degenerates and eventually becomes the ligamentum arteriosum
If it does not close can treat with prostaglandin inhibition
o Clinical correlation Patent Ductus Arteriosus
Ductus arteriosus does not close Small – asymptomatic Large
o Significant left-to-right shunt Embryology: Head and Neck I
o Skull Arise from two sources
Paraxial mesoderm (In red)o Somitomereso Occipital somites
Neural crest (In blue)o Pharyngeal arches
Dividing line is sella turcica Bone formation
Membranous ossificationo Flat bones of neurocranium and most viscerocranium
Endochondral ossificationo Base of skull
Newborn skull Fontanelles
o Bones not fused together and create soft spotso Head is largest part of body and during birth process the bones
can move to allow passage and then realign later (molding)o Usually close around 18 months
o Pharyngeal Arches Swellings of mesenchyme covered by ectoderm
Swellings = pharyngeal arches Separations = pharyngeal clefts
Appear in neck region during 4-5 weeks Outpocketings of foregut (endoderm) also form in the same areas as the
pharyngeal cleft (pharyngeal pouches) Each pharyngeal arch
Covered by ectoderm Lined by endoderm Contains
o Mesenchyme Neural crest – bones; skeletal segments of each arch Paraxial mesoderm – muscles, dermis Lateral plate – laryngeal cartilages, CT
o Cranial nerve Any muscle that derives from a certain arch is
innervated by the cranial nerve of that archo Aortic arch
4 archeso 1st
o 2nd
o 3rd
o 4th & 6th
Pharyngeal arches – skeletal (neural crest cells) 1st arch
o Meckel’s cartilage Part of Maxilla Mandible
o Inner ear ossicles Malleus Incus
2nd archo Styloido Stapeso Stylohyoid ligamento Lesser horn of hyoid bone
3rd archo Body of hyoid boneo Greater horn of hyoid bone
4th arch o Thyroid cartilage
6th archo Cricoid cartilage
Pharyngeal arches – Muscles 1st arch
o Muscles of mastication, mylohyoid 2nd arch
o Muscles of facial expression 3rd arch
o Stylopharyngeus 4th/6th arch
o Muscles of pharynx and larynx Muscles of tongue
o Formed from occipital somites Pharyngeal Arches – Nerves
o Pharyngeal arches – nerves 1st arch
Trigeminal 2nd arch
Facial 3rd
Glossopharyngeal 4th/6th
Vagus nerve and cranial part of accessory o Clinical Correlation
Treacher Collins Syndrome Malformed external ear, mandibular, and malar hypoplasia, conductive
hearing loss Malformed development of 1st pharyngeal arch
o Pharyngeal Pouches and Clefts 1st pharyngeal pouch
Auditory (eustachian) tube 2nd pharyngeal pouch
Palatine tonsil 3rd pharyngeal pouch
Inferior parathyroid glands Thymus
4th pharyngeal pouch Superior parathyroid glands Parafollicular cells of thyroid (C cells)
o Secrete calcitonino Tongue
Forms from 1st and 3rd pharyngeal arches Anterior 2/3 from 1st arch
o General sensory – lingual nerve (CN V)o Taste CN VII (chordae tympani hitchhiking onto lingual)
Posterior 1/3 from 3rd archo General sense and taste from CN IX
o Thyroid Gland Forms from a diverticulum of endoderm between 1st and 2nd arches Descends into neck
Connection is called the thyroglossal duct
Original point of invagination becomes foramen cecum Embryology Head and Neck II
o Face Formed
Frontonasal prominenceo Mesenchyme cranial to pharyngeal arches
V1 First pharyngeal arch
o Maxillary prominence – V2o Mandibular prominence – V3
Nasal placodeso Medial nasal prominence
Fuse to form intermaxillary segment –philtrum Dimple on upper lip is from fusion of medial nasal
prominence Then fuses with the maxillary prominence to form
upper lipo Lateral nasal prominence
Nasolacrimal groove (wings on side of nose) Lacrimal sac Nasolacrimal duct
o
o Palate Primary palate is intermaxillary segment (philtrum)
Forms with 4 incisors Secondary palate
Formed by the palatine shelves from maxillary prominenceo Separates oral from nasal cavities
Point of junction is incisive foramen
o Clinical correlation
Cleft lip Males > Females Picture B
Cleft Lip and palate Females > Male Picture C
Median cleft palate Picture E Rare
Median cleft palate and lip Picture F Most rare
Problems with sucking with this disorder
o Derivatives of Germ Layers
Most sense organs derive from ectodermo Nasal Cavity
Forms from nasal placode which invaginates to form nasal pits Placode = thickening of ectoderm
Olfactory epithelium forms from olfactory placode (ectoderm) Source of 1st cranial nerve
Pits deepen and are separated from oral cavity by oronasal membrane Oronasal membrane breaks down Final separation of nasal cavity from oral cavity is secondary palate Paranasal sinuses develop from diverticula from nasal cavity
o Ear Middle Ear
Tympanic membrane Ear ossicles
o Stapes Carries vibrations to inner ear by vibrating perilymph
o Malleus Sits on tympanic membrane
o Incus Carries vibrations from malleus to stapes
Inner Ear Cochlear
o Contains perilympho Endolymph is contained within endolymph ducts
Sacculeo Horizontal sensation
Semilunar canalso Angular sensation
o Inner ear Thickenings of the ectoderm near rhombencephalon form otic placodes Otic placode invaginates to form otic vesicles Otic vesicles components
Ventral componento Sacculeo Cochlear duct
Doral componento Utricleo Semicircular canalso Endolymphatic duct
o Middle ear Stapedius
Connects neck of stapes to stiffen the stapes to help dampen the vibration of stapes
o To help withstand loud sounds Tympanic cavity comes from 1st pharyngeal pouch
Connects to nasopharynx and remains as auditory tube Ossicles from neural crest
Trigeminal innervates the muscles that connect to malleus and incuso 1st arch – malleus and incus
Innervation of stapes is from facial nerveo 2nd arch – stapes
o External Ear External auditory meatus
1st pharyngeal cleft Tympanic membrane
Externally – ectodermal lining Internally – endodermal lining
Auricle Mesenchyme from 1st and 2nd pharyngeal arches
o 6 auricular hillockso Eye
Wall of eye from 3 primary layers Inner layer – retina Middle layer – choroid (pia mater of brain) Outer layer – sclera (dura mater of brain)
o Optic cup & lens Outpocketings from the developing forebrain from optic vesicle Come into contact with ectoderm which induces lens placode which forms lens
vesicle Optic vesicle invaginate to form two layered optic cup
Choroid fissure allows hyaloid artery into cup Mouth of the cup forms the pupil
o Retina, Iris, & Ciliary Body Optic cup
Posterior 4/5thso Outer layer forms the pigmented layer
Colored layer of iriso Intraretinal space
Typical site for detachment of retina (separation of an embryonic union)
No longer functions of photo receptiveness o Inner layer forms the neural retina
Rods, cones, and ganglionic cell layer Anterior 1/5
o Inner layer of iriso Ciliary body
Lens Cells of posterior wall elongate
Lumen disappearso Choroid, sclera, cornea & optic nerve
Surrounding mesenchyme Posteriorly
o Inner layer forms choroid (highly vascular and pigmented)o Outer layer forms sclera
Anteriorlyo Anterior chambero Outer layer of iriso Cornea
Vitreous body formed from mesenchyme that invades optic cup Axons from ganglionic layer invade stalk forming the optic nerve
o Hyaloid artery becomes the central artery of retina which runs through optic nerve