logical Malignancies. Prstn
Transcript of logical Malignancies. Prstn
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
1/28
Click to edit Master subtitle style
3/19/12
HAEMATOLOGICAL
MALIGNANCIESOncology group presentation
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
2/28
3/19/12
OUTLINE
Definition of haematologicalmalignancies
Definition of BM Classification of BM malignancies
ALL
CLL
AML
CML
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
3/28
3/19/12
Introduction
The haematological malignancies areclonal diseases that derive from asingle cell in the marrow or
peripheral lymphoid tissue which hasundergone a genetic mutation
Represent approximately 7%of all
malignant disease
BM is the soft, spongy fatty vasculartissue which fill cavities of bones
responsible for production of
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
4/28
3/19/12
Etiology
Exactly how genetic mutationsaccumulate in haematologicalmalignancies is largely unknown.
As in most diseases it is thecombination of genetic backgroundand environmental influence that
determines the risk of developing amalignancy.
However, in the majority of individual
cases neither a genetic susceptibility
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
5/28
3/19/12
Etiology cont
Genetic factors :
incidence of leukaemia is greatly
increased in some genetic diseases,particularly Down's syndrome (whereacute leukaemia occurs with a 20 to30 fold increased frequency),
Bloom's syndrome, Fanconi'sanaemia, ataxia telangiectasia,Klinefelter's syndrome
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
6/28
3/19/12
Etiology cont
Environmental influences
Chemicals eg. Benzene and otherindustrial solvents
Drugs eg. Alkyating agents(chlorambucil)
Radiation
Infections eg. HTLV-1, H.pylori
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
7/28
3/19/12
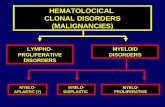
Classification
Haematological malignancies arisefrom two major cell lineages i.e.myeloid and lymphoid
4 main types;
1. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia(ALL)
2. Chronic lymphoblasticleukemia(CLL)
3. Acute myeloid leukemia(AML)
4. Chronic myeloid leukemia(CML)
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
8/28
3/19/12
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
9/28
3/19/12
Acute lymphoblasticleukemia
Is caused by anaccumulation/proliferation ofimmature lymphoid cells
(lymphoblasts) in the bone marrow It can arise from B or T lymphocytes
(85% arise from B cell)
Common malignancy of childhoodwith male predominance
Incidence highest at 3-7 yrs andthere is a secondar rise after a e of
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
10/28
3/19/12
Clinical features
Bone marrow failure
Anemia(pallor,lethargy and
dyspnoea) Neutropenia(fever,malaise,mouth,ski
n,respiratory infections)
Thrombocytopenia(spontaneousbruises,purpura,bleedinggums,menorrhagia)
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
11/28
3/19/12
Clinical features cont
Organ infiltration
Tender bones
Lymphadenopathy Moderate splenomegally
Hepatomegally
Meningeal syndrome(headache,nausea,vomiting,blurredvision)
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
12/28
3/19/12
Diagnosis
FBP (anaemia, thrombocytopenia,leukopenia or leukocytosis)
Peripheral smear study-circulatingblasts can be seen
Biochemical tests(raised serum uric
acid, LDH) Confirmatory-bone marrow
aspiration/biopsy
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
13/28
3/19/12
Diagnosis cont
Cytogenic analysis-may also beperformed on bone marrow specimento look for chromosomal
abnormalities associated withleukemia
Immunophenotyping -pathologist
look at specimen to see if leukemiaoriginates from B or T lymphocytes
Lumbar puncture
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
14/28
3/19/12
Management
Supportive therapy (central venouscanula, blood products support;prevention of tumour lysis syndrome)
Specific therapy (chemotherapy,radiotherapy, chemotherapy withstem cell transplant)
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
15/28
3/19/12
chemotherapy
Induction therapy: to bring aboutbone marrow remission. (vincristine,dexamethasone/prednisolone
,methotrexate, daunorubicin andasparaginase)
Consolidation/intensification therapy:
to eliminate any remaining leukemiacells and
Maintenance: (methotrexate and 6-
mecaptopurine)
Prognostic Factors Good Poor
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
16/28
3/19/12
Prognostic Factors:
Prognostic Factors Good Poor
WBC Low High (>50x109/L)
Sex Girls Boys
Immunophenotype B-ALL T-ALL (in children)
Age Child ( 4 weeks
CNS disease atpresentation
Absent Present
Minimal residual disease Negative at 1-3 months Still positive at 3-6 months
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
17/28
3/19/12
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
18/28
3/19/12
Chronic LymphocyticLeukemia (CLL)
most often affects adults over theage of 55
It sometimes occurs in youngeradults (15%), but it almost neveraffects children.
Two-thirds of affected people aremen. The male to female ratio of 2:1
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
19/28
3/19/12
CLL
Is characterized by the accumulationof non-proliferating matureappearing lymphocytes
In most cases the cells aremonoclonal B lymphocytes
T cell CLL can occur rarely
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
20/28
3/19/12
Etiology & Risk factors
High familial risk with two-fold toseven-fold higher risk.
No documented association withenvironmental factors.
No established viral etiology.
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
21/28
3/19/12
Clinical findings
Most patients are asymptomatic
Most symptomatic patients haveenlarged lymph nodes (commonlycervical and inguinal). The lymphnodes are usually descret,movableand non tender
Splenomegally
Tonsillar enlargement
Hepatomegally (later stages)
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
22/28
3/19/12
Lab findings
FBP-Lymphocytosis >4000cells/ L;anincrease in one type of white bloodcell, with mature appearing cells
Hypogammaglobulinemia seen>50%
Positive Combs test 30%
Immunophenotyping: B cells
Normocytic, normochromic Anaemia
in later stages
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
23/28
3/19/12
Bone Marrow
Not required for diagnosis.
Recommended to estimate theextent for prognostic implications.
Diffuse infiltration has poorprognosis.
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
24/28
3/19/12 J Mol Med 1999;
Cytogenetics
Deletions in chromosome 13 at q 14
Chromosome 11 at q22 or q23.
Trisomy-12. Less common are deletions in
chromosome 17 & 6.
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
25/28
3/19/12
Treatment
The primary chemotherapeutic planis combination chemotherapy(CHOP-cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin,
vincristine and prednisolone) Radiotherapy
Bone marrow transplant
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
26/28
3/19/12
The Rai Staging System
Stage 0 Lymphocytosis only (> 15,000/mm3)
Stage 1 Lymphocytosis and lymphadenopathy
Stage 2 Lymphocytosis and splenomegaly withor without lymphadenopathy
Stage 3 Lymphocytosis and anemia (Hgb
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
27/28
3/19/12
Modified Rai Staging Low-risk: stage 0, MS > 13 years. Intermediate-risk: stage I & II with MS
about 8 years.
High-risk: stages III & IV with MSabout
3 years
-
8/2/2019 logical Malignancies. Prstn
28/28
3/19/12
The Binet Staging System
Stage ANo anemia, nothrombocytopenia, =3 involvednodal areas
Stage CAnemia (Hgb < 10 g/dL)and/or thrombocytopenia (Plt