Lungs Presentation Finaldsfds
-
Upload
paterno-aparente -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
2
description
Transcript of Lungs Presentation Finaldsfds

LUNG PERFUSION
• A lung perfusion scan is a test to see how blood flows to the lungs

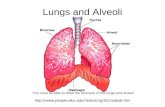
ANATOMY

INDICATION• the diagnosis of a suspected
pulmonary embolus; and• the assessment of regional lung
function.• Other indications are quantifying
right to left shunts and differential pulmonary blood flow

PATIENT PREPARATION• How to Prepare for the Test• You do not need to stop eating (fast),
eat a special diet, or take any medications before the test.
• A chest x-ray is usually done before or after a ventilation and perfusion scan.
• You wear a hospital gown or comfortable clothing that does not have metal fasteners.

PROCEDURE• A pulmonary ventilation/perfusion scan is a series of
two scans that measure how well air and blood are able to flow through your lungs (ventilation scan), as well as the blood supply through the lungs (perfusion scan). The scans are either performed together or one after the other, but are often discussed as one scan: the pulmonary ventilation/perfusion scan.
• During a pulmonary ventilation/perfusion scan, a radioactive dye is injected into your veins. This dye will show up on a special type of scanner, and will give your doctor information about how well your lungs are working. The dye will gather at areas of abnormal blood flow, which may indicate a blockage in the lung artery.

• During the perfusion scan, a health care provider injects radioactive albumin into your vein. You are placed on a movable table that is under the arm of a scanner. The machine scans your lungs as blood flows through them to find the location of the radioactive particles.
• During the ventilation scan, you breathe in radioactive gas through a mask while you are sitting or lying on a table under the scanner arm.
• This test may also be called a V/Q scan or a radionuclide pulmonary scan

DISEASES

PNEUMONIA• is an infection that
inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. The air sacs may fill with fluid or pus (purulent material), causing cough with phlegm or pus, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing

PNEUMOTHORAX
• the presence of air or gas in the cavity between the lungs and the chest wall, causing collapse of the lung

LUNG CANCER• Lung cancer is a
type of cancer that begins in the lungs. Your lungs are two spongy organs in your chest that take in oxygen when you inhale and release carbon dioxide when you exhale

ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS)
• occurs when fluid builds up in the tiny, elastic air sacs (alveoli) in your lungs. More fluid in your lungs means less oxygen can reach your bloodstream

PLEURAL EFFUSION• A pleural
effusion is a buildup of fluid between the layers of tissue that line the lungs and chest cavity

CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD)
• Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs

INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE• Interstitial lung disease
describes a large group of disorders characterized by progressive scarring of the lung tissue between and supporting the air sacs. The scarring associated with interstitial lung disease may cause progressive lung stiffness, eventually affecting your ability to breathe and get enough oxygen into your bloodstream.

PULMONARY EDEMA• Pulmonary
edema is an abnormal buildup of fluid in the lungs. This buildup of fluid leads to shortness of breath

THANK YOU!