Mathematical Modeling of Signal Transduction Pathways Biplab Bose IIT Guwahati.
-
Upload
reynold-cole -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
5
Transcript of Mathematical Modeling of Signal Transduction Pathways Biplab Bose IIT Guwahati.

Mathematical Modeling of
Signal Transduction Pathways
1
1
. .( )
( )
k T
m T
k E Y YpdYp dt
K Y Yp
Biplab Bose
IIT Guwahati

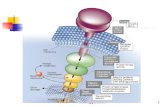
Cellular Communication
Ligand
Receptor
Rel
ay
Output
Message
FunctionE
ncod
ing/
Dec
odin
g
Image: BioCarta

Encoding-decoding in Dynamics
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011, 12(2):104-17.Cell. 1995, 80(2):179-85.

Why Model?
• To understand empirical observations
• To generate new hypothesis

Linear Network Network with Negative Feedback
Signaling beyondsaturation
PLoS Comput Biol 4(10): e1000197

Weber’s Law
Weber’s Law in Signaling
min tanbackground
sCons t
S
Circuit that senses only fold change
Mol Cell. 2009, 36(5):724-7

Deterministic Modeling
• Assumes that the system is large
• Uses Law of Mass Action
• Homogenous system: Ordinary Differential
Equation (ODE)
• Non-homogenous system: Partial Differential
Equation (PDE)

1 2
[ ][ ][ ] [ ]
d Ck A B k C
dt
production degradation
3 4
3 4
[ ]([ ] [ ]) [ ][ ][ ]
([ ] [ ]) [ ]T
m T m
k C D pD k E pDd pD
dt k D pD k pD
Deterministic Modeling
System of ODEs
[A], [B] and [E] considered constant

Deterministic Modeling
Solve the ODEs
Analytical solution
Numerical solution
[C]
[pD]

1 2
[ ][ ][ ] [ ]
d Ck A B k C
dt
3 4
3 4
[ ]([ ] [ ]) [ ][ ][ ]
([ ] [ ]) [ ]T
m T m
k C D pD k E pDd pD
dt k D pD k pD
Modeling Strategy
Model
Data
Estimate parameters
Simulate to predict
Images: Mol Cell. 2012, 46(6):820-32.

X
Yp
Sustained signaling: both X and Yp reach steady state
Simple but Complex

The system has memoryCan lead to two population of cells
Simple but Complex

IRS1
PI3K
Akt
mTOR
Insulin/IGF-1
The mTor Story
Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007,6(11):871-80

Database Web Address
KEGG http://www.genome.jp/kegg
REACTOME http://www.reactome.org/ReactomeGWT/entrypoint.html
PATHWAY INTERACTION DATABASE (PID)
http://pid.nci.nih.gov
PANTHER http://www.pantherdb.org/pathway
WikiPathways http://www.wikipathways.org
SMPDB http://www.smpdb.ca
Pathway Database

The parameters
http://bionumbers.hms.harvard.edu/

Database Web Address
BioModels http://www.ebi.ac.uk/biomodels-main
CellML http://www.cellml.org/models
JWS Online http://jjj.biochem.sun.ac.za/index.html
Model Database

Tools forDynamic Simulation
• JSim• COPASI• GEPASI• CellDesigner
• MATLAB• Mathematica
Extended list: Biochimie. 2006, 88(3-4):277-83.

Stochasticity in Chemical Reaction
Conventional reactions involve large number of molecules
A + B C
[ ].[ ].[ ]
d Ck A B
dt
Follows Law of Mass Action
When number of molecules is low
Can not apply Law of Mass Action
Uncertainty in reactions

Some misconceptions about random/stochastic process:
Any thing can happen.
Things are mixed-up
Does not have cause-and-effect relation.
We can not make predictions.
What is Random?

What is Random?
Random walk in Brownian motion
1. Water molecules are in motion.
2. Hit each other and the pollen.
3. Classical mechanics can be used to
understand (approximately)
trajectories due to collisions.
Facts:
Problem:
We do not (or can not have) have exact information of the system (ie. position and momentum of each particle)
Consequence:1. Can not predict exact trajectory. 2. Get surprised by the movement of the pollen3. Call this random or stochastic process
Image source: wikipedia

Beyond uncertainties
1. We can calculate average
behaviour
2. We can calculate
probability of an outcome
3. We can calculate
distribution of outcomes F
requ
ency
Displacement
Can not calculate exact displacement of a pollen in a particular duration
But Can calculate the PROBABILITY of a particular amount of displacement.
What is Random?

Protein expression similar to coin toss:You may get Head or Tail in a tossAt one moment cell may make one copy protein or not
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 5
Cell 1
Cell 2
Y Y Y
Y YY Y
N N
N
1 2 3 4 5
time
time
time
Pro
tein
num
ber
1
2
3
4
5
Protein Expression Like Coin Toss

Stochasticity in Gene Expression

Linear Circuit
Positive feedback
Transcriptional Circuit Affects Expression Heterogeneity
PLoS ONE. 2015 10(2): e0116748

Modeling Stochastic Systems
Kinetic Monte Carlo
Gillespie algorithm
MATLAB
Dizzy
StochSim
STOCKS

Constrains of Dynamic Modeling
Difficult to model very large system
Difficulty in parameter estimation:
How to design experiment?How to estimate parameters?
Problem in connecting different scales