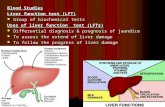
Liver Function Test
-
Upload
mirza-shaharyar-baig -
Category
Documents
-
view
225 -
download
2
Transcript of Liver Function Test

Liver Function TestLiver Function Test

ObjectivesObjectives By the end of this lecture, students
should know how to Describe the anatomy of liver, blood supply
and the function of liver. Outline the component of liver function test
(LFT) and its clinical use.

Anatomy of liverAnatomy of liver


Normal histology of the liver

The Function of LiverThe Function of Liver• Liver is largest and most complex internal organ• All blood flow fm intestine and pancreas reaches liver via
portal venous system• Liver is a multifunctional organ that is involved in diverse
body functions.
1. Metabolic Functions Liver actively participates in carbohydrate metabolism,
lipid, protein, mineral and vitamin metabolisms.2. Excretory Functions Bile pigments, bile salts and cholesterol are excreted in bile
into intestine.

3. Protective functions & detoxification Kupffer cells of liver perform phagocytosis to eliminate
foreign compounds. For example ammonia is detoxified to urea and metabolism of xenobiotics (detoxification).
Clearance of hormones such as insulin, parathyroid hormone, oestrogen, cortisol
4. Hematological and synthetic functions Liver participates in formation of blood (particularly in
embryo)• Synthesis of plasma proteins (albumin and prothrombin),
hormones e.g angiotensinogen, insulin-like growth factor and triiodothyronine.
• Destruction of erythrocytes (Bilirubin)

5. Storage functions Glycogen, vitamins A, D and B12
6. Serum enzymes Acting as markers of liver damage

Test to assess liver functionTest to assess liver function• Liver function tests(LFT) are helpful to detect the
abnormalities and extent of liver damage.• LFT assays are frequently more sensitive than clinical
signs and symptoms.• Typically the LFT comprises of: - Total protein
• Albumin and globulin• (Prothrombin Time)• Transaminases – AST & ALT • Alkaline PO4ase• Bilirubin, usually fractionated• Gamma Glutamyl Transpeptidase (GGT)

Total proteinTotal protein• Not a very useful measure, non-specific; only
provides information on:• General nutritional status• Severe organ disease (esp protein losing d/s)• Fractionated values of greater use
• Methods of measurement:• Electrophoresis followed by,• Precipitation, followed by,• Column separation.• Nitrogen content is usual method in automation

Total proteinTotal protein• Note! Measures of protein are in serum –
avoid dilution of proteins fm anticoagulant• Precipitation is used to fractionate proteins
into albumin and globulin• Addn of NaSO4, Na sulfite, Ammonium SO4,
methanol will ppt globulins• A/G ratio is a frequently used value in determining
serum protein abnormalities• Albumin changes [see later]• Globulin changes:
in disease fm increased synthesis

Total proteinTotal protein
• Nitrogen content measurement is reference method (Kjeldahl technique)
• This technique uses acid digestion of proteins to release ammonium ions, which are quantified by nesslerisation to form a coloured complex in an alkali environment

Total proteinTotal protein
• Refractive index (useful if level > 2.5g/dL)
• SG – pipetting serum into graded CuSO4 soln
• UV absorption (280nm)• Tubidimetric methods• Colourimetric – biuret method, most common
method in automated instruments. Can be made more sensitive using Folin-Ciocalteu reagent

Albumin and globulinAlbumin and globulin• Albumin
• Usu most abundant protein in serum [120 mg/kg/day]• ↓albumin
• Impaired synthesis (malnutrition, malabsorption, hepatic dysfunction, cirrhosis)
• Loss (ascites, protein losing-nephropathy, enteropathy)• May result in peripheral oedema
• Up to 25% of albumin in hyperglycaemia becomes glycosylated with HbA1c – aka fructosamine useful in monitoring DM

Albumin and globulinAlbumin and globulin• Albumin
albumin• Unusual – can occur in dehydration or as artifact fm tourniquet use
• Types of globulin of clinical significance: 1-antitrypsin (AAT) 2-macroglobulin• Haptoglobin• Transferrin • Ceruloplasmin

11-antitrypsin (AAT)-antitrypsin (AAT)
• Most abundant 1-globulin• Inhibits trypsin• Several genetic variations• May be associated with incidence
emphysema and neonatal jaundice

22-macroglobulin-macroglobulin
• Largest non-immunoglobulin protein in plasma in nephrotic syndrome

HaptoglobinHaptoglobin
• Another major 2 protein• Function – to combine with Hb released by RBC lysis
to preserve Fe and protein stores• Circulating half-life approx 4 days in stress, infection, acute inflamm, tissue necrosis• ↓ post haemolytic episode• Useful to monitor slow rate of haemolysis i.e. fm
mechanical valves, exercise associated trauma, haemoglobinopathies

CeruloplasminCeruloplasmin
• Cu containing enzyme (ferroxidase) in serum
• ↓ in Wilson’s d/s
• Associated with chronic hepatitis (occ acute) and may
have neurologic/ psychiatric sequelae

-Fetoprotein-Fetoprotein• One of the major plasma proteins in foetal life• Function not known, similar structure to albumin• Falls thru-out gestation (~10,000 ng/mL at birth) and
by age one yr (<10 ng/mL – adult levels)• In acute hepatic injury AFP 10 – 20X upper ref
limits• Abt 10% pt with viral hepatitis have AFP• Fibrosis post chronic liver d/s, AFP • Used to screen and diagnose HCC & hepatoblastoma

Prothrombin TimeProthrombin Time• Most coag factors made in liver (particularly those assoc with
vitamin K)• Hence in liver d/s, coagulopathies are common• Commonly PT is used for detecting liver assoc coagulopathies• Best PT method not clear• PT INR is useful for monitoring oral anti-coag therapy, not
very useful for liver disease• An indirect test of hepatic synthetic function includes
administration of vitamin K (10mg) subcutaneously over three days. Several days later, the prothrombin time may be measured. If the prothrombin time becomes normal, then hepatic synthetic function is intact. This test does not indicate that there is no liver disease, but is suggestive that malnutrition may coexist with (or without) liver disease.

TransaminasesTransaminases
• Tests of liver injury• Hepatocytes contain high levels of enzymes
that can leak into the plasma when there is liver injury
• Enzymes found in hepatocytes are:• Cytoplasmic = LDH, AST, ALT• Mitochondrial = ASTm
• Canalicular = ALP, GGT

Alanine Aminotransferase Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)(ALT)
• The test is primarily used to diagnose liver disease, to monitor the course of treatment for hepatitis, active postnecrotic cirrhosis, and the effect of drug therapy.
• The level of ALT abnormality is increased in conditions where cells of the liver have been inflamed or undergone cell death
• As the cells are damaged, the ALT leaks into the bloodstream leading to a rise in the serum levels
• Any form of hepatic cell damage can result in an elevation in the ALT
• ALT level may or may not correlate with the degree of cell death or inflammation
• ALT is the most sensitive marker for liver cell damage. ALT differentiates between hemolytic jaundice and jaundice due to liver disease.

Alanine Aminotransferase Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)(ALT)
• Increased ALT levels are found in the following conditions:
- Hepatocellular disease
- Active cirrhosis (mild increase)
- Metastatic liver tumor
- Obstructive jaundice or billiary obstruction (mild to moderate increase)
- viral, infectious or toxic hepatitis (30-50x normal)
- infectious mononucleosis)

Aspartate Aminotransferase Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)(AST)
• Also reflects damage to the hepatic cell• It is less specific for liver disease• It may be elevated and other conditions such as a myocardial
infarct and muscle disease • Although AST is not a specific for liver as the ALT, ratios
between ALT and AST are useful to physicians in assessing the aetiology of liver enzyme abnormalities
• Viral heptitis, mononucleosis, and acute hepatotoxicity typically show elevations in ALT that are equal to or greater than AST elevations (AST/ALT less than or equal to 1.0)
• ALT is elevated to a lesser degree than AST in alcoholic liver disease and cirrhosis, passive congestion, bile duct obstruction, or metastatic tumor to the liver (AST/ALT greater than 1.0)

MeasurementMeasurement• Uses coupled enzymatic reactions with NADH as
final reaction product measured• Reagents with NH4
+ should be avoided as it may artificially the AST/ALT values
• Values also affected by buffers

SpecimensSpecimens• Stable in whole blood for 24 hrs (then gradually
from release fm RBC)• AST/ALT stable at 4oC for up to 3 weeks• AST stable indefinitely with freezing• ALT may show ↓ with freezing depending on
buffer used

Alkaline PhosphataseAlkaline Phosphatase• Source: liver, bone, placenta and intestine.• ↑ ALP activity in liver disease are the result of increased
synthesis of the enzymes by cells lining the bile canaliculli, usually in response to cholestasis (intra or extra-hepatic).
• ALP ↑ 2x the reference interval in cholestasis.• Also ↑ in infiltrative diseases of liver, when space occupying
lesions (e.g tumours) are present. • Growing bones need ALP.• ↑ serum ALP by osteoblast-rapid growth of bone (growth,
healing of fracture, bone cancer, Paget’s disease,rickets).• For pregnant women, ALP is produce by the placenta.• ALP from the intestine is increased in a person with
inflammatory bowel disease such as ulcerative colitis.

Gamma Glutamyl Transferase (GGT) Gamma Glutamyl Transferase (GGT) EnzymeEnzyme
• GGT is used by the body to synthesize glutathione tri peptide
• GGT is present in liver, kidney, pancreas, intestinal cells and prostrate glands
• Elevated levels (> 10 - 30 IU/l) are observed in : chronic alcoholism, pancreatic disease, myocardial
infarction, renal failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and in diabetes mellitus
• In liver diseases, GGT elevation parallels that of ALP• In alcoholic liver disease GGT levels may be parallel to
alcohol intake

BilirubinBilirubin• Normal serum bilirubin levels:• Total bilirubin: 4 to 19mol/L• Conjugated bilirubin (Direct ; glucuronide): 0
to 4 mol/L • Unconjugated bilirubin ( Indirect; bilirubin -
albumin complex): up to 12 mol/L

BILIRUBINBILIRUBIN is estimated by is estimated by van den Berghvan den Bergh reactionreaction
• Principle of this test is the reaction between sulfanilic acid (sulfanilic acid in HCl and sodium nitrate) with bilirubin
• Aforementioned reaction forms a purple coloured complex, azobilirubin

BILIRUBINBILIRUBIN is estimated by is estimated by van den Berghvan den Bergh reactionreaction
• Conjugated bilirubin produces purple color immediately on mixing with reagent
• This response is known van den Bergh as direct positive
• Unconjugated bilirubin gives purple color only on addition of alcohol
• This response is called as indirect positive• If both, conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin, are
present in increased amounts, a purple color is produced immediately
• The purple color, so obtained, is intensified on adding alcohol. The the reaction is called biphasic

Thank youThank you