Metamorphic Rocks
description
Transcript of Metamorphic Rocks

Metamorphic Rocks
Change is Good

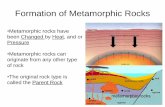
Metamorphic Rocks
• Formed from intense heat and pressure!

Sources of Heat
• 300-1400 degree Celsius temperatures are needed for Metamorphism.
• Sources of heat include:– Magma or lava– Friction from faulting

Sources of Pressure
• Mountain building (plate movements)• Intrusions of magma into surrounding rocks• Weight of overlying layers (1-5 miles thick)

Types of Metamorphism
• 1. Contact - (local) due to heat and pressure of magma intrusions or faulting.
• 2. Regional - due to mountain building (affects a wide area)

Types of Metamorphic Rocks
• 2-Types: Foliated and Nonfoliated• Foliated – Minerals are aligned into parallel
layers. Often looks like banding of dark and light minerals (sort of like a zebra). Results from pressure in two directions.
• Nonfoliated - (recrystallized) from thermal metamorphism (intense heat); the enlargement or the formation of new minerals; large inter-locking crystals with a shiny appearance.

Texture of Metamorphic Rocks
• Foliated or Nonfoliated• Nonfoliated usually look chrystalline (marble,
quartzite)• Grain Size: (Fine, Medium, Coarse)

Foliated Rocks
• Slate • Phyllite
• Schist• Gneiss

Foliation: How it happens!

Nonfoliated Rocks
• Marble
• Quartzite
• Anthracite coal• Hornfels• Greenstone

Parent Rocks
Metamorphic Rock• Slate• Phyllite• Schist• Gneiss• Greenstone• Marble• Quartzite• Anthracite Coal• Hornfels
Parent Rock• Shale or Mudstone• Slate• Shale or Mudstone• Granite or Diorite• Basalt• Limestone• Sandstone (with quartz)• Bituminous Coal• Anything

Tectonic Boundaries for Metamorphic Rocks
• Continent-Continent Convergent Boundary.
• Example: India and Asia forming the Himalayas.
• Regional Metamorphism

Transform Boundary (Strike-Slip Fault)
• Two plates slide past each other
• Example: San Andreas fault in California.
• Contact/Regional Metamorphism.

Contact Metamorphism from magma
• Magma intrusions cause metamorphism.
• Contact metamorphism is caused by dikes and sills.
• Regional metamorphism is caused by laccoliths and batholiths, which are large chambers of magma.
• The intense heat can metamorphose the surrounding and intruded rock layers.