Mrs. Ashley Medical Assistant Science. PANCREAS ANATOMY stomach esophagus ductus choledocus duodenum...
-
Upload
britton-ray -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
0
Transcript of Mrs. Ashley Medical Assistant Science. PANCREAS ANATOMY stomach esophagus ductus choledocus duodenum...

Mrs. AshleyMedical Assistant Science


PANCREAS ANATOMY
stomach
esophagus
ductus choledocus
duodenum
duct of Santorini
duct of Wirsung
pancreas

Exocrine and endocrine cells 90% of pancreas related to exocrine
(digestive function) 10% endocrine (homeostasis for glucose
levels in the body)

5

◦ Both an exocrine and endocrine organ◦ Cells with exocrine function release
an alkaline fluid containing sodium bicarbonate and enzymes → pancreatic duct → small intestine
◦ Pancreatic “juice” aids in breakdown and digestion of food in the small intestine
◦ Pancreatic exocrine cells = acinar cells

Acinar cells - exocrine cells of the pancreas that produce and transport digestive enzymes
Amylase, lipase, phospholipase, proteases (trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen)

PANCREATIC SECRETIONS
1. PROTEASES (70%)
Endopeptidases (trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastases)
Exopeptidases (carboxypeptidases)
trypsinogen trypsin activates all other precursors
enterokinase(duct walls)
2. NUCLEASES (DNAase, RNAase)
3. PANCREATIC AMYLASE (hydrolyse starch and gl;ycogen)
4. PANCREATIC LIPASE (triglycerides fatty acids and glycerol)

PANCREAS (PANORAMIC)
pancreatic acini
islet ofLangerhans
islet ofLangerhans
BV
pancreatic lobe

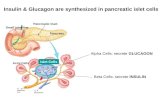
Islets of Langerhans - endocrine cells of the pancreas that produce and secrete hormones into the bloodstream
Glucagon - Alpha cells (A cells) - raises the level of glucose (sugar) in the blood by causing liver to break down stored glycogen
Insulin - Beta cells (B cells) - stimulates cells to use glucose and reduce glucose levels in blood
Antagonistic Hormones

11
Endocrine Function :Cells of the Islet of Langerhans synthesize and release hormones into the circulation.
Hormones travel through the bloodstream to target tissues (especially liver and muscle)
At the target cells, hormones bind specific receptors and cause cell changes that control metabolism

12

13
Chemically – high levels of glucose and amino acids in the blood
Hormonally – beta cells are sensitive to several hormones that may inhibit or cause insulin secretion
Neurally – stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system causes insulin to be secreted.

14
Transported through the blood to target tissues where it binds to specific receptors
The binding of insulin to target cells:◦ Acts as a biochemical signal to the inside of the cell Overall, cell metabolism is stimulated There is increased glucose uptake into the cell Regulation of glucose breakdown within the
cell Regulation of protein and lipid breakdown
within the cell

Blood glucose is decreased because insulin causes glucose to leave the bloodstream and enter the metabolizing cells.
With the exception of brain, liver and erythrocytes, tissues require membrane glucose carriers.

Inflammation of the pancreas

Pancreas suddenly becomes inflamed Causes: Gallstones Ethanol Trauma
Steroids Mumps Autoimmune Scorpion venom Hyperlipidaemia, hypothermia ↑Ca2+
Drugs

Symptoms epigastric and central abdominal pain vomiting and nausea swollen and tender abdomen fever dehydration and low blood pressure
Diagnosis medical history and physical exam blood test: ↑ amylase, lipase abdominal ultrasound, Endoscopic
Ultrasound, CT scan

Treatment nothing to eat or drink intravenous fluids analgesia ERCP and gallstone removal
Complications shock, Acute respiratory distress
syndrome, renal failure, Disseminated intravascular coagulation, sepsis, ↓Ca2+
pancreatic necrosis, pseudocyst, abscesses, bleeding, thrombosis

inflammation of the pancreas - gets worse over time and leads to permanent damage
Causes: many years of alcohol use hereditary disorders of the
pancreas cystic fibrosis haemochromatosis autoimmune conditions

Symptoms nausea and vomiting weight loss diarrhea steatorrhea

Treatment drugs - analgesia, lipase, fat-soluble
vitamins diet surgery – pancreatectomy pancreaticojejunostomy
Complications pseudocyst, diabetes, biliary obstruction,
local arterial aneurysm, splenic vein thrombosis


The single most common endocrine disorder – group of glucose intolerance disorders
Incidence is estimated at 8.3% of the North American population
35% are pre-diabetic Many of these cases are undiagnosed

25
Historically ‑ distinguished by weight loss, excessive urination, thirst, hunger
Excessive urination = polyuriaExcessive thirst = polydipsiaExcessive hunger = polyphagia
Modern characterization is by hyperglycemia and other metabolic disorders

increased level of glucose in the blood (normal blood glucose level 3.5-6.0 mmol/l)
90 mg/100ml
Type 1 ( insulin-dependent DM, IDDM) destruction of insulin-secreting pancreatic β
cells (autoimmune response) juvenile diabetes-tends to begin in early
childhood patient always needs insulin

Type 2 (non-insulin dependent DM, NIDDM) insulin resistance Β cell dysfunction, ↓insulin secretion
Causes of insulin resistance: metabolic syndrome (central obesity,
hyperglycaemia, hypertension, ↓HDL cholesterol, ↑triglycerides)
renal failure pregnancy cystic fibrosis polycystic ovarian syndrome

28
Glucose in urine- Because when insulin is not present, glucose is not taken up out of the blood at the target cells.
So blood glucose is very highly increased → increased glucose filtered and excreted in the urine (exceeds transport maximum)

Mechanisms of insulin resistance:
post-receptor defects in insulin action
gene mutation circulating
autoantibodies


Diagnosis
blood glucose level urine sample HbA1c test

Treatment:
diet oral
hypoglycaemics

33
Control dietCarbohydrates should make up about
55-60% of patient’s total caloriesFats should make up <30% of patient’s
total caloriesProteins should make up about 15-20%
of patient’s total calories

34
Monitor exerciseRemember: muscles are a target tissue of
insulin, and metabolize much glucose for energy
Sometimes exercise →irregular blood glucose levels So diabetic patients should be monitored when they are exercising

insulin injections (long-acting, short-acting, rapid-acting)
insulin pen insulin pump therapy

Complications

diabetec ketoacidosis hypoglycaemia diabetic retinopathy

atherosclerosis (heart disease and stroke) neuropathy (diabetic foot care)

Age over 40 years Diabetes during a previous pregnancy Excess body weight Family history of diabetes Dyslipidaemia (large amount of lipids in
body) Hypertension Low activity level Metabolic syndrome Polycystic ovarian syndrome Acanthosis nigricans- darkening and
thickening of skin