Meiosis: Formation of gametes Utilizing BioCoach Activity “Meiosis”
MEIOSIS
description
Transcript of MEIOSIS

Reduction-DivisionGenetic
Recombination
1

The form of cell divisioncell division by which GAMETESGAMETES, , with HALFHALF the number of CHROMOSOMESCHROMOSOMES, , are produced.
DIPLOIDDIPLOID (2n) (2n) HAPLOIDHAPLOID (n) (n) MeiosisMeiosis is SEXUALSEXUAL
reproduction.reproduction. TWOTWO divisions divisions (MEIOSIS IMEIOSIS I and
MEIOSIS IIMEIOSIS II).2

Sex cells divide to produce GAMETESGAMETES (sperm or egg)(sperm or egg).
Gametes have HALFHALF the # of chromosomes.
Occurs only in GONADSGONADS (testes (testes or ovaries).or ovaries).
Male: Male: SPERMATOGENESIS -SPERMATOGENESIS -spermsperm
Female: Female: OOGENESIS - OOGENESIS - egg or ovaegg or ova
3

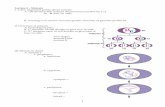
2n=46
humansex cell
diploid (2n)
n=23
n=23
Meiosis I
n=23
n=23
n=23
n=23
sperm
haploid (n)
Meiosis II4

2n=46
humansex cell
diploid (2n)
n=23
n=23
Meiosis I
n=23egg
Haploid (1n)
Meiosis II5
Polar Bodies (die)

Similar to mitosismitosis interphase. CHROMOSOMESCHROMOSOMES (DNA)(DNA) replicate in the S S
phasephase Each duplicated chromosomechromosome consist
of twotwo identicalidentical SISTER SISTER CHROMATIDS CHROMATIDS attached at their CENTROMERESCENTROMERES.
CENTRIOLECENTRIOLE pairs also replicate.
6

Nucleus and nucleolus visiblevisible. Nucleus
nucleolus
cell membrane
chromatin
7

Cell division Cell division that reduces the chromosome number chromosome number by one-half.one-half.
Four phasesFour phases:a.a. Prophase IProphase Ib.b. Metaphase IMetaphase Ic.c. Anaphase IAnaphase Id.d. Telophase ITelophase I
8
Prophase IProphase I

LongestLongest and and most complex most complex phase (90%).phase (90%).
ChromosomesChromosomes condense. SynapsisSynapsis occurs - Homologous chromosomesHomologous chromosomes come togetherto form a tetradtetrad.
TetradTetrad is two chromosomestwo chromosomesor four chromatids four chromatids (sister and non-sister chromatids).
9

10
•Homologs contain DNA that codes for the same genes , but different versions of those genes
•Genes occur at the same loci

Homologous chromosomes
sister chromatids sister chromatidsTetrad11

Pair of chromosomeschromosomes (maternalmaternal and paternalpaternal) that are similar in shape and similar in shape and sizesize..
Homologous pairs ((tetradstetrads) carry ) carry GENES controlling the SAME inherited GENES controlling the SAME inherited traitstraits.
Each locuslocus (position of a gene) (position of a gene) is in the same position on homologues.
HumansHumans have 23 pairs 23 pairs of homologous homologous chromosomes:chromosomes:a. First 22 pairs 22 pairs of autosomesautosomesb. Last pair of sex chromsex chromosomesosomes
12
LOCLOCII

Paternal Maternal
eye color locus
eye color locus
hair color locus
hair color locus
13

Crossing over Crossing over may occur between non-sister chromatidschromatids at sites called chiasmatachiasmata.
Crossing overCrossing over: segments of nonsister chromatidschromatids break and reattach to the other chromatidchromatid.
Chiasmata (chiasma) Chiasmata (chiasma) are where chromosomes touch each other and exchange genes exchange genes (crossing overcrossing over.)
Causes Genetic RecombinationGenetic Recombination
14

nonsister chromatids
chiasmata: site of crossing over
variation
Tetrad
15

16

XX chromosome - female XY chromosome - male
17

Homologs Homologs separateseparate
18
Meiosis Meiosis II

• Nucleus & Nucleolus Nucleus & Nucleolus disappear• SpindleSpindle forms• Chromosomes coilcoil & SynapsisSynapsis
(pairing) occurs• TetradsTetrads form & Crossing over Crossing over Occurs
centriolesspindle fiber
asterfibers
19TETRADTETRAD

Shortest phase Tetrads align on the equator. Independent assortment occurs –
chromosomes separate randomly causing GENETIC RECOMBINATION
20

Homologs line up at equator or metaphase plate
OR
21

Formula: 2n
Example:Example: 2n = 42n = 4 then then 1n = 21n = 2 thusthus 222 2 = 4= 4
combinations combinations
22

In terms of In terms of Independent Independent AssortmentAssortment -how many -how many different combinations of different combinations of sperm could a sperm could a humanhuman malemale produce? produce?
23

Formula: 2Formula: 2nn
Human chromosomes:Human chromosomes:2n = 462n = 46
n = 23n = 23 222323 = ~8 million = ~8 million combinationscombinations
24

Homologous chromosomes Homologous chromosomes separate and move towards the poles.
Sister chromatids Sister chromatids remain attached at their centromerescentromeres.
25

26
HomologsHomologs separate separate

Each pole now has haploidhaploid (1n) set of chromosomeschromosomes.
CytokinesisCytokinesis occurs and two haploid daughter cells are formed.
27

28
cytokinesis

Sister Sister Chromatids Chromatids SeparateSeparate
29
Meiosis IIMeiosis II

No Interphase II No Interphase II or very or very shortshort
No DNA ReplicationNo DNA Replication Remember: Meiosis II is Remember: Meiosis II is
similar to mitosissimilar to mitosis
30

Same as Same as ProphaseProphase in in mitosismitosis
Nucleus & nucleolus disappearNucleus & nucleolus disappear Chromosomes condenseChromosomes condense Spindle formsSpindle forms
31

Same as Metaphase in mitosis
Chromosomes (not homologs) line up at equator32

Same as AnaphaseAnaphase in mitosismitosis
SISTER CHROMATIDS SISTER CHROMATIDS separateseparate
33

Same as Same as TelophaseTelophase in mitosis. in mitosis. Nuclei and Nucleoli Nuclei and Nucleoli reform, spindle reform, spindle
disappearsdisappears CYTOKINESISCYTOKINESIS occurs. occurs. Remember: Remember: FOUR HAPLOID FOUR HAPLOID
DAUGHTER cells DAUGHTER cells are produced.are produced.
Called Called GAMETESGAMETES (eggs and sperm) (eggs and sperm)
34
1n Sperm cell fertilizes 1n
egg to form 2n zygote

35

36

Also known as Also known as GENETIC GENETIC RECOMBINATIONRECOMBINATION
Important to population as the raw Important to population as the raw material for material for NATURAL SELECTION.NATURAL SELECTION.
All organisms are All organisms are NOTNOT alike alike StrongestStrongest “ “most fit” most fit” survive to survive to
reproduce & pass on traitsreproduce & pass on traits
37

What are the What are the 33 sources of sources of genetic recombination genetic recombination or or variation? variation?
38

1.1. CROSSING OVER CROSSING OVER (prophase (prophase I)I)
2.2. INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT (metaphase I)(metaphase I)
3.3. RANDOM FERTILIZATIONRANDOM FERTILIZATION
39

A cell containing 20 20 chromosomeschromosomes (diploid)(diploid) at the beginning of meiosis would, at its completion, produce cells containing how many chromosomeschromosomes?
40

1010 chromosomes (haploid chromosomes (haploid or 1n)or 1n)
41

AAn organized organized picture picture of the chromosomes of a human arranged in pairs arranged in pairs by size by size from largest to smallest.
PPairs 1-221-22 called AUTOSOMESAUTOSOMES
LLast pair are SEX SEX CHROMOSOMESCHROMOSOMES
42
Male - XYMale - XY

43Female - XXFemale - XX

44Female - XXFemale - XXDown Syndrome –
Trisomy 21

The fusion of a spermsperm and eggegg to form a zygotezygote.
A zygote is a FERTILIZED EGGFERTILIZED EGG
n=23egg
sperm n=23
2n=46zygote
45

A cell containing 40 40 chromatidschromatids at the beginning of meiosis would, at its completion, produce cells containing how many chromosomeschromosomes?
46

10 chromosomes10 chromosomes
47

48