Mandible, temperomandibular joint & muscle of mastication (M.C.Qs.)
-
Upload
scarlet-chaney -
Category
Documents
-
view
45 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Mandible, temperomandibular joint & muscle of mastication (M.C.Qs.)
Mandible, temperomandibular joint & muscle of mastication (M.C.Qs.)
By
Prof. Samir Malik
Dental students
M.C.Qs.The muscles attache to the both surface of the mandible are one of the following?A-5 muscles.B-6 muscles.C-7 muscles.D-9 muscles.
Answer:The muscles attache to the both surface of the mandible are one of the following?A-5 muscles.B-6 muscles.C-7 muscles.D-9 muscles.
Answerplatysma n.supply: facial nerve.Mentalis ,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,Buccinator ,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,, Temporalis Trigeminal nerve.
M.C.Qs.The condylar process of the mandible showing all the following are true except one sentence is wrong?A-neck.B-pterygoid fovea.C-HeadD-shaft.
AnswerThe condylar process of the mandible showing all the following are true except one sentence is wrong?A-neck.B-pterygoid fovea.C-HeadD-shaft.
Answer :Lingual nerveInferior alveolar nerveNerve to mylohyoidMental nerve.Mandibular branches of facial nerve..Auriculotemperal nerve.
Answer:Abovegenohyoid musclesublingual glandbelow;anterior belly of the digastric muscle& submandibular gland
The temporal fossa above zygomatic arch? A-true B-false.The infratemporal fossa above the zygomatic arch? A-true B-false
AnswerThe temporal fossa above zygomatic arch? A-true B-false.The infratemporal fossa above the zygomatic arch? A-true B-false
M.C.QsWhich structure dividing the temperomandibular joint into two cavities; upper &lower?A-intrarticular disc.B-tendon.C-ligamentsD-menisci.
Answer:Which structure dividing the temperomandibular joint into two cavities; upper &lower?A-intrarticular disc.B-tendon.C-ligamentsD-menisci.
M.C.Qs.The mental foramen of the mandible in the extremity of the age lying near?A-alveolar processB-lower borderc-near the ramusd-near the symphysis menti
Answer The mental foramen of the mandible in the extremity of the age lying near?A-alveolar processB-lower borderc-near the ramusd-near the symphysis menti
M.C.Qs.The elevation of the temperomandibular joint (T.M.J.) is done by the following muscle except one muscle doesnot charing in elevation?A-Temporalis Muscle .B-Masseter muscle .C-Medial pterygoid muscleD-Auricularis superior muscle
Answer:The elevation of the temperomandibular joint (T.M.J.) is done by the following muscle except one muscle doesnot charing in elevation?A-Temporalis Muscle .B-Masseter muscle .C-Medial pterygoid muscleD-Auricularis superior muscle
M.C.Qs.The protrusion of the mandible is caused by one of the following ? A-lateral pterygoid muscle assisted by medial pterygoid . B- posterior belly of digastric muscle & stlyohyoid muscle.C-orbicularis oris & mentalis muscle D-mylohyoid & genohyoid
Answer.The protrusion of the mandible is caused by one of the following ? A-lateral pterygoid muscle assisted by medial pterygoid . B- posterior belly of digastric muscle & stlyohyoid muscle.C-orbicularis oris & mentalis muscle D-mylohyoid & genohyoid
M.C.Qs.The depression of the mandible is done by the following factor except one is wrong?A-Gravity.B-mylohyoid & genohyoid muscles.C-masseter muscle.D-Digastric muscle
Answer:The depression of the mandible is done by the following factor except one is wrong?A-Gravity.B-mylohyoid & genohyoid muscles.C-masseter muscle.D-Digastric muscle
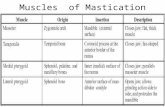
• 2- Masseter :
origin inner surface &lower border of zygomatic arch.
Insertion outer surface of ramus .
Nerve supply:massetric n.(first branchial arch)
1-TEMPRALIS MUSCLE
• Origin temporal fossa ,fascia & inbetween 2 temporal lines
• Insertion: cronoid process
• Nerve supply from deep temporal nerves; 1st branchial arch.
4-MEDIAL PTRYGOID
• Origin:deep head inner surface of lateral (medial) ptrygopid plate
• Superficial head: tuberosity of maxilla
• Insertion :inner surface of angle of mandible; 1st pharyngeal arch.
3-LATERAL PTRYGOID
• Origin:upper head infratemporal surface of greater wing of the sphenoid bone.
• lower head outer surface of lateral ptrygoid plate.
• Insertion: neck of the condyle ,ptrygoid fovea & capsule of TMJ.
• Nerve supply from mandibular nerve.
Mandibular NerveMandibular Nerve•The largest division of the trigeminal nerve•A mixed nerve, sensory and motor root•leave through the Foramen Ovale•Below the foramen ovale, the 2 roots unite to form the trunk of the nerve•Divides into anterior & posterior divisions•The ant. is mainly motor•The post. is mainly sensory
Branches:From the trunk:• Nerve to medial pterygoid (motor):
supply the tensor palati and tensor tympani ms & medial pterygoid • Nervus spinosus (sensory) for meninges
Passes through Foramen spinosum into the cranial cavity
Motor & sensory rootsof mandibular n
Nervusspinosus
Lesserpetrosal n.
Auriculotemporal n.
Chorda tympani
Inferior alveolar n.
Mylohoid nerve
Medial pterygoid
Lingual n.
Tensor palati
Otic ganglion
Tensor tympani
Ant. Division:
3 motor branches for muscles of mastications
•Deep temporal nerves (temporalis ms)
•Nerve to masseter
•Nerve to lateral pterygoid
one sensory branch•Buccal nerve (sensory): supplies skin over the buccinator, and mucosal lining of buccinator ms.
Deep temporalnerves
Buccal nerve
Lingualnerve
Inferior alveolarnerve
Auriculotemporalnerve
Posterior division: sensory branches 1.Auriculotemporal nerve• arises by 2 roots (which embrace the middle
meningeal artery) and passes backwards deep to the neck of the mandible
• supplies the scalp• sensory the parotid gland and carries
postganglionic parasympathetic to the parotid gland
Deep temporalnerves
Buccal nerve
Lingualnerve
Inferior alveolarnerve
Auriculotemporalnerve
2. Lingual nerve• Joined by the chorda tympani• Carries general sensations from the anterior 2/3 of
the tongue• The chorda tympani carries taste sensations from
the anterior 2/3 of the tongue and preganglionic parasympathetic fibres to the submandibular and sublingual glands
3. Inferior alveolar nerve•Runs behind the lingual nerve to reach mandibular foramen•The inferior alveolar nerve continues through mandibular canal and divides into mental and incisive branches
•The mental branch comes out of the mental foramen to supply skin of the chin•Before it passes through the mandibular foramen it gives the mylohyoid nerve (motor)
•The mylohyoid nerve supplies the mylohyoid muscle and anterior belly of digastric
Lingual nerveInferior alveolarnerve
Mylohoid nerve& vessels Mylohoid m.
•deep temporal (dt)
• auriculotemporal (at)
•inferior alveolar (ia)
•nerve to the mylohyoid (nmh)
•lingual (l)
•buccal (b)
Mandibular NerveMandibular Nerve
Recall of relevant structures
Muscles of the masticatory apparatus
masseter muscle
temporalis muscle
pterygoid muscles, medial and lateral
Highlight
• Temporalis superficial temporal vessels auricular temporal nerve N B P
• Masseter parotid parotid duct
• Medial ptrygoid lingual&inferior alveolar nerves
• Lateral ptrygoid parts of maxillary artery
Highlight• The disc is avascular in the centre so ,the
regenerative power is low.
• The disc is composed of dense collagen fibers only in its centre but in posterior & anterior ends it contains elastic fibers
• Synovial membrane has 3 types of cells :type A(fibroblast like cell) ,type B(macrophage like ) and intermediate cell.
• The disc having two nodules