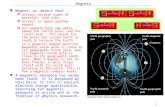
Magnets. Magnetic poles Magnets have two poles with opposite polarity (north and south poles).
Magnetism. Magnetism Magnets have two poles that attract opposite poles and repel similar Magnets...
-
Upload
james-houston -
Category
Documents
-
view
243 -
download
5
Transcript of Magnetism. Magnetism Magnets have two poles that attract opposite poles and repel similar Magnets...

MagnetismMagnetism

MagnetismMagnetism• Magnets have two poles Magnets have two poles that attract opposite poles that attract opposite poles and repel similarand repel similar
• Domains are alignedDomains are aligned• Has a magnetic fieldHas a magnetic field• Easy to detect magnetism, although it is not easy to measure its Easy to detect magnetism, although it is not easy to measure its
strengthstrength• Make a magnet by rubbing steel against another magnetMake a magnet by rubbing steel against another magnet

Properties of Magnetism
• Magnetism is a force that attracts iron, nickel and cobalt
• Combinations of these metals as alloys can become permanent sources of magnetism
• A lodestone is the naturally occurring magnetite that has the chemical formula Fe3O4

Two Poles•Opposite ends of a magnet are
called its north and south poles–should be called the "north seeking" and "south seeking" poles, because they seek the Earth's North Pole and South Pole, respectively
•Like poles repel–north pole of magnet will push the north pole of another magnet

What is attracted to the north end What is attracted to the north end of the magnet?of the magnet?
A) The northA) The north
B) The southB) The south
C) The east C) The east
D) The westD) The west

What do similar poles do?What do similar poles do?A. AttractA. AttractB. RepelB. RepelThey meltThey meltThey expandThey expand

MagnetismMagnetism• Magnets have two poles that attract opposite poles and repel Magnets have two poles that attract opposite poles and repel
similarsimilar
• Domains are alignedDomains are aligned• Has a magnetic fieldHas a magnetic field• Easy to detect magnetism, although it is not easy to measure its Easy to detect magnetism, although it is not easy to measure its
strengthstrength• Make a magnet by rubbing steel against another magnetMake a magnet by rubbing steel against another magnet

Magnetic Field Nature• Magnetism
originates in the motion of the electrons
• Spinning electrons act like tiny magnets
• Cancellation of this effect occurs in most materials
• Iron, nickel, cobalt are exceptions

Magnetic Domains• The magnetic
north-south axes of groups of iron atoms line up in the same direction– Magnetic domains
• Domains are randomly oriented unmagnetized iron

Magnetization• An external magnetic
field will twist the domains into alignment– Domains are
randomly oriented in unmagnetized iron
– Incomplete alignment of domains in slightly magnetized iron
– Virtually all of the domains are aligned in strongly magnetized iron

Make a magnet by rubbing iron against another magnet

What are magnetic domains?What are magnetic domains?
A. Atoms randomly alignedA. Atoms randomly aligned
B. Electrons flowing in an ironB. Electrons flowing in an iron
C. Moving electric charge C. Moving electric charge
D. Clusters of protonsD. Clusters of protons
E. Clusters of aligned atomsE. Clusters of aligned atoms

Which of the following domain is Which of the following domain is the strongest magnet?the strongest magnet?
A. Electrons spinning in opposite directions A. Electrons spinning in opposite directions
B. Electrons spinning in the same directionB. Electrons spinning in the same direction
C. Electrons merging with protonsC. Electrons merging with protons
D. Half a magnetD. Half a magnet
E. Electrons not spinning E. Electrons not spinning

How is a magnetic field produced?How is a magnetic field produced?
A. flow of electrons and neutronsA. flow of electrons and neutrons
B. motion of electric chargeB. motion of electric charge
C. force exerted by the polesC. force exerted by the poles
D. path of magnetic domainsD. path of magnetic domains

A magnet is broken into two equal A magnet is broken into two equal pieces. What happens to each piece?pieces. What happens to each piece?
A. One piece stays magnetized while the other A. One piece stays magnetized while the other becomes unmagnetized.becomes unmagnetized.
B. One piece is stronger than the otherB. One piece is stronger than the other
C. Each piece retains equally strong polesC. Each piece retains equally strong poles
D. One piece acquires the North Pole while D. One piece acquires the North Pole while the other has the South Pole. the other has the South Pole.

MagnetismMagnetism• Magnets have two poles that attract opposite poles and repel Magnets have two poles that attract opposite poles and repel
similarsimilar• Domains are alignedDomains are aligned
• Has a magnetic field Has a magnetic field • Easy to detect magnetism, although it is not easy to measure its Easy to detect magnetism, although it is not easy to measure its
strengthstrength• Make a magnet by rubbing steel against another magnetMake a magnet by rubbing steel against another magnet

Detecting Magnetic Detecting Magnetic FieldField
• Iron filings on a Iron filings on a piece of paper piece of paper – Spread fine iron Spread fine iron
filings on a filings on a piece of paper piece of paper laid on top of a laid on top of a magnetmagnet• Outline of the Outline of the
magnetic lines magnetic lines of force or the of force or the magnetic fieldmagnetic field

Detecting Magnetic Detecting Magnetic FieldField
• Compass Compass – Thin magnet or Thin magnet or
magnetized iron magnetized iron needle balanced needle balanced on a pivoton a pivot
– needle will rotate needle will rotate to point toward to point toward the opposite pole the opposite pole of a magnetof a magnet
– One end marked One end marked N and the other SN and the other S

A Compass →Magnetic A Compass →Magnetic FieldField

Electric Currents and Electric Currents and Magnetic FieldMagnetic Field33
• Magnetic field lines around a long wire Magnetic field lines around a long wire which carries an electric current form which carries an electric current form concentric circles around the wireconcentric circles around the wire
• The direction of the magnetic field is in The direction of the magnetic field is in the direction the fingers if your right the direction the fingers if your right hand curls around the wire with your hand curls around the wire with your thumb in the direction of the currentthumb in the direction of the current

Iron Filings form Iron Filings form Concentric Circles around Concentric Circles around
WireWire

Electric Currents and Magnetic Electric Currents and Magnetic FieldField

Electric Currents and Electric Currents and Magnetic FieldMagnetic Field
• Spinning or rotating Spinning or rotating electrons are electrons are responsible for responsible for magnetism in ironmagnetism in iron
• Moving charges set up Moving charges set up magnetic fieldsmagnetic fields
• Compasses (bar Compasses (bar magnets) line up in magnets) line up in circles around a wire circles around a wire carrying current.carrying current.

Which of these are not used to find Which of these are not used to find magnetism?magnetism?
A) A compassA) A compass
B) A wire with current B) A wire with current
C) An ammeter C) An ammeter
D) Iron fillingsD) Iron fillings

The direction of the field arrows outside The direction of the field arrows outside the magnet isthe magnet is
A. From the north to the south poleA. From the north to the south pole
B. From the south to the north poleB. From the south to the north pole
C. From the center to both polesC. From the center to both poles

Which of these are not used to find Which of these are not used to find magnetism?magnetism?
A) A compassA) A compass
B) A wire with current B) A wire with current
C) An ammeter C) An ammeter
D) Iron fillingsD) Iron fillings

How do you detect magnetic field How do you detect magnetic field direction?direction?
A) A thermometerA) A thermometer
B) A compassB) A compass
C) A metal detector C) A metal detector
D) An ammeterD) An ammeter

What are the three elements that are What are the three elements that are magnetic?magnetic?
A) Iron, Nickel, and CopperA) Iron, Nickel, and Copper
B) Nickel, Zinc, and CopperB) Nickel, Zinc, and Copper
C) Copper, Cobalt, ZincC) Copper, Cobalt, Zinc
D) Iron, Nickel, and CobaltD) Iron, Nickel, and Cobalt

MagnetismMagnetism• Magnets have two poles that attract opposite poles and repel Magnets have two poles that attract opposite poles and repel
similarsimilar• Domains are alignedDomains are aligned• Has a magnetic fieldHas a magnetic field
• Easy to detect Easy to detect magnetism, although it is magnetism, although it is not easy to measure its not easy to measure its strengthstrength
• Make a magnet by rubbing steel against another magnetMake a magnet by rubbing steel against another magnet

Measuring Magnetic Measuring Magnetic Strength Strength
• The average flux density in the Earth's outer core was calculated to be 25 Gauss.
• The earth's magnetic field is 0.5 Gauss
• A refrigerator magnet is 10 Gauss

What is used to measure magnetism?What is used to measure magnetism?
A) AmmeterA) Ammeter
B) Compass B) Compass
C) Gage meterC) Gage meter
D) Gauss meter D) Gauss meter
E) B and DE) B and D

What causes a current measuring What causes a current measuring apparatus to work?apparatus to work?
A) magicA) magic
B) A device measures electronsB) A device measures electrons
C) Current pushes a spring C) Current pushes a spring
D) A current makes a magnetD) A current makes a magnet

MagnetismMagnetism• Magnets have two poles that attract opposite poles and repel Magnets have two poles that attract opposite poles and repel
similarsimilar• Domains are alignedDomains are aligned• Has a magnetic fieldHas a magnetic field• Easy to detect magnetism, although it is not easy to measure its Easy to detect magnetism, although it is not easy to measure its
strengthstrength
• Make a magnet by Make a magnet by rubbing steel against rubbing steel against another magnetanother magnet

Make a magnet by rubbing Make a magnet by rubbing iron against another magnetiron against another magnet

Make a Make a magnet by magnet by
cooling cooling molten iron molten iron
in a magnetic in a magnetic fieldfield

Uses of MagnetismUses of Magnetism• LevitationLevitation• Forces Through a Magnetic FieldForces Through a Magnetic Field
• Earth Magnetic FieldEarth Magnetic Field
• The SunThe Sun

Magnetic LevitationMagnetic Levitation• Trains float above guide Trains float above guide
way due to magnetic fieldway due to magnetic field• Travel at speeds of up to Travel at speeds of up to
300 mph (500 kph)300 mph (500 kph)

39
RailgunRailgun• Electromagnetic current is used to accelerate a
nonexplosive bullet at several times the speed of sound. • Projectile zips along a set of electrically charged parallel
rails and out of the barrel at speeds up to 5000 mph or Mach 7
• The result: a weapon that can hit a target 100 miles or more away within minutes.
Read more: http://www.foxnews.com/scitech/2010/12/10/navy-railgun-shoots-bullets-electromagnet/#ixzz1S7fXUGB0

40
Space Launch System Space Launch System There is a proposed plan that would start with launching a drone like those the Air Force uses. More advanced models would follow until they are ready to build one that can launch a small satellite into orbit.
38

What is a true example of What is a true example of levitation? levitation?
A) magic carpetA) magic carpet
B) A magicianB) A magician
C) A magnetic trainC) A magnetic train
D) A helicopter hoveringD) A helicopter hovering

How does the Superman ride work?How does the Superman ride work?
A) A rocketA) A rocket
B) A lift chainB) A lift chain
C) Magnetic fields C) Magnetic fields
D) Differences in pressureD) Differences in pressure

Uses of Uses of MagnetismMagnetism• LevitationLevitation
• Forces Through a Forces Through a Magnetic FieldMagnetic Field
• Earth Magnetic FieldEarth Magnetic Field
• The SunThe Sun

Magnetic Forces on Moving Charged Magnetic Forces on Moving Charged ParticlesParticles
If charge particles move in a magnetic field, If charge particles move in a magnetic field, they experience a sideways forcethey experience a sideways force

Magnetic Forces on Current Magnetic Forces on Current Carrying WiresCarrying Wires
• Moving electrons in wire are pushed up, or Moving electrons in wire are pushed up, or down, depending on their directiondown, depending on their direction

Measuring CurrentsMeasuring Currents• Coils of current-carrying wires set up Coils of current-carrying wires set up
magnetic field perpendicular to plane of coilmagnetic field perpendicular to plane of coil• Compass needle aligns itself with the field Compass needle aligns itself with the field
lines lines

Current-Measuring ApparatusCurrent-Measuring Apparatus
• Electromagnet tends to Electromagnet tends to align its north face align its north face with the iron magnet's with the iron magnet's south facesouth face
• A spring resists this A spring resists this tendency to twist; the tendency to twist; the greater the current, the greater the current, the greater the deflection greater the deflection of the needleof the needle

If current carrying wire travels If current carrying wire travels through a magnet how does the through a magnet how does the
current bend?current bend?
A) UpA) Up
B) DownB) Down
C) BothC) Both
D) NeitherD) Neither

The direction of the magnetic force is The direction of the magnetic force is always________ to both the magnetic field always________ to both the magnetic field lines and the velocity of charged particle.lines and the velocity of charged particle.
A. PerpendicularA. Perpendicular
B. ParallelB. Parallel
C. There is no correlationC. There is no correlation
D. Both parallel and perpendicularD. Both parallel and perpendicular

What decides whether the wires go up What decides whether the wires go up or down?or down?
A) Their directionA) Their direction
B) Their massB) Their mass
C) Their energyC) Their energy
D) Their speedD) Their speed

If the direction of current in the wire is If the direction of current in the wire is reversed:reversed:
A. The deflecting force acts in the opposite A. The deflecting force acts in the opposite directiondirection
C. The deflecting force acts in the same C. The deflecting force acts in the same directiondirection
B. The deflecting force acts both, in the B. The deflecting force acts both, in the opposite and same directionopposite and same direction
D. The deflecting force acts perpendicular to D. The deflecting force acts perpendicular to the directionthe direction

Uses of Uses of MagnetismMagnetism• LevitationLevitation
• Forces Through a Magnetic FieldForces Through a Magnetic Field
• Earth Magnetic FieldEarth Magnetic Field• The SunThe Sun

Earth as a Giant magnetEarth as a Giant magnet• Earth's magnetic field is thought to be Earth's magnetic field is thought to be
generated deep inside the planetgenerated deep inside the planet• An inner core of solid iron is surrounded by An inner core of solid iron is surrounded by
an outer core of molten ironan outer core of molten iron• They rotate at different rates, and the They rotate at different rates, and the
interaction between the regions creates what interaction between the regions creates what scientists call a "hydromagnetic dynamo."scientists call a "hydromagnetic dynamo."

Earth’s Magnetosphere Earth’s Magnetosphere LayerLayer44
• Also named Van Allen Belts Also named Van Allen Belts • Protects the Earth from celestial bodies, Protects the Earth from celestial bodies,
harmful cosmic rays and particlesharmful cosmic rays and particles• Belts at thousands of kilometers above the Belts at thousands of kilometers above the
earth protect the living things on the Earth earth protect the living things on the Earth
from the fatal energy from the fatal energy that would otherwise that would otherwise
reach it from spacereach it from space

Earth’s Magnetic FieldEarth’s Magnetic Field55
• The Earth has a The Earth has a magnetic field with magnetic field with north and south polesnorth and south poles– reaches 36,000 miles reaches 36,000 miles
into space. into space. – surrounded in a surrounded in a
region called the region called the magnetospheremagnetosphere
– prevents most of the prevents most of the particles from the sun, particles from the sun, carried in solar wind, carried in solar wind, from hitting the Earthfrom hitting the Earth

AuroraAurora• High Speed electrons
and protons from space travel along magnetic field lines
• Field lines are nearly horizontal near the equator which protects the atmosphere
• The field lines are nearly vertical at high latitude, thus the high speed particles can enter the atmosphere



Magnetic Pole LocationMagnetic Pole Location• Location of magnetic pole is not fixedLocation of magnetic pole is not fixed• Geographic north is called the Earth's Geographic north is called the Earth's
North Magnetic Pole by conventionNorth Magnetic Pole by convention• The North Magnetic Pole is actually the The North Magnetic Pole is actually the
south pole of the Earth's magnetic fieldsouth pole of the Earth's magnetic field– the north pole of a compass was defined the north pole of a compass was defined
as the pole that points to the geomagnetic as the pole that points to the geomagnetic northnorth


Earth’s Magnet FlipsEarth’s Magnet Flips• Magnetosphere can flip its orientation so that the Magnetosphere can flip its orientation so that the
field lines which were pointed toward the north field lines which were pointed toward the north pole change and point toward the south polepole change and point toward the south pole– record preserved in magnetic rocks which lie along record preserved in magnetic rocks which lie along
the ocean floorthe ocean floor
• Magnetism in these rocks points first in one Magnetism in these rocks points first in one direction, then in another direction, giving the direction, then in another direction, giving the ocean floor a stripped appearance (from a ocean floor a stripped appearance (from a magnetic point of viewmagnetic point of view– many times in the past the north pole has become the many times in the past the north pole has become the
south pole, and vice versasouth pole, and vice versa


Where is the location of the north Where is the location of the north magnetic pole of the Earth? magnetic pole of the Earth?
A) At the EquatorA) At the Equator
B) Bermuda Triangle B) Bermuda Triangle
C) Hudson BayC) Hudson Bay
D) In AustraliaD) In Australia

What two components make up the magnetic declination:
A. The magnetic pole and the Northern Hemisphere
B. The orientation of a compass and true north
C. The direction of the force and its magnetic field lines
D. The magnetic fields and its current

What is another name for earth’s What is another name for earth’s magnetosphere?magnetosphere?
A) The asteroid beltA) The asteroid belt
B) The Van Allen beltsB) The Van Allen belts
C) The Van Halen beltsC) The Van Halen belts
D) The VanderbeltsD) The Vanderbelts

The location of magnetic poles is The location of magnetic poles is fixed. fixed.
A) trueA) true
B) falseB) false

Uses of Uses of MagnetismMagnetism• LevitationLevitation
• Forces Through a Magnetic FieldForces Through a Magnetic Field
• Earth Magnetic FieldEarth Magnetic Field
• The SunThe Sun


Sun’s Magnet FieldSun’s Magnet Field• The Sun is a big magnetThe Sun is a big magnet• During solar minimum the Sun's magnetic During solar minimum the Sun's magnetic
field resembles that of an iron bar magnet, field resembles that of an iron bar magnet, with great closed loops near the equator and with great closed loops near the equator and open field lines near the polesopen field lines near the poles
• The Sun's dipolar field is about as strong as The Sun's dipolar field is about as strong as a refrigerator magnet, or 50 gaussa refrigerator magnet, or 50 gauss
• Earth's magnetic field is 100 times weakerEarth's magnetic field is 100 times weaker

SunspotsSunspots• Sunspots are places where intense magnetic Sunspots are places where intense magnetic
loops -- hundreds of times stronger than the loops -- hundreds of times stronger than the ambient dipole field -- poke through the ambient dipole field -- poke through the photospherephotosphere
• Sunspot magnetic fields overwhelm the Sunspot magnetic fields overwhelm the underlying dipoleunderlying dipole
• The Sun's magnetic field isn't confined to The Sun's magnetic field isn't confined to the immediate vicinity of our starthe immediate vicinity of our star
• The solar wind carries it throughout the The solar wind carries it throughout the solar systemsolar system


Magnetic Fields on the Magnetic Fields on the SunSun
The Earth fits inside the loop
• Plasma, like iron Plasma, like iron filings, follows filings, follows magnetic field magnetic field lineslines
• Coronal loops Coronal loops created by hot, created by hot, glowing plasma glowing plasma flow along flow along magnetic field magnetic field lineslines

When there are many sun spots, it is called the solar maximum
– lots of solar flares – strong solar wind– radiation is also extra
strongAll this solar activity All this solar activity can interfere with can interfere with electromagnetic waves electromagnetic waves -cell phones don't workcell phones don't work-solar static on car radiosolar static on car radio

The Sun is a magnet.The Sun is a magnet.
A) trueA) true
B) falseB) false

What are strong magnetic fields What are strong magnetic fields on the sun called? on the sun called?
A) SunspotsA) Sunspots
B) Solar flares B) Solar flares
C) Solar PowerC) Solar Power
D) StarburstsD) Starbursts

What can solar activity interfere What can solar activity interfere with? with?
A) Operation of motor vehiclesA) Operation of motor vehicles
B) EM waves B) EM waves
C) The tides C) The tides
D) The time continuumD) The time continuum

High Speed electrons and protons High Speed electrons and protons from space travel along magnetic from space travel along magnetic
field lines cause what?field lines cause what?
A. The magnetosphereA. The magnetosphereB. Solar windB. Solar windC. AuroraC. AuroraD. Plasma flowD. Plasma flow

What carries sunspots throughout What carries sunspots throughout the solar system?the solar system?
A. Solar windA. Solar windB. PlasmaB. PlasmaC. The sun’s dipolar fieldC. The sun’s dipolar fieldD. Cosmic raysD. Cosmic rays

BibliographyBibliography1.1. Magnetism information fromMagnetism information from School for Champions Website by Ron Kurtus School for Champions Website by Ron Kurtus
(revised 29 January 2002)(revised 29 January 2002) @ @ http://www.school-for-champions.com/science/magnetism.htm, 4/15/04http://www.school-for-champions.com/science/magnetism.htm, 4/15/04
2.2. Magnetism: Chapter 9Magnetism: Chapter 9 by Joseph F. Alward, PhD, Department of Physics, by Joseph F. Alward, PhD, Department of Physics, University of the PacificUniversity of the Pacific @ @ http://sol.sci.uop.edu/~jfalward/physics17/chapter9/chapter9.html, 4/15/04http://sol.sci.uop.edu/~jfalward/physics17/chapter9/chapter9.html, 4/15/04
3.3. HyperPhysicsHyperPhysics by Carl R. (Rod) Nave Department of Physics and Astronomy by Carl R. (Rod) Nave Department of Physics and Astronomy Georgia State UniversityGeorgia State University @ @ http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/magnetic/magcur.html, 4/15/04http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/magnetic/magcur.html, 4/15/04
4.4. Creation of the UniverseCreation of the Universe The Qur’an and LifeThe Qur’an and Life by Harun Yahyaby Harun Yahya @ @ http://www.creationofuniverse.com/html/science_06.html , 4/15/04 http://www.creationofuniverse.com/html/science_06.html , 4/15/04
5.5. Earth’s Magnetic Field Earth’s Magnetic Field by Windows to the Universe, Last modified June 3, by Windows to the Universe, Last modified June 3, 20032003 @ @ http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link=/earth/Magnetosphere/overview.html , http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link=/earth/Magnetosphere/overview.html , 4/16/044/16/04
6.6. Windows to Universe Windows to Universe by Windows to the Universe, Last modified June 3, 2003by Windows to the Universe, Last modified June 3, 2003 @ http://www.windows.ucar.edu/spaceweather/location_mag_poles.html, @ http://www.windows.ucar.edu/spaceweather/location_mag_poles.html, 4/16/044/16/04
7.7. New clues to Earth's magnetic flip-flopsNew clues to Earth's magnetic flip-flops by CNN News, April 7, 2004by CNN News, April 7, 2004 @http://www.cnn.com/2004/TECH/space/04/07/poles.reverse/, 4/16/04@http://www.cnn.com/2004/TECH/space/04/07/poles.reverse/, 4/16/04