Memory. Atkinson and Shiffrin, (1968) classic model of memory.
-
Upload
earl-lawson -
Category
Documents
-
view
232 -
download
2
Transcript of Memory. Atkinson and Shiffrin, (1968) classic model of memory.

Memory

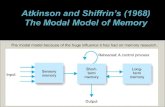
Atkinson and Shiffrin, (1968) classic model of memory

Baddeley, (1992) ‘modern’ model of memory

Ebbinhaus’ retention curve
GOV, NUV, LOM, KEL

Serial Position Effect
Primacy Effect
Recency Effect
Next-in-line Effect

Encoding

MnemonicsPeg wordMethod of lociChunking
1776, 1812, 1861, 1898, 1917, 1941, 1950, 1963, 1991

Storage: Sensory Memory

Short-Term/Working MemoryOn the next slides you will see a
series of numbers. I will also say the numbers out loud. After I say the last number, the numbers will disappear.
Silently, write the numbers, in the exact order, on your paper.

2831

74139

497215

5183926

16953472

362514798

6154983287

89316427513

STM – The Magic #7 +/- 2• Short-Term Memory – memory that
holds onto about seven sensory inputs for about twenty seconds
• An experiment in STM:• Look at each of the following words –
one at a time – for ONLY two seconds. Silently repeat the word as I say it out loud.• When we have gone through all 15
words, then try to reproduce the words, in the correct order, on the piece of paper.

Peach

Book

Sword

Car

Enemy

Mirror

Shoe

Thermometer

Clock

Brick

Bed

Salt

Flower

Calendar

Airplane

Reproduce the list of words in the correct order
1. Peach
2. Book
3. Sword
4. Car
5. Enemy
6. Mirror
7. Shoe
8. Thermometer
9. Clock
10. Brick
11. Bed
12. Salt
13. Flower
14. Calendar
15. Airplane

Long-Term Memory

A Quick Exercise in LTM
Answer the following questions about everyday things that should be in your LTM
1. Whose portrait is on the ten dollar bill?2. What two letters do not appear on a
standard land phone?3. What is the color of the top stripe of the
American flag? 4. The bottom stripe? 5. How many red and how many white
stripes does the flag have?

FeatureSensoryMemory
Working Memory
LTM
Encoding Copy Phonemic Semantic
Capacity Unlimited7±2
ChunksVery Large
Duration 0.25 sec. 20 sec. Years


RetrievalRecall vs. Recognition, Part 1
◦Write down the number of any word that you believe is misspelled.
1. Acomplishment2. Acheivement3. Consolidate4. Consistant5. Reccommend6. Maintainance
Write out the word with the correct spelling.

Recall vs. Recognition, Part 1I
1. Accomplishment2. Achievement3. Consolidate4. Consistent5. Recommend6. Maintenance

More recall vs. recognitionOn the sheet of paper, write
down as many of the names of the seven dwarfs from the Disney version of Snow White and the 7 Dwarfs.

Snow White and the 7 DwarfsSniffy Ziggy Happy
Skippy
Dopey Stumbly DocGiggly
Scooby GrumpyStubby Goofy
Bashful ScrappySleepy Snoozy
Bossy SneezyWheezy Giggles

Watch and listen carefully . . .
G X C O T R L M B W Q

Silently, begin counting backwards by threes from 100 until I tell you to stop.
100 . . . 97 . . . 94 . . .
• G X C O T R L M B W Q

Proactive or Retroactive Interference?
Proactive – (forward-acting) the disruptive effect of prior learning on the recall of new information
Retroactive – (backward-acting) the disruptive effect of new learning on the recall of old information