mrs-butterfield.weebly.com · Web viewObjectives: Explain the role of ATP in cellular activities....
Transcript of mrs-butterfield.weebly.com · Web viewObjectives: Explain the role of ATP in cellular activities....

1
CONNECTIONS ACADEMY
Biology Science Journal
Unit 3: CellsImages are copyright of, and used with permission from Clipart.com, © 2010 Jupiterimages Corporation, a wholly owned subsidiary of Jupiter Media Corporation. All rights reserved.

2Table of Contents
1. THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE ................................................................................................... 5
OBJECTIVES:...................................................................................................................................5DISCOVERING THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE.......................................................................................5FROM MACROSCALE TO MICROSCALE TO NANOSCALE.............................................................5TEXTBOOK READING (PAGES 190-194).........................................................................................5
2. CELL STRUCTURE ................................................................................................................ 7
OBJECTIVES:...................................................................................................................................7THE NUCLEUS.................................................................................................................................7TEXTBOOK READING (PAGES 196-207).........................................................................................8
3. MATERIAL TRANSPORT ..................................................................................................... 9
OBJECTIVES:...................................................................................................................................9MOVEMENT ACROSS THE CELL MEMBRANE...............................................................................9PASSIVE TRANSPORT OF WATER...................................................................................................9TEXTBOOK READING (PAGES 208-213).........................................................................................9
4. LAB: THE EFFECT OF CELL SIZE ON MATERIAL TRANSPORT .......................... 11
OBJECTIVES:.................................................................................................................................11MEASURING CELL SIZE................................................................................................................11
5. CELLS AND HOMEOSTASIS ............................................................................................. 12
OBJECTIVES:.................................................................................................................................12TEXTBOOK READING (PAGES 214-217).......................................................................................12
6. ENERGY AND LIFE ............................................................................................................. 13
OBJECTIVES:.................................................................................................................................13ATP: ENERGY CURRENCY OF THE CELL...................................................................................13TEXTBOOK READING (PAGES 226-228).......................................................................................13
7. OVERVIEW OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS ............................................................................... 15
OBJECTIVES:.................................................................................................................................15DISCOVERY OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS...............................................................................................15TEXTBOOK READING (PAGES 230-233).......................................................................................15
8. THE PROCESS OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS .......................................................................... 17
OBJECTIVES:.................................................................................................................................17THE REACTIONS OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS.......................................................................................17TEXTBOOK READING (PAGES 235-241).......................................................................................17
9. OVERVIEW OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION ................................................................. 19

3OBJECTIVES:.................................................................................................................................19BREATHING AND RESPIRATION....................................................................................................19STAGES OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION..........................................................................................19TEXTBOOK READING (PAGES 250-253).......................................................................................19
10. THE PROCESS OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION .......................................................... 21
OBJECTIVES:.................................................................................................................................21THE REACTIONS OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION...........................................................................21TEXTBOOK READING (PAGES 254-260).......................................................................................21
11. FERMENTATION ............................................................................................................... 23
OBJECTIVES:.................................................................................................................................23TEXTBOOK READING (PAGES 262-265).......................................................................................23
12. CELLS OVERVIEW- MID-UNIT REVIEW .................................................................... 24
OBJECTIVES:.................................................................................................................................24REVIEW OF CELL CONCEPTS.......................................................................................................24
13. CELL GROWTH, DIVISION, AND REPRODUCTION ................................................ 25
OBJECTIVES:.................................................................................................................................25LIMITS TO CELL SIZE...................................................................................................................25MANAGING CELL GROWTH.........................................................................................................25TEXTBOOK READING (PAGES 274-278).......................................................................................25
14. CELL DIVISION .................................................................................................................. 27
OBJECTIVES:.................................................................................................................................27CELL DIVISION..............................................................................................................................27TEXTBOOK READING (PAGES 279-285).......................................................................................27
15. THE CELL CYCLE ............................................................................................................. 28
OBJECTIVES:.................................................................................................................................28THE STRUCTURE OF CHROMOSOMES..........................................................................................28STAGES IN THE CELL CYCLE.......................................................................................................28VOCABULARY TERMS...................................................................................................................28
16. REGULATING THE CELL CYCLE ................................................................................. 29
OBJECTIVES:.................................................................................................................................29REGULATORS OF THE CELL CYCLE............................................................................................29TEXTBOOK READING (PAGES 286-290).......................................................................................29
17. CELL DIFFERENTIATION ............................................................................................... 30
OBJECTIVES:.................................................................................................................................30CELL DIFFERENTIATION..............................................................................................................30TEXTBOOK READING (PAGES 292-297).......................................................................................30

418. CELLS UNIT REVIEW ....................................................................................................... 32
OBJECTIVES:.................................................................................................................................32TEST PREPARATION......................................................................................................................32

51. The Basic Unit of Life
Objectives:
State the cell theory Describe how the different types of microscopes work Distinguish between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Discovering the Basic Unit of LifeCell TheoryAnswer the following questions after watching the “Cell Theory” video:
1. What contribution did Rudolf Virchow make to the growing understanding of cells?
2. What are the three principles that make up the cell theory?
From Macroscale to Microscale to NanoscaleTypes of Microscopes:Watch the “Different Kinds of Microscopes” video then answer the following questions
1. What magnification is possible with a light microscope? 2. What magnification is possible with an electron microscope? 3. What does an electron microscope use in place of a stream of light?
Prokaryotes and EukaryotesTake notes in the following chart regarding the similarities and differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes as you watch the “What is a Cell?” video
Prokaryote Eukaryote
Textbook Reading (pages 190-194)Vocabulary Terms
cell cell membrane cell theory eukaryote nucleus organelle prokaryote
Notes7.1 Life is Cellular
A. The Discovery of the Cell

61. Early Microscopes 2. The Cell Theory
B. Exploring the Cell 1. Light Microscopes and Cell Stains 2. Electron Microscopes
C. Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes 1. Prokaryotes 2. Eukaryotes
Questions
1. a. What is a cell? b. What three statements make up the cell theory? c. How did the invention of the microscope help the development of the cell theory?
2. a. How do microscopes work? 3. a. What features do all cells have?
b. What is the main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?

72. Cell Structure
Objectives:
Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus Describe the role of vacuoles, lysosomes, and the cytoskeleton Identify the role of ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus in making
proteins Describe the function of chloroplasts and mitochondria in the cell
The NucleusThe NucleusFill in the following chart with notes about the nucleus and related structures while watching “The Nucleus” video
Nucleus Chromatin Chromosome Nucleolus Nuclear Pore Nuclear Envelope (nuclear membrane)
Cytoplasmic StructuresFill in the following chart with notes about the common cytoplasmic structures while watching the “Cytoplasmic Cell Structures”Ribosome Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Apparatus Mitochondria
Comparing Plant and Animal CellsFill in the following chart with notes comparing the presence or absence of the cell structures in plant and animal cells while watching the “Plant Cells Versus Animal Cells” video
Plant AnimalChloroplast Centriole Spindle Fibers Cytoskeleton Vacuole Lysosome Cell Wall Cell Membrane

8Textbook Reading (pages 196-207)Vocabulary Terms
cytoplasm lipid bilayer
Notes7.2 Cell Structure
A. Cell Organization 1. Comparing the Cell to a Factory 2. The Nucleus
B. Organelles That Store, Clean Up, and Support 1. Vacuoles and Vesicles 2. Lysosomes 3. The Cytoskelton
a) Microfilaments b) Microtubules
C. Organelles That Build Proteins 1. Ribosomes 2. Endoplasmic Reticulum 3. Golgi Apparatus
D. Organelles That Capture and Release Energy 1. Chloroplasts 2. Mitochondria
E. Cellular Boundaries 1. Cell Walls 2. Cell Membranes
a) The Properties of Lipids b) The Fluid Mosaic Model
Textbook Questions3. b. Describe the steps involved in the synthesis, packaging, and export of a protein
from a cell. 5. c. Why do you think it’s important that cell membranes are selectively permeable?

93. Material Transport
Objectives:
Explain the process of diffusion as it relates to transport across a cell membrane Describe two types of material transport across the cell membrane Analyze effects of osmosis on cells
Movement Across the Cell MembraneAnswer the following two questions after watching the “Cell Membrane: Homeostasis” video
1. What does the term “selectively permeable” mean? 2. What is the difference between passive transport (or diffusion) and active transport
through the cell membrane?
Passive Transport of WaterAnswer the following questions after watching the demonstration on the “Osmosis” page from the St. Olaf College website.
1. Why does the water move in the direction of the added salt? 2. Why doesn’t the salt move through the membrane?
Textbook Reading (pages 208-213)Vocabulary Terms
aquaporin diffusion facilitated diffusion hypertonic hypotonic isotonic osmosis osmotic pressure
Notes7.3 Cell Transport
A. Passive Transport 1. Diffusion 2. Facilitated Diffusion 3. Osmosis: An Example of Facilitated Diffusion
a) How Osmosis Works b) Osmotic Pressure
B. Active Transport 1. Molecular Transport

102. Bulk Transport a) Endocytosis b) Exocytosis

114. Lab: The Effect of Cell Size on Material Transport
Objectives:
Explain why cell size is limited
Measuring Cell SizeAnswer the following questions after watching the “Cell Size” video
1. How was the surface area determined? 2. How was volume determined?

125. Cells and Homeostasis
Objectives:
Explain how unicellular organisms maintain homeostasis Explain how multicellular organisms maintain homeostasis
Textbook Reading (pages 214-217)Vocabulary Terms
homestasis multicellular specialization unicellular
Notes7.4 Homeostasis and Cells
A. The Cell as an Organism B. Multicellular Life
1. Cell Specialization a) Specialized Animal Cells b) Specialized Plant Cells
2. Levels of Organization 3. Cellular Communication
Questions
1. a. What is homeostasis? b. What do unicellular organisms do to maintain homeostasis? c. The contractile vacuole is an organelle found in paramecia, a group of unicellular organisms. Contractile vacuoles pump out fresh water that accumulates in the organisms by osmosis. Explain how this is an example of the way paramecia maintain homeostasis.

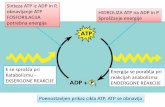
136. Energy and Life
Objectives:
Explain the role of ATP in cellular activities Explain where plants get the energy they need to produce food
ATP: Energy Currency of the CellAnswer the following questions after watching the “ATP: The Energy Currency” video
1. What part of the ATP molecule is used for storing and releasing energy? 2. What molecule is formed from ATP when it transfers energy to drive an endergonic
reaction?
An Overall Picture of Energy FlowAnswer the following questions after watching the “Respiration & Photosynthesis” video
1. How are photosynthesis and cellular respiration related? 2. What organisms undergo cellular respiration? 3. What organisms undergo photosynthesis?
Textbook Reading (pages 226-228)Vocabulary Terms
adenosine triphosphate (ATP) autotroph heterotroph NADPH Photosynthesis
Notes8.1 Energy and Life
A. Chemical Energy and ATP 1. Storing Energy 2. Releasing Energy 3. Using Biochemical Energy
B. Heterotrophs and Autotrophs
Questions
1. a. What is ATP and what is its role in the cell? b. How does the structure of ATP make it an ideal source of energy for the cell? c. Explain how ADP and ATP are each like a battery. Which one is “partially charged” and which one is “fully charged”? Why?

142. a. What is the ultimate source of energy for plants? b. How do heterotrophs obtain energy? How is this different from how autotrophs obtain energy? c. Why are decomposers, such as mushrooms, considered heterotrophs and not autotrophs?

157. Overview of Photosynthesis
Objectives:
Describe the role of light in photosynthesis Explain the requirement for chlorophyll in photosynthesis Describe two sequential processes for photosynthesis Identify the reactants and products of photosynthesis
Discovery of PhotosynthesisAnswer the following questions after watching the “Photosynthesis” video
1. What did Priestley mean by “injured” air? 2. What happened when Priestly added the mint leaf to the jar with the injured air? 3. What additional condition did Jan Ingenhousz determine to be necessary for Priestley’s
experiments to work?
Products of PhotosynthesisAnswer the following questions after watching the “Biology: The Science of Life: Photosynthesis” video
1. What is the overall balanced chemical reaction for photosynthesis? 2. What pigment present in plants is required for photosynthesis? 3. Name two things that are made available to humans by photosynthesis.
Textbook Reading (pages 230-233)
Vocabulary Terms
chlorophyll light-dependent reactions light-independent reactions pigment stroma thylakoid
Notes8.2 Photosynthesis: An Overview
A. Chlorophyll and Chloroplasts 1. Light 2. Pigments 3. Chloroplasts 4. Energy Collection
B. High-Energy Electrons

16C. An Overview of Photosynthesis 1. Light-Dependent Reactions 2. Light-Independent Reactions

178. The Process of Photosynthesis
Objectives:
Explain what happens during the light-dependent reactions Explain what happens during the light-independent reactions
The Reactions of PhotosynthesisLight HarvestingAnswer the following questions while watching the “Photosynthesis” video (1:08-1:54)
1. What are clusters of chlorophyll called? 2. What happens to chlorophyll after it absorbs light? 3. What change occurs to two water molecules in this process?
Electron Transport ChainAnswer the following questions while watching the “Photosynthesis” video (2:00-2:37)
1. Where do high-energy electrons from chlorophyll go? 2. What ion forms a concentration gradient as a result of the electron transport chain? 3. Where is the concentration gradient higher- inside or outside the thylakoid membrane?
4. Which two energy carrier molecules are formed? 5. What process occurs that allows ATP to be made?
Calvin CycleAnswer the following questions while watching the “Photosynthesis” video (2:08-1:54)
1. Where does this cycle occur? 2. What happens to the ATP formed during the light-dependent reactions? 3. How many turns of the cycle are needed to make one molecule of glucose?
Textbook Reading (pages 235-241)
Vocabulary Terms
ATP synthase Calvin cycle electron transport chain photosystem
Notes8.3 The Process of Photosynthesis
A. The Light-Dependent Reactions: Generating ATP and NADPH 1. Photosystem II

182. Electron Transport Chain 3. Photosystem I 4. Hydrogen Ion Movement and ATP Formation 5. Summary of Light-Dependent Reactions
B. Light-Independent Reactions: Producing Sugars 1. Carbon Dioxide Enters the Cycle 2. Sugar Production 3. Summary of the Calvin Cycle 4. The End Results
C. Factors Affecting Photosynthesis 1. Temperature, Light, Water 2. Photosynthesis Under Extreme Conditions
a) C4 Photosynthesis b) CAM Plants

199. Overview of Cellular Respiration
Objectives:
Make comparisons between cellular respiration and photosynthesis Analyze the energy content of food Explain the function of cellular respiration in the cell
Breathing and RespirationCellular RespirationAnswer the following questions after watching the “Cellular Respiration” video
1. What is the word equation that describes cellular respiration? 2. How does the equation for cellular respiration compare to the equation for
photosynthesis? 3. What is the function of cellular respiration?
Stages of Cellular RespirationAnswer the following questions after watching the “Cytoplasm: Mitochondria Used for Releasing Energy” video
1. Where do some reactions of cellular respiration take place? 2. What general equation describes the combustion of sugar? 3. What energy carrier molecule is produced as a result of cellular respiration?
Textbook Reading (pages 250-253)Vocabulary Terms
aerobic anaerobic Calorie
Notes9.1 Cellular Respiration: An Overview
A. Chemical Energy and Food B. Overview of Cellular Respiration
1. Stages of Cellular Respiration 2. Oxygen and Energy
C. Comparing Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Questions1. a. Why do all organisms need food?
b. Why do macromolecules differ in the amount of energy they contain?

202. a. Write the overall reaction for cellular respiration. b. How does the process of cellular respiration maintain homeostasis at the cellular level?
3. a. In what ways are cellular respiration and photosynthesis considered opposite processes? b. How is the chemical energy in glucose similar to money in a savings account?

2110. The Process of Cellular Respiration
Objectives:
Explain what happens during glycolysis Explain what happens during the Krebs cycle Explain how high-energy electrons are used by the electron transport chain
The Reactions of Cellular RespirationAnswer the following questions for each stage of cellular respiration
Stage 1: GlycolysisWhere does it occur? What happens? How much ATP is formed? Stage 2: Pyruvate Oxidation and the Krebs CycleWhere does it occur? What happens? How much ATP is formed? Stage 3: Electron Transport ChainWhere does it occur? What happens? How much ATP is formed?
Textbook Reading (pages 254-260)Vocabulary Terms
FAD glycolysis Krebs cycle mitochondrial matrix NAD
Notes9.2 The Process of Cellular Respiration
A. Glycolysis 1. ATP Production 2. NADH Production 3. The Advantages of Glycolysis
B. The Krebs Cycle 1. Citric Acid Production 2. Energy Extraction
C. Electron Transport and ATP Synthesis

221. Electron Transport 2. ATP Production
D. The Totals
Questions1. a. What are the products of glycolysis? 2. a. What happens to pyruvic acid in the Krebs cycle?
b. Look at Figure 9-5 and list the products of the Krebs cycle. What happens to each of these products?
4. a. How many molecules of ATP are produced in the entire breakdown of glucose?

2311. Fermentation
Objectives:
Compare aerobic and anaerobic respiration Explain conditions leading to anaerobic respiration Distinguish between the two types of fermentation Analyze everyday examples of fermentation
Textbook Reading (pages 262-265)Vocabulary Terms
aerobic anaerobic fermentation
Notes9.3 Fermentation
1. Fermentation 1. Alcoholic Fermentation 2. Lactic Acid Fermentation
2. Energy and Exercise 1. Quick Energy 2. Long-Term Energy
Questions1. a. Name the two main types of fermentation?
b. How are alcoholic fermentation and lactic acid fermentation similar? How are they different?
2. a. Why do runners breathe heavily after a sprint race? b. List the body’s sources of energy in the order in which they are used during a long-distance race.

2412. Cells Overview- Mid-unit Review
Objectives:
Review basic cell biology Review Key Words
Review of Cell Concepts
1. Review the objectives from each lesson2. Review your notes, focusing on the objectives3. Review the questions and answers from the assessment questions from the textbook4. Review the key words from each lesson5. Review the “Summary of Cell Concepts” marking each one that you are unsure of. Then
go back and review those specific concepts

2513. Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction
Objectives:
Explain why cells divide Analyze the requirements for passing intact genetic information from parent to offspring
during reproduction or from cell to cell during cell division
Limits to Cell SizeAnswer the following questions after watching the “Cell Size” video
1. What happens to the surface area-to-volume ratio of a cell as the cell grows larger? 2. Why is the surface area-to-volume ratio a factor in limiting the size of a cell?
Managing Cell GrowthAnswer the following questions after watching the “Bacteria and Binary Fission” video
1. What happens when a bacterial cell grows large enough that it has reached its upper size limit?
2. What component of the bacterial cell is replicated?
Answer the following questions after watching the “Asexual and Sexual Reproduction” video
1. How many parents are required to carry out asexual reproduction? 2. How many parents are required to carry out sexual reproduction? 3. Which parent passes its complete set of genetic information to offspring during sexual
reproduction?
Textbook Reading (pages 274-278)Vocabulary Terms
asexual reproduction binary fission cell division chromosome DNA gene genetic information
Notes10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction
A. Limits to Cell Size 1. Information Overload 2. Exchanging Materials
a) Ratio of Surface Area to Volume

26b) Traffic Problems 3. Division of the Cell
B. Cell Division and Reproduction 1. Asexual Reproduction 2. Sexual Reproduction 3. Comparing Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
Questions1 a. Identify the two reasons why a cell’s growth is limited?
b. As a cell’s size increases, what happens to the ratio of its surface are to its volume? c. Why is a cell’s surface area-to-volume ratio important?
2 a. What is asexual reproduction? What is sexual reproduction? b. What types of organisms reproduce sexually? c. What are the advantages and disadvantages of both asexual and sexual reproduction?

2714. Cell Division
Objectives:
Describe processes occurring at each stage of mitosis Describe what happens to chromosomes during cell division
Cell DivisionAnswer the following questions after watching the “Interphase, Mitosis, and Cytokinesis” video
1. What are the five phases of the cell cycle? 2. What happens to chromosomes during the S portion of interphase?
Textbook Reading (pages 279-285)Vocabulary Terms
anaphase centriole centromere chromatid cytokinesis metaphase mitosis prophase telophase
Notes10.2 The Process of Cell Division
A. The Cell Cycle 1. The Prokaryotic Cell Cycle 2. The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle
a) G1 Phase: Cell Growth b) S Phase: DNA Replication c) G2 Phase: Preparing for Cell Division d) M Phase: Cell Division
B. Mitosis 1. Prophase 2. Metaphase 3. Anaphase 4. Telophase
C. Cytokinesis 1. Cytokinesis in Animal Cells 2. Cytokinesis in Plant Cells

2815. The Cell Cycle
Objectives:
Analyze the structure of a eukaryotic chromosome Analyze the stages of the cell cycle Compare and contrast the amount of time a cell spends at the different stages of the cell
cycle
The Structure of ChromosomesAnswer the following questions after watching the “DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid” video
1. What two types of molecules are present in a chromosome? 2. How are these molecules organized in a chromosome?
Answer the following questions after watching the “Chromatin, Chromosomes, and DNA Subunits” video
1. How do the histones allow a very long DNA molecule to condense into a much shorter length?
2. Chromosomes are not visible during the S phase of the cell cycle when DNA is being replicated. Would replication be able to occur if the DNA were packaged into the condensed form of a chromosome?
Stages in the Cell CycleAnswer the following questions after watching the “Life Cycle of a Cell and Cell Division” video
1. What happens during G1? 2. What happens during S? 3. What happens during G2? 4. What is G0 and what happens during this phase?
Vocabulary Terms
G0 phase G1 phase G2 phase histone interphase nucleosome S phase

2916. Regulating the Cell Cycle
Objectives:
Describe cell cycle regulation Analyze ways that the cell cycle can be manipulated Evaluate the benefits and problems associated with human intervention in cell cycle
regulation
Regulators of the Cell CycleAnswer the following questions after watching the “DNA and the Genetics of Cancer” video
1. What is cancer? 2. Why does someone with a defective gene for p53 get cancer? 3. What process besides cancer occurs when p53 function is lost?
Textbook Reading (pages 286-290)Vocabulary Terms
apoptosis cancer cyclin growth factor tumor
Notes10.3 Regulating the Cell Cycle
A. Controls on Cell Division 1. The Discovery of Cyclins 2. Regulatory Proteins
a) Internal Regulators b) External Regulators c) Apoptosis
B. Cancer:Uncontrolled Cell Growth 1. What Causes Cancer? 2. Treatments for Cancer

3017. Cell Differentiation
Objectives:
Analyze the process of differentiation Explain why stem cells are important to multicellular organisms
Cell DifferentiationAnswer the following questions after watching the “Cell Differentiation” video
1. In an embryo, what are the cells called that have the potential to develop into specialized cells?
2. What type of regulation allows differentiation to occur?
Answer the following questions after watching the “Formation of Structures in a Developing Embryo” video
1. What is cytoplasmic localization? How does it affect cell differentiation? 2. What is induction? How does it affect cell differentiation?
Take notes on the three levels of differentiation found in human stem cells based on the “Stem Cell Primer” article
Multipotent Pluripotent Totipotent
Textbook Reading (pages 292-297)Vocabulary Terms
differentiation embryo stem cell
Notes10.4 Cell Differentiation
C. From One Cell to Many 1. Defining Differentiation 2. Mapping Differentiation 3. Differentiation in Mammals
D. Stem Cells and Development 1. Human Development 2. Stem Cells
a) Embryonic Stem Cells

31b) Adult Stem Cells

3218. Cells Unit Review
Objectives:
Review the concepts presented in the unit
Test Preparation Read the Chapter 7 Study Guide on p. 219 Answer the following questions from pp. 220-221
o 1. o 2. o 3. o 5. o 7. o 8. o 11. o 12. o 15. o 16. o 19. o 21.
Read the Chapter 8 Study Guide on p. 243 Answer the following questions from pp. 244-245
o 1. o 2. o 3. o 5. o 6. o 10. o 11. o 12. o 19. o 20. o 21. o 25. o 26. o 28. o 29.
Read the Chapter 9 Study Guide on p. 267 Answer the following questions from pp. 268-269
o 1. o 3.

33o 4. o 5. o 7. o 9. o 11. o 12. o 13. o 14. o 20. o 23. o 24. o 26. o 30.
Read the Chapter 10 Study Guide on p. 299 Answer the following questions from pp. 300-301
o 1. o 2. o 3. o 4. o 9. o 10. o 11. o 14. o 19. o 21. o 22. o 26.