CH339K Lecture 2. Bonding Covalent Ionic Dipole Interactions Van der Waals Forces Hydrogen Bonds.
Lipids CH339K. What are lipids? Grab bag of molecular types Common link is their hydrophobicity...
-
Upload
leonard-casey -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of Lipids CH339K. What are lipids? Grab bag of molecular types Common link is their hydrophobicity...

Lipids
CH339K

What are lipids?
• Grab bag of molecular types• Common link is their hydrophobicity
– Fats– Glycerophospholipids– Sphingolipids– Waxes– Eicosanods– Steroids– And other stuff

FATTY
ACIDS

You can’t make fatty acids where the double bond is 6 carbons or closer to the end of the molecule

In living systems, the double bonds of unsaturated fatty acids are usually cis-.


Melting Temps of Fatty Acids
Formula Common Name Melting Point Formula Common Name Melting PointCH3(CH2)10CO2H lauric acid 45 ºC CH3(CH2)5CH=CH(CH2)7CO2H palmitoleic acid 0 ºCCH3(CH2)12CO2H myristic acid 55 ºC CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7CO2H oleic acid 13 ºCCH3(CH2)14CO2H palmitic acid 63 ºC CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7CO2H linoleic acid -5 ºCCH3(CH2)16CO2H stearic acid 69 ºC CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7CO2H linolenic acid -11 ºCCH3(CH2)18CO2H arachidic acid 76 ºC CH3(CH2)4(CH=CHCH2)4(CH2)2CO2H arachidonic acid -49 ºC
Saturated Unsaturated


(Glycerol tripalmitate)

Grandma’s Lye Soap (Saponification)

Fatty Acid Salts are Amphipathic

Waxes
Very often – fatty acid + long-chain alcohol.Very often – fatty acid + long-chain alcohol.

Plant leaf cuticle

Insect epicuticle

Beeswax components

Spermaceti•Largely cetyl palmitate•Large whale may have 3 tons•May function as lens in echolocation•May function as shock absorber in combat•Sank the whale ship Essex in 1820

What happens if I substitute something else for a fatty acid in a fat?Like a Phosphate?


This also is Amphipathic

Phospholipids in H2O

Cardiolipin(s)
Major component of inner mitochondrial membrane (up to 20%)R groups usually c18:2
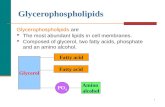
Glycerol

Major component in heart muscle membranes

Causes platelet aggregation and vasodilation (inflammatory mediator). Important to the process of hemostasis. Important in implantation.Concentration of 10-12 M causes life threatening inflammation of the airways (asthma-like symptoms).Toxins such as fragments of destroyed bacteria induce synthesis of PAF
causes drop in blood pressure reduced volume of blood pumped by the heartshock and possible death.

Glycolipids

Archaea have weird membrane lipids

Archaean membrane lipids
Polymers ofisoprene
Sulfolobus solfataricus

Sphingolipids
Sphingosine by itself




Defective ganglioside digestive enzymes cause disease

Tay-Sachs – a Defect inSphingolipid Metabolism
As a child with Tay-Sachs grows older, he or she may become blind, mentally retarded, paralyzed, and unresponsive to the environment. The child also may have seizures, difficulty swallowing, and difficulty breathing. Children with Tay-Sachs disease rarely live beyond 4 or 5 years of age.

Tay-Sachs – a Defect inSphingolipid Metabolism
Mutation in lysosomal enzyme Hexosaminidase A

Cholesterol

Steroid Hormones

Steroid Function SourceTestosterone Boys Testis (ovary)Estradiol Girls Ovary (testis)
Cortisol
Turns on gluconeogenesisInhibits immune responseTurns on Metabolism Adrenal Cortex
Aldosterone
Increases sodium retentionIncreases potassium secretionIncreased blood pressure Adrenal Cortex
PrednisoloneInflammatory and autoimmune diseases Drug
Prednisone Immunosuppressant Drug


Bile Salts Bile salts are steroid acids

Bile Salts solubilize fats in the digestive tract

ProstacyclinProstacyclin
Derivatives of Arachidonic Acid• Leukotrienes – conjugated double bonds
•vasoconstrictors• Thromboxanes – 6-membered ring
•Clot formation• Prostaglandins – 5-membered ring
•Many functions•Inflammatory response•Vasodilators•Pyogenic

Eicosanoid functions
• Prostaglandins have 5- or 6-membered ring– Short-range hormones mediating (among other
things) pain and inflammation, uterine contraction
• Prostacyclins have a double ring structure– Inhibit clotting, vasodilators
• Thromboxanes are made in platelets, contain oxygen in the ring– Vasoconstrictors, hypertensives, aggregate platelets
• Leukotrienes have 3 conjugated double bonds– Asthmatic, allergic, and inflammatory responses

NSAIDs like aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen inhibit eicosanoid formation

Phospholipids in H2O

Lipid Bilayer

Cell Membrane

Integral and Peripheral Proteins

Membrane Functions


Membrane Composition

Membrane Composition

Erythrocyte Membrane – differences between inner and outer layers

2-Dimensional Fluids

Membranes exist in 2 states

Phase transition

Factors Impacting Tm
• Chain length– Longer chains more vdW contacts (higher Tm)
• Unsaturation– Unsaturated FAs fewer vdW contacts (lower Tm)
• Size / Charge of head groups– Big head groups steric interference lower Tm)– Charged head groups electrostatic repulsion lower
Tm)
• Cholesterol– Interferes with packing at low temps– Stiffens membrane at high temps– Broadens melting curve

Some organisms change their membrane composition seasonally in order to maintain constant fluidity
Egregia menziesii
Winter Spring Summer Fall
SFA 29.6 35.6 34.1 31.4
MUFA 13.3 17.8 16.7 16.3
PUFA 57.1 46.9 49.3 52.3