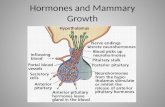
Mammals Chapter 32 What’s a mammal? hair mammary glands breathe air and have a diaphragm 4 chamber...
-
Upload
brent-small -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of Mammals Chapter 32 What’s a mammal? hair mammary glands breathe air and have a diaphragm 4 chamber...

Mammals Chapter 32

What’s a mammal?
• hair• mammary glands• breathe air and have a diaphragm• 4 chamber heart/ double loop circulation• endotherms

Evolution
• -first mammals appeared 220 million years ago, very small creatures
• - stayed small until dinosaurs died out, then underwent a burst of adaptive radiation in Cenozoic era


Characteristics
• Body temp control- allows mammals to move at night and in dark
• -endotherms
• -sweat glands for cooling, dogs pant instead, pigs wallow in mud
• -subcutaneous fat- under skin, insulates
• -high metabolism to generate internal heat

Feeding • eats 10 times as much food as a reptile of same size• some whales are filter feeders• omnivores/carnivores/ herbivores• early mammals ate insects• stronger jaws to support teeth: molars, premolars,
canines, incisors• carnivores-short intestines, herbivores- long intestines• Cows and their relatives have a stomach chamber
called “rumen” that holds symbiotic bacteria that helps with digestion

Respiration
• breathe air using diaphragm and chest muscles/ribs
Wake up!!

Circulation
• 4 chamber/ double loop

Excretion
• kidneys- extract nitrogenous waste in the form of urea. Urea and other waste mixed with water to become urine. Urine moves to urinary bladder for storage. Kidneys retain sugars, salts, and other compounds. (urine test)

Response
• -“Most highly developed brains?” • -3 parts: cerebrum, cerebellum, medulla
oblongata• -cerebrum-complicated behaviors such as
thinking and learning• -cerebellum- muscular coordination• -medulla oblongata-involuntary controls such as
breathing and heart rate• -highly refined senses: bloodhounds’ sense of
smell, bats’ hearing, color vision,

Movement
• backbone that flexes in many dimensions
• shoulder and pelvic girdles
• run, walk, climb, burrow, hop, pounce, swing, fly, leap, swim, etc.

Reproduction • internal fertilization• Oviparous- “monotremes”- duck bill platypus and 2
species of spiny anteaters• Viviparous- 1) “marsupials”- young crawls into
pouch before full grown – 2) “placentals”- young develops full term in
uterus