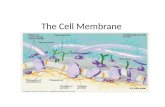
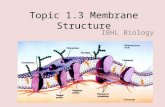
Membrane Structure Fluid like Membrane #1 Phospholipid (#5) -creates bilayer of membrane.
-
Upload
patrick-underwood -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
0
Transcript of Membrane Structure Fluid like Membrane #1 Phospholipid (#5) -creates bilayer of membrane.
Membrane Structure Fluid like Membrane #1 Phospholipid (#5) -creates bilayer of membrane. Three Types of Proteins in Membrane Channels: allow some molecules to pass through Receptors: transfer information from outside cell to inside; once molecule bound to receptor triggers response in cell Markers: help body identify its cells; direct cells to proper location Cell Size Volume vs. Surface Area 1.Organelles would be too far apart if cell was bigger more chances for errors to occur 2.Needs more food and expell more waste Key Points Passive transport Diffusion : movement of particles from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration due to random molecular motion. What Effects the Rate of Diffusion 1-concentration of different substances on each side of the membranes 2-Temperature 3- size of membrane pores 4- size of molecules Situation -diffusion Osmosis diffusion of water Solutions Water diffuses from high to low concentration Isotonic- Concentration of solute is the same inside the cell as it is outside the cell - water flows freely in both directions across membrane Hypotonic- Concentration of solute outside the cell is lower than inside the cell -water enters cell Hypertonic- Concentration of solute is higher outside the cell than it is inside the cell- water leaves cell Hypodermic needle injects water (hypotonic) Plasmolysis Isotonic/Hypotonic/Hypertonic solutions and their cells Active Transport requires cell energy - ATPs Active transport- uses energy Phagocytosis-solids Pinocytosis - liquids Swelling solutes Can fish drown? What type of solution would a fish be placed into to cause its cells to fill-up with water? _____________ What type of solution would a fish be placed into to cause its cells to lose water and dehydrate? _____________ Can fish drown? What type of solution would a fish be placed into to cause its cells to fill-up with water? __Hypotonic_ What type of solution would a fish be placed into to cause its cells to lose water and dehydrate? _Hypertonic___ What does osmosis do for you? Why do you gargle with warm salt water? What does it do to the cells of your throat that are swollen? Why do your fingers wrinkle when your in a pool or in a warm bath? Active transport Phagocytosis-solids Pinocytosis - liquids Respiratory System pg 31 Review G sacs H I Diaphragm & Intercostals change air pressure of the chest cavity Alveoli in the lungs Increase surface area in the lungs to have a larger diffusible area for O2 and CO2 Alveoli gaseous exchange pg 32 Carbon Monoxide poisoning What Organs Are Involved? 1.Kidneys maintains homeostasis; remove wastes; regulate water in the blood and balances various blood components ; receive large amounts of blood to clean! What Organs Are Involved? 2.Ureter carries urine from the kidney to the bladder 3.Bladder Stores urine 4.Urethra used for urine to exit the body 5.Renal Artery blood enters kidney 6.Renal Vein blood exit kidney Packet page 34 stages 1 & 2 (filtration and reabsorption really important stages) Pg 34 packet