Microscopy Special Techniques in Microscopy: Immunohistochemistry.
-
Upload
samantha-bailey -
Category
Documents
-
view
237 -
download
2
Transcript of Microscopy Special Techniques in Microscopy: Immunohistochemistry.

Microscopy
Special Techniques in Microscopy:Immunohistochemistry

Immunohistochemistry
• The process for detecting antigens (Ags) in histological material– uses antibodies (Abs) directed against specific
antigenic sites in cells and tissues– labeling with colouring agents (or fluorescence, or
electron opaque material) to visualise Ag-Ab reaction products

History of Immunocytochemistry

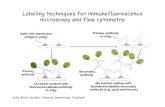
Immunohistochemical methods
• Direct method– antigen + [antibody + marker substance]
• Indirect method– antigen + 1° antibody + [2° antibody + marker
substance]• Indirect method is amplification process
– large amount of marker substance can be attached
• Most widely used method– PAP and ABC methods

Fluorescent ICC
• Direct method– antigen + [antibody + fluorescent dye]
• Indirect method– antigen + 1° antibody + [2° antibody + fluorescent
dye]• fluorescent dye is often fluorescein isothiocyanate
(FITC)

ICC methodology

Chromagen localisation
ABC-complexed chromagen (red) localising estrogen receptors in breast tumor.Tissue is counter stained with haematoxylin to show nuclei.

Fluorescent ICC

Enzyme-labelled antibody methods
• Immunoperoxidase method– Nakane and Pierce (1966): introduced a method for
the application of enzymes as markers of antibodies in cells and tissues
– Graham and Karnovsky (1966): developed a method for histochemical demonstration of horse-radish peroxidase enzyme (HRP) at ultrastructural level
• HRP conjugation technique• antigen + [antibody + coupling agent + HRP]
– p,p’-difluoro-m,m’-dinitrophenyl sulphon (FNPS)– glutaraldehyde– sodium periodate

Peroxidase-Antiperoxidase (PAP)
• Designed to overcome the problems inherent in fluorescent labelling– Signal reduction in fluorescent staining (bleaching)
• wavelength stimulation• time
– Must use fluorescent microscope• expensive• special filters
– Cannot be used in electron microscopy

PAP technique - 1
Antigen + 1º antibody + 2º antibody + PAP complex
• Prestaining preparation– Remove Fixatives
• wash thoroughly with PBS• sodium borohydrate pretreatment
– Enhancing penetration of antibodies• LM -- use detergent (Triton X-100, etc.)• EM -- use graded ethanol
– Blocking non-specific antibody determinants• pretreatment with animal serum
– normal goat serum (NGS)– bovine serum albumin (BSA)

PAP technique - 2
• Remove fix• Reaction with primary antiserum
– Primary antibody (polyclonal or monoclonal)• human or animal (X) Ag animal (Y) Ag Y-anti X Ab• determination of 1º antibody dilution
• Reaction with secondary antiserum– Bridging process
• primary antibody + secondary Ab + PAP complex
– Secondary antibody: Z origin anti-Y IgG• one Fab directed primary Ab• other Fab directed toward Y origin PAP complex

PAP technique - 3
• Reaction with PAP complex– Amplification process
• Y origin PAP complex (peroxidase Y-antiperoxidase complex)• anti-Y secondary Ab + Y PAP complex
– Visualisation of PAP end products• DAB (3,3’-diaminobenzidine) - an insoluble phenazine
polymer– oxidative polymerisation - serves as electron donor
• Peroxidase• Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) - substrate

PAP localisation
Substance P from dorsal horn of rat spinal chord.

Avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) method
• Alternative method to PAP technique– More sensitive than PAP method
• amplification is much greater• more staining sites
– Based on avidin-biotin affinity• avidin with Mol Wt = 7000• biotin (vitamin H)
– More convenient• availability of ABC kits from several companies

ABC technique - 1
Antigen + 1º antibody + biotin-labelled 2º antibody + HRP-labelled streptavidin
• Prestaining preparation– Remove Fixatives
• wash thoroughly with PBS• sodium borohydrate pretreatment
– Enhancing penetration of antibodies• LM -- use detergent (Triton X-100, etc.)• EM -- use graded ethanol
– Blocking non-specific antibody determinants• pretreatment with animal serum
– normal goat serum (NGS)– bovine serum albumin (BSA)

ABC technique - 2
• Reaction with primary antiserum– Primary antibody (polyclonal or monoclonal)
• human or animal (X) Ag animal (Y) Ag Y-anti X IgG
• Reaction with biotin-labelled secondary antiserum– Bridging process
• 1º antibody + biotin-labelled 2º Ab + PAP-streptavidin complex• Secondary antibody: Z origin anti-Y IgG
• Reaction with PAP-streptavidin complex– biotin + streptavidin-PAP (strong biotin reaction)
• Visualisation of PAP end products– DAB, peroxidase, H2O2

Suppliers
• http://www.vectorlabs.com/index.htm