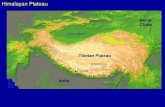
Mountains and Plateaus 3 Physical Subdivisions of the Realm ATLAS MTS. CAUCASUS MTS ZAGROS MTS...
-
Upload
ashley-west -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
1
Transcript of Mountains and Plateaus 3 Physical Subdivisions of the Realm ATLAS MTS. CAUCASUS MTS ZAGROS MTS...
- Slide 1
- Slide 2
- Mountains and Plateaus
- Slide 3
- 3 Physical Subdivisions of the Realm ATLAS MTS. CAUCASUS MTS ZAGROS MTS ANATOLIAN PLATEAU IRANIAN PLATEAU
- Slide 4
- Mountains & Plateaus Atlas Mts. Elburz Mts. Taurus Mts. Zagros Mts. Iranian Plateau Anatolian Plateau Caucasus Mts. Hejaz Mts.
- Slide 5
- Physical Geography of Northern Africa & Southwest Asia Mountains Atlas Mountains in Northern Algeria and Morocco Thorus Mts in Southern Turkey Elburz & Zagros Mts. In Iran Golan Heights in Israel
- Slide 6
- Physical Geography Plateaus - Anatolian Highland Peninsulas - Saudi Arabian, Suez
- Slide 7
- Sinai Peninsula located between Egypt and the Arabian Peninsula
- Slide 8
- Asia Minor and Cyprus: Pontic Mountains north of North Anatolian Transform Fault Slippage and earthquakes (August 1999) Taurus Mountains on southern side of Asia Minor
- Slide 9
- Iranian Plateau and Ranges: Compression, subduction between Arabian plate and Iranian sub-plate Creation of Zagros Mountains Makran Range farther SE as uplifted crust Up folding of Elburz Mountains and Kopet Mountains between Iranian sub- plate and Eurasian plate Connected tectonic activity and volcanoes
- Slide 10
- Atlas Mountains The Atlas Mountains of North Africa, the physiographic base of the settled Maghreb (Algeria, Morocco and Tunisia), are also a part of the Alpine System. The Atlas Mountains receive an average rainfall of 750 mm (30 inches), something unusual for this region. The role of altitude is clear. Even 240 km (150 miles) into the interior, the slopes of the Atlas receive more than 250 mm (10 inches) of rainfall.
- Slide 11
- Atlas Mountains Continued SSeparates the northern moist Mediterranean climate from the arid south.
- Slide 12
- Slide 13
- Slide 14
- Slide 15
- Taurus and Zagros Mountains Taurus Spreads across Turkey Runs east-west along the northern edge of Turkey Highest Point- Mt. Ararat-16, 583 ft., Biblical historians believe Noahs Ark landed here. Zagros Extends through southwestern Iran, and through northern Iraq Highest point- ZardKuh, 14, 921 ft.
- Slide 16
- Slide 17
- Slide 18
- Mountain Ranges in Mid-East Elburz Mts., Iran Zagros Mts., Iran Lebanese Mts. Taurus Mts., Turkey
- Slide 19
- Anti-Taurus Mountains Taurus Mountains Pontic Mounatins Elburz Mountains
- Slide 20
- Anatolian Plateau Fertile soil Conducive (helpful) for farming
- Slide 21
- Iranian Plateau Very dry Sparsely populated
- Slide 22
- Pair-Share With your partner, using the PowerPoint and Reading Notes, summarize the effects of the mountain ranges on the Middle East region.
- Slide 23
- Deserts
- Slide 24
- Sahara Desert Arabian Desert Negev Desert Sinai Desert Libyan Desert Rub al-Khali
- Slide 25
- Physical Geography of Northern Africa & Southwest Asia Deserts The Sahara Desert The Saudi Arabian Desert The Libyan Desert Negev Desert
- Slide 26
- 26 NEGEV DESERT
- Slide 27
- Where is the driest desert? 27
- Slide 28
- Sandy Deserts Rub al-KhaliArabian Peninsula desert, known as the Empty Quarter 250,000 square miles, with dunes as high as 800 feet 10 years can pass without rain Nearby An-Nafud Desert contains the occasional oasis -desert area where underground spring water supports vegetation Syrian Desert is between Lebanon, Israel, Syria, and the Fertile Crescent Israels Negev Desert produces crops through irrigation
- Slide 29
- Two ways of lifenomadic and sedentarydeveloped in the desert. Nomadic life- people moved from place to place within tribes for protection, and as the seasons changed. Sedentary- people settled in oases, where they could farm. These settlements often became towns. Towns became centers of trade. Many had a souk, a market or bazaar, where goods were traded.
- Slide 30
- Nomadic Life: Bedouins Many people in North Africa and the Middle East still live a nomadic lifestyle. Nomads live on the Arabian Peninsula and in the Sahara Desert. The deserts have also led to a way of life that developed around the need to survive in such harsh surroundings. These people are known as Bedouins or desert nomads They survive and make a living by Living in tent camps Surviving as sheep and camel herders Trading animals and handmade goods
- Slide 31
- Slide 32
- Desert Bedouins
- Slide 33
- Rub al-Khali: The Empty Quarter
- Slide 34
- Rub Al-Khali Size of Texas One of largest sandy deserts in world It is the largest area of continuous sand in the world. Surface temps, can reach 150 Very Arid 10 years may pass w/out rain No permanent streams exist
- Slide 35
- The Rub 'al-Khali, or "Empty Quarter" is a large desert in Saudi Arabia. It is the largest area of continuous sand in the world. The climate is extremely arid. Few places receive more than 7 inches of rain a year, and no permanent streams exist. Summer temperatures reach as high as 130 F in some areas.
- Slide 36
- Arabian Peninsula Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, United Arab Emirates (UAE), Oman, Yemen Small population Lack of water BUT lots and lots of oil!!! Birthplace of Islam Very dry, sandy, & windy Wadis- riverbeds that remain dry except for the rainy season.
- Slide 37
- The Arabian Peninsula is primarily steep and has a desert climate
- Slide 38
- Slide 39
- Salt Deserts In Iran, high mountains block rain; dry winds increase evaporation Loss of moisture in soil leaves chemical salts, creates a salt flat (a flat expanse of land covered in salt and other minerals; usually shines white under the sun) Irans salt flat deserts: Dasht-e Kavir in central Iran Dasht-e Lut in eastern Iran Land is salt-crusted, surrounded by salt marshes, its very hot Almost uninhabited, its a barrier to easy travel across Iran
- Slide 40
- Iranian Salt Flat
- Slide 41
- Sahara Desert:
- Slide 42
- Sahara Desert Location Atlantic Ocean on the west Atlas Mountains and the Mediterranean Sea on the north Red Sea and Egypt on the east Sudan and the valley of the Niger River on the south.
- Slide 43
- The Sahara The Sahara is the worlds largest desert, stretching 3.5 million square miles. Very dry, so very few people live there Averages less than five inches of rain each year. Temperatures there can run to the extreme freezing at night Can be more than 130 degrees Fahrenheit at the peak of day. Nearly every settlement in the Sahara is located near an oasis, a wet and fertile area in a desert where a spring or well provides water. Common features in the Sahara include broad gravel plains, tall sand dunes, and dry streambeds.
- Slide 44
- Slide 45
- Slide 46
- Breeding Areas of Desert Locusts
- Slide 47
- Swarms of Desert Locusts! Locusts Swarm the Pyramids Complex at Giza! Israel Hit By Worst Locust Plague Since the 1950s!
- Slide 48
- Sahel: - Area separating the Sahara from the tropical rainforest of Africa.
- Slide 49
- Pair-Share What has surprised you about the desert of the Middle East region? Why?
- Slide 50
- Completed Map Tigris River Nile River Euphrates River Jordan River Persian Gulf Arabian Sea Mediterranean Sea Indian Ocean Red Sea Black Sea Gulf of Aden Strait of Hormuz Suez Canal Dardanelles Strait Atlantic Ocean Gulf of Oman Caspian Sea Arabian Desert Negev Desert Sinai Desert Rub al-Khali Atlas Mts. Elburz Mts. Taurus Mts. Zagros Mts. Iranian Plateau Anatolian Plateau Caucasus Mts. Hejaz Mts. Sahara Desert Libyan Desert
- Slide 51
- The Natural Resources of the Middle East
- Slide 52
- Major Resources of the Middle East Petroleum Water Cotton Natural Gas Coal Iron
- Slide 53
- Oil
- Slide 54
- Petroleum- remains of plants & animals, formed from pressure & heat over millions of years. Oil is not in big pools under the ground, it is trapped in the pores of rocks. Taken out of ground by pressure Economy oil dominated industry
- Slide 55
- Crude Oil- unprocessed petroleum Refinery- converts crude oil into useful products like gasoline & kerosene
- Slide 56
- Oil Oil is certainly the most important resource of North Africa and Southwest Asia. Deposits are concentrated around the Persian Gulf. It is the most economically important export of the realm. Between 1994-1996, on average, these countries together produced 28.0 percent of the worlds total output. Saudi Arabia ranked as the worlds leading producer with 13.1 percent followed by: Iran with 5.8 percent; the United Arab Emirates with 3.6 percent; Kuwait with 3.3 percent; and Libya with 2.2 percent (Table 6.2). Additional detailed statistics on the worlds leading oil countries are shown in Table 6.3. In 1997, the world estimates in petroleum reserves were 1,160,069,500,000,000 barrels. These countries collectively account for 56.3 percent of the world's total reserves. Saudi Arabia has 22.6 percent, Iraq 9.7 percent, Kuwait 8.2 percent, Iran 7.8 percent, U.A.E. 5.5 percent, and Libya 2.5 percent.
- Slide 57
- Oil Reserves vs. Economy The Southwest Asian countries with the largest reserves of natural gas and oil are: Saudi Arabia Iran Iraq Kuwait These countries have seen tremendous growth in national wealth and an improved standard of living in the past 50 years. Some other countries have smaller reserves, especially around the Arabian Gulf. Those countries without the reserves have had a much harder time improving living conditions for their people. This difference has lead to much conflict.
- Slide 58
- Reserves Until the Gulf War, Kuwait had a 21 billion- barrel proven reserve. Iraq has a 7 billion barrel proven reserve.
- Slide 59
- Saudi Arabia Have a proven 200 year reserve. The Saudi Government could purchase the entire National Football League (contracts, salaries, stadiums, etc.) with 6 weeks of their oil reserves.
- Slide 60
- Kuwait: An Island Floating on a Sea of Oil Kuwait City
- Slide 61
- Oil
- Slide 62
- World Oil Reserves
- Slide 63
- Saudi Oil Fields & Refineries
- Slide 64
- Importance of Oil For this reason, countries in the Middle East have a steady market for all the oil and natural gas they produce. Saudi Arabia and Iran are two of the worlds largest suppliers / producers of oil. Over half of the worlds known supply comes from them. Israel has very few natural resources and practically no oil. They have a high industrial economy, so the world price of oil has a huge impact on their economy.
- Slide 65
- Importance of Oil Oil is one of the most important and valuable natural resources in the Middle East. Oil and natural gas are considered fossil fuels which means they were created centuries ago. They are also non-renewable natural resources which means they cannot be replaced Most of the worlds industrial nations depend on a steady supply of both resources The US imports over half of its supply, almost 18 million barrels every day.
- Slide 66
- Oil Transport
- Slide 67
- How are oil and gas transported?
- Slide 68
- Saudi Pipeline
- Slide 69
- Oil Tanker (Knock Nevis)
- Slide 70
- Effects of Oil
- Slide 71
- However, oil has also been a source of conflict. Over the last few decades, major conflicts have erupted in the Middle East. Issues that have contributed to the conflicts include the presence of huge oil reserves, the growth of Islamism, and the conflict between Israel and its neighbors. About two-thirds of worlds known oil reserved located in Middle East Reserves have been great source of wealth for Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, other countries Most members of Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries Oil in the Middle East Regional Issues OPEC attempts to regulate production of oil exports to maximize revenues Oil revenues allowed Middle East governments to modernize countries, promote industrialization, economic, social development Oil Revenues
- Slide 72
- Importance of Oil Oil as source of conflict in Middle East Some governments have used oil revenues to build up military, maintain power, threaten neighbors Oil wealth has caused internal clashes within countries, societies Regions strategic importance as source of oil has led outside nations to become involved in Middle Eastern affairs, politics
- Slide 73
- 73 THE IMPACT OF OIL HIGH INCOMES MODERNIZATION INDUSTRIALIZATION REGIONAL DISPARITIES FOREIGN INVESTMENT IN THIS REALM INVESTMENT IN FOREIGN COUNTRIES
- Slide 74
- Oil Industries Disputes over access to other natural resources, like oil, also cause conflict. The Persian Gulf has the largest source of oil in the world. The countries that border the Persian Gulf also have a large oil industry. Many wars have been fought over oil in Southwest Asia. These wars have had a major impact on the environment.
- Slide 75
- 75 Lands of Wealth and Poverty The Geography of Fossil Fuels Oil unevenly distributed in the area Saudi Arabia, Iran, U.A.E., Libya, Algeria contribute significantly to oil production, while Morocco & Sudan have few developed reserves Region has 7% of the worlds population; holds 68% of the worlds proven petroleum reserves Regional Economic Patterns Higher-Income Oil Exporters Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar, Bahrain, U.A.E. Cultural landscape reshaped because of oil wealth Not all benefit rural Shiite Muslims and foreign workers
- Slide 76
- 76 Lands of Wealth and Poverty (cont.) Regional Economic Patterns (cont.) Lower-Income Oil Exporters Algeria: oil and natural gas are its top exports; but political instability remains a problem Iran: huge oil reserves, but long war with Iraq (1980- 90), & fundamentalist government withdrawal from world trade under have lowered living standards Prospering Without Oil Israel has highest living standard in the region Turkey has a diversified economy; has seen growth Economic reforms in Tunisia Lebanon has potential for prosperity through tourism & telecommunications
- Slide 77
- 77 Natural Gas Oil Deposits
- Slide 78
- The Oil Curse The Resource Curse Prone to authoritarian rule, slow growth, corruption and conflict. Resources used to finance armies, corruption and patronage. Oil is a good example. Modernization High incomes. Industrialization. Regional and national disparities (oil wealth distribution). Migration Brought populations from outside the realm. Foreign incursions
- Slide 79
- What is done with Oil Wealth? Oil rich nations typically provide healthcare and improved schooling. However those segments of the population not employed in the oil industry tend to have lower standards of living. Girls school in Saudi Arabia Bedouin in S.Arabia
- Slide 80
- Persian Gulf War Over Oil Much of the oil refining machinery in Iraq was badly damaged in the Persian Gulf War, in 1991. The Iraqi government did not repair the equipment that makes refining oil safer for the environment. For years, pollution from Iraqi oil refineries leaked into the water supply and in the air. Today, the Iraqi oil industry is not productive because of the current war in Iraq. However, many of Iraqs oil refineries were destroyed and burned during the war, so that the air was polluted.
- Slide 81
- Oil in War During the first Gulf War, Iraq used pollution as a strategy for fighting. Iraqi soldiers dumped over 300 gallons of oil into the Persian Gulf. They also burned hundreds of oil wells in order to keep the U.S. from taking control of their oil industry.
- Slide 82
- Oil Pollution Oil is the basis of most of the economy of the Middle East, but pollution from the oil industry is one of the biggest threats to its environment. This pollution endangers the water supply in particular. Since there is not much fresh water in the region, these environmental problems directly affect the lives of Middle Easterners.
- Slide 83
- Oil Pollution For years, pollution from Iraqi oil refineries leaked into the water supply and in the air. Today, the Iraqi oil industry is not productive because of the current war in Iraq. However, many of Iraqs oil refineries were destroyed and burned during the war, so that the air was polluted.
- Slide 84
- Oil Spills are a risk when transporting oil in narrow straits or around reefs Largest in U.S. History is the Exxon Valdez spill in 1989
- Slide 85
- OPEC
- Slide 86
- In 1960, Venezuela, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, and Saudi Arabia founded OPEC (Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries) in an effort to dictate oil prices. Later additions included Algeria, Ecuador, Nigeria, Gabon, Indonesia, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, and Libya. This 13-member cartel was designed to control world pricing and production of a single commodity, oil. Currently, OPEC has 11 members after the withdrawal of Ecuador and Gabon.
- Slide 87
- Slide 88
- Problems with unequal oil distribution: Oil producing country (OPEC) can raise prices, and cut off oil supply Oil spills
- Slide 89
- These 12 countries (from 3 different continents) produce 1/3 the worlds oil and set the price of oil Members: AlgeriaIranIraq KuwaitQatarSaudi Arabia LibyaNigeriaUnited Arab Emirates EcuadorVenezuelaAngola
- Slide 90
- Top Five Oil Producing Countries: -Saudi Arabia -Iraq -Kuwait -Iran -United Arab Emirates
- Slide 91
- Top Oil Consuming Countries -United States -Russia -Japan -Germany -China
- Slide 92
- Where America gets Oil
- Slide 93
- INCOME LEVELS
- Slide 94
- Pair-Share After what we have learned about the geography of the Middle East, which resource do you think is more precious and important---fresh water or oil? Why?




![The Role of the Zagros Suture on Three Dimensional ...journals.ut.ac.ir/article_20881_d08239240afe41517836baec...Zagros Reverse Fault’ by various authors [e.g., 75,33,27,9] in the](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5f0be6817e708231d432c598/the-role-of-the-zagros-suture-on-three-dimensional-zagros-reverse-faulta.jpg)