Mitosis & Meiosis - Weeblybiologywithmsgeorge.weebly.com/.../2/2/4/3/22439118/mitosis___me… ·...
Transcript of Mitosis & Meiosis - Weeblybiologywithmsgeorge.weebly.com/.../2/2/4/3/22439118/mitosis___me… ·...

Mitosis & Meiosis
SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis
and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual
reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation.

1. Students will describe specific events
occurring in each stage of the cell cycle
and/or phases of mitosis, including cytokinesis.
Cell Division: the process of copying and dividing entire cells
The cell grows, prepares for division, and then divides to form new
daughter cells.
Unicellular organisms – allows duplicate using asexual reproduction
Multicellular organisms – allows to grow, develop from single cell to
multicellular, makes other cells to repair and replace worn out cells
Three types: binary fission (bacteria and fungi), mitosis, and meiosis

1. Students will describe specific events
occurring in each stage of the cell cycle
and/or phases of mitosis, including cytokinesis.
Cells divide
through a process
called the cell
cycle which
consists of
interphase, mitosis,
and cytokinesis.
Note: majority of
the cell cycle is
Interphase, while a
smaller portion is
mitosis/cytokinesis.

1. Students will describe specific events
occurring in each stage of the cell cycle
and/or phases of mitosis, including cytokinesis.
Interphase: longest part of the cell cycle; growth, metabolism, and
preparation for division occurs, duplicates chromosomes (DNA
Replication)

1. Students will describe specific events
occurring in each stage of the cell cycle
and/or phases of mitosis, including cytokinesis.
MITOSIS – division of nucleus of the cell
Prophase: duplicated chromosomes and spindle fibers
appear
Metaphase: duplicated chromosomes line up randomly in
center of cell between spindle fibers
Anaphase: duplicated chromosomes pulled to opposite
ends of cell
Telophase: nuclear membrane forms around
chromosomes at each end of the cell; spindle fibers
disappear; chromosomes disperse

1. Students will describe specific events
occurring in each stage of the cell cycle
and/or phases of mitosis, including cytokinesis.
Cytokinesis: division of plasma membrane; two daughter cells result
with exact genetic information
In plants, a cell plate forms along the center and cuts the cell in
half.
In animals, a cleavage furrow develops to cut the cell in half.

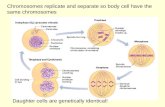
RESULTS OF MITOSIS:
Two identical daughter cells
Produces and occurs in somatic cells (body cells)
Diploid = same number of chromosomes as
original cell (humans = 46)
1. Students will describe specific events
occurring in each stage of the cell cycle
and/or phases of mitosis, including cytokinesis.

2. Students will explain how meiosis results in
the formation of haploid gametes or spores.
In meiosis, the cells will also start with interphase.
There are TWO cell divisions instead of one, but the cell only
does interphase ONCE prior to the first cell division.
Meiosis is a reduction division process (chromosome numbers
are divided in half)
Each cell division consists of prophase, metaphase, anaphase,
and telophase
Occurs only in sex cells (gametes) and produces only gametes
(egg and sperm)

First Division: Produces cells containing half # of double stranded
chromosomes
Prophase 1 –
crossing over
occurs
Metaphase 1 –
chromosomes line up in
homologous pairs,
independent assortment
occurs
Anaphase 1 –
chromosomes
move towards
each side
Telophase 1 – cells
contain HALF of #
of chromosomes
2. Students will explain how meiosis results
in the formation of haploid gametes or
spores.

2. Students will explain how meiosis results
in the formation of haploid gametes or
spores.
Crossing over: genes are essentially “switching” places
on chromosomes in prophase I
Independent assortment: the genes randomly move
towards ends of cell in metaphase I
THESE BOTH RESULT IN GENETIC VARIATION!

Second Division: Results in formation of four cells, each haploid
(half the number of original chromosomes) (humans = 23)
2. Students will explain how meiosis results in
the formation of haploid gametes or spores.

RESULTS OF MEIOSIS:
Four unique daughter cells
Unique due to genetic variation such as crossing over and independent assortment
Produces and occurs in gametes (sex cells)
Haploid = half number of chromosomes as original cell (humans = 23)
Sex cells combine during sexual reproduction to produce a diploid individual
2. Students will explain how meiosis results in
the formation of haploid gametes or spores.

3. Students will compare and contrast
sexual and asexual reproduction.
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
Pattern of reproduction that involves the production
and fusion of haploid sex cells
Haploid sperm from father fertilizes haploid egg from
mother to make a diploid zygote

3. Students will compare and contrast
sexual and asexual reproduction.
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
A single parent produces one or more identical
offspring by dividing into two cells.
Diploid cells are clones of parent cell.