Lecture%21:%November%6,%2012 -...
Transcript of Lecture%21:%November%6,%2012 -...

CHM 223 • Organic Chemistry IFall 2012, Des Plaines • Prof. Chad Landrie
More Addi)on Reac)ons to Alkenes:Sec)ons 8.2-‐8.5; 287
Oxida)on of Alkenes:Sec)ons 8.7-‐8.8
Lecture 21: November 6, 2012

CHM 223 • Organic Chemistry IFall 2012, Des Plaines • Prof. Chad Landrie
Compe))on Between Subs)tu)on and Elimina)on:
Sec)on 11.12
We Almost Forgot. . .

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Elimina'on-‐Subs'tu'on Compe''on
3
When the nucleophile is anionic, elimination competes with substitution

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Elimina'on-‐Subs'tu'on Compe''on
4
When the nucleophile is anionic, elimination competes with substitution
BrHCH3CH2O
BrHCH3CH2O
E2
SN2
OCH2CH3
Anion must be more basic than hydroxide (pKa of conjugate acid > 15.7) for E1 or E2 to be a competing mechanism

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Elimina'on-‐Subs'tu'on Compe''on
5
Br
Br
E1
SN1
H
OCH2CH3
OCH2CH3
OCH2CH3
When the nucleophile is anionic, elimination competes with substitution
Anion must be more basic than hydroxide (pKa of conjugate acid > 15.7) for E1 or E2 to be a competing mechanism

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
1.Low steric hinderance: a. small nucleophilesb.least substituted alkyl halide possible
2.Neutral nucleophiles (like solvolysis)3.Or anionic nucleophiles less basic than OH–
Condi'ons Favoring Subs'tu'on
6

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
1.Low steric hinderance: a. small nucleophilesb.least substituted alkyl halide possible
2.Neutral nucleophiles (like solvolysis)3.Or anionic nucleophiles less basic than OH–
Condi'ons Favoring Subs'tu'on
7

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
1.Low steric hinderance: a. small nucleophilesb.least substituted alkyl halide possible
2.Neutral nucleophiles (like solvolysis)3.Or anionic nucleophiles less basic than OH–
Condi'ons Favoring Subs'tu'on
8
KOC(CH3)3 is so large that it prefers E2 even when the alkyl halide is primary.

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
1.Low steric hinderance: a. small nucleophilesb.least substituted alkyl halide possible
2.Neutral nucleophiles (like solvolysis)3.Or anionic nucleophiles less basic than OH–
Condi'ons Favoring Subs'tu'on
9
Neutral nucleophiles are not basic enough to deprotonate a β-hydrogen in an E2 mechanism; they also undergo addition to carbocations faster in
SN1 than deprotonation in an E1 mechanism.
CH3Cl+
methanol
CH3OmethanolysisH3COH
H3Ckrel = 4

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
1.Low steric hinderance: a. small nucleophilesb.least substituted alkyl halide possible
2.Neutral nucleophiles (like solvolysis)3.Or anionic nucleophiles less basic than OH–
Condi'ons Favoring Subs'tu'on
10
pKa (H2O) = 15.7 pKa (HCN) = 9.1stonger acid = weaker conjugate base

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
1.Large steric interactions: a. large nucleophilesb.most substituted alkyl halide possible
2. Anionic nucleophiles more basic than OH–
Condi'ons Favoring Elimina'on
11
CH3Br
O CCH3
CH3CH3K++
CH3
DMSO
pKa (H2O) = 15.7 pKa (tert-butanol) = 18stonger acid = weaker conjugate base

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
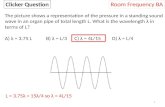
i>Clicker Ques'on
12
H3CO
H3CO
CH2
H3CO
H3CO
CH3
H3CO
H3CO
CH3
NC
S
H3CO
H3CO
CH3
SCN
H3CO
H3CO
CH3
ClS C N+ S C N
DMF
DMF = N,N-dimethylformamide(common polar aprotic solvent) N
O
HCH3
H3C
What is the major product of the reaction below?
Chauncey says. . .
A
B
C
D

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
i>Clicker Ques'on
13
Although the Markovnikov rule generally applies to the addition of hydrogen halides across unsymmetrically substituted alkenes, this terminology is often expanded to include other additions to alkenes. Which reaction, then, would provide the anti-Markovnikoff product?
Markovnikoff rule: H is added to least substituted C of alkene; X is added to most substituted carbon of alkene
A
B
C
D
E. A & D
Markovnikov
anti-Markovnikov
Markovnikov
neither

CHM 223 • Organic Chemistry IFall 2012, Des Plaines • Prof. Chad Landrie
Sec)on 8.5You are responsible for sec0on 8.4 and 8.9!
Hydrobora)on–Oxida)on

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Pa=ern: Hydrobora'on
15
C C X Y+ addition C CX Y
C C H BH2+ hydroboration C CH BH2alkene borane alkyl borane
alcohol
oxidation
C CH OH
oxidation is a separate step and requires a separate set of conditions and reagents

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Condi'ons: Hydrobora'on
16
B HHH
• boron is an exception to octet rule• sp2-hybridized (only 3 valence e-s)• contains an empty p-orbital• strong Lewis acid (electron pair acceptor)• forms 3-bonds (neutral) & 4-bonds (-/ve)
2 BH3dimerization B2H6
“Free” borane (BH3) only exists in gas phase, otherwise undergoes dimerization to diborane (B2H6)
borane diborane

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Condi'ons: Hydrobora'on
17
“Free” borane (BH3) only exists in gas phase, otherwise undergoes dimerization to diborane (B2H6)
borane diborane
B BH
H
H HH
HB
HB
HHH
HH+ dimerization
B HHH
• boron is an exception to octet rule• sp2-hybridized (only 3 valence e-s)• contains an empty p-orbital• strong Lewis acid (electron pair acceptor)• forms 3-bonds (neutral) & 4-bonds (-/ve)

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Condi'ons: Hydrobora'on
18
“Free” borane (BH3) only exists in gas phase, otherwise undergoes dimerization to diborane (B2H6)
borane diborane
BH
HH B
H HH dimerization
B HHH
• boron is an exception to octet rule• sp2-hybridized (only 3 valence e-s)• contains an empty p-orbital• strong Lewis acid (electron pair acceptor)• forms 3-bonds (neutral) & 4-bonds (-/ve)

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Condi'ons: Hydrobora'on
19
OO
OCH3H3C
diglyme: diethylene glycol dimethyl ether
• diglyme is a common solvent (reaction liquid; does not participate in the reaction)
• hydroborations typically at room temperature (rt) or below• generally very fast reactions

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Condi'ons: Hydrobora'on
20
Other hydroborating reagents with different reactivities may be prepared by adding Lewis bases to diborane (B2H6)
B2H6O
tetrahydrofuran (THF)
H3CS
CH3
dimethyl sulfide (DMS)
N
triethylamine (TEA)
CH3
SCH3
OH3B
H3B•THF
H3B
H3B•DMS
N(CH2CH3)3H3B
H3B•TEA
diborane+
+
+
B2H6diborane
B2H6diborane
}Le
wis
Aci
d-Ba
se C
ompl
exes

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Condi'ons: Oxida'on
21
HBH2
H2O2, NaOH (aq)oxidation
HOH
• boron is replaced by more electronegative atom (O); therefore: oxidation
• only requires hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and hydroxide (OH–); usually added immediately following hydroboration
• I will not ask you to learn the mechanism for this step; for the curious, see textbook page 250

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
• usually written as a two-step process
• works with diborane (B2H6) or a borane complex with another Lewis base
• diglyme is a common solvent
• affords alcohol products; similar to hydration (H2O/H3O+)
Pa=ern & Condi'ons: Hydrobora'on-‐Oxida'on
22
1. B2H6, diglyme
2. H2O2, NaOHOH
CH3 1. H3B•S(CH3)2
2. H2O2, NaOH
CH3
OH
1. H3B•S(CH3)2
2. H2O2, NaOHOH
Which carbon of the alkene becomes bonded to the -OH group? Do you see a pattern here?

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Hydrobora'on is Regioselec've
23
O O O OHBH2H3B•THF H2O2/OH–
• boron atom is added to least substituted carbon atom, hydrogen atom is added to most substituted
• after oxidation, gives the least substituted product• opposite regioselectivity of Markovnikov addition
compare to . . .
OO OH2SO4 H2O/heat
OSO3H OH

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Hydrobora'on Mechanism
24
• concerted processes = B and H add to same side (face) of double bond
• hydride (H:) adds to most substituted carbon• boron adds to least substituted carbon• this is NOT a PROTONATION
CH3
H2B H
CH3
HH2B
Why this regioselectivity?

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Hydrobora'on Mechanism
25
Regioselectivity Argument One: Boron is larger than hydrogen; it prefers to add to the least sterically hindered side of the double bond, which is the least substituted side.
C
B H
CH3
HH2BH
HH
HH
CH3
BH HH
CH3
BH2H
X

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Hydrobora'on Mechanism
26
Regioselectivity Argument Two: both carbons in alkene develop partial positive charge in transition state; more substituted = more partially positively charged = hydride (H:) transfer prefered (faster) to that carbon atom.
π-complex
Lewis acid
Lewis base
π-complex rearrangedπ-complex
most substituted = most partially positively charged =most electrophilic carbon atom =
want electrons from a nucleophile most

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Stereochemistry of Hydrobora'on
27
Hydroboration is a syn addition since the mechanism is concerted. Bonds are being formed to the boron atom and the hydrogen atom at the same time from one face of the π-bond.
syn

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
i>Clicker Ques'on
28
1. Br2, CH2Cl2, hv2. NaOC(CH3)2, DMSO
3. B2H6, diglyme4. H2O2, NaOH (aq)
HO
HO
HO
Br
HO
What is the major organic product after the following sequence of reactions?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.

CHM 223 • Organic Chemistry IFall 2012, Des Plaines • Prof. Chad Landrie
Sec)on 8.2-‐8.3
Halogen Addi)on to Alkenes

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Pa=ern: Halogen Addi'on
30
C C X Y+ addition C CX Y
halogen must either be bromine (Br2) or chlorine (Cl2); no other halogens work
vicinal dibromide
vicinal dichloride
C C Br Br+ halide addition C CBr Br
C C Cl Cl+ halide addition C CCl Cl

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Condi'ons: Halogen Addi'on
31
• only bromine (Br2) and chlorine (Cl2) undergo this reaction• typically use a halogenated solvent like chloroform (CHCl3)• low temperature (0 ºC)• no light (avoid radical halogenation at saturated carbons)

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Halogen Addi'on is Stereoselec've
32
• anti addition of Br2 or Cl2 across double bonds• two halogen atoms are trans to each other in rings

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Halogen Addi'on Mechanism? No!
33
X
• concerted process would require syn addition of to two halogen atoms
• therefore mechanism is not conerted.

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Halogen Addi'on Mechanism? No!
34
CH2BrHH
• carbocation intermediate are planar (flat)• addition of second halide could approach either lobe of empty p-
orbital on carbocation• therefore this mechanism is not possible because it would not be
stereoselective
X

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Halogen Addi'on Mechanism? No!
35
X
Since only trans vicinal dihalides are obtained, a carbocation intermediate is not possible since it would give a mixture of trans and cis products.
+

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Correct Halogen Addi'on Mechanism: Halonium Ion Intermediates
36
H3C CH3
Br Br
H3C CH3
Br
Br
δ+ δ+
δ−
H3C CH3
Br
Br H3C
CH3Br
Br
• electron pair in π-bond form new bond to bromine atom as Br-Br bond breaks
• lone pair of electrons on bromide form new bond to alkene carbon losing a bond at the same time (concerted)
• halonium ions (three-membered rings with one halogen) are intermediates; no carbocation intermediates
halonium ion

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
An# Addi'on: Steric Perspec've
37
BrBr....
....
BrBr
::....
....::::
....
––BrBr:: ::....
....
attack of bromide (Br–) from opposite side C-Br bond that is
breaking gives anti product Br

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
An# Addi'on: MO Perspec've
38
BrBr....
....
BrBr
::....
....::::
....
––BrBr:: ::....
....
bonding (σ) orbital of Br– overlaps best with the antibonding (σ*) orbital of the C-Br bond from
the back Br

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
An# Addi'on: MO Perspec've
39
BrBr....
....
BrBr
::....
....::::
....
––BrBr:: ::....
....
bonding (σ) orbital of Br– overlaps best with the antibonding (σ*) orbital of the C-Br bond from
the back Br
attack from the side involves equal amounts of constructive and destructive interference = no change

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
An# Addi'on: MO Perspec've
40
BrBr....
....
BrBr
::....
....::::
....
bonding (σ) orbital of Br– overlaps best with the antibonding (σ*) orbital of the C-Br bond from
the back Br
attack at Br involves electrostatic repulsion as well as weaker orbital overlap; notice in the C-Br bond, the orbital on Br is smaller than the orbital on carbon. Don’t worry about why.
––BrBr:: ::....
....

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Rela've Rates of Bromina'on
41
C C CHH
H
• more alkyl groups attached to double bond =• more σ➞π orbital donation/overlap (hyperconjugation) • double bond has more electron density =• double bond is a stronger nucleophile (Lewis base) =• reacts faster with electrophiles like Br-Br
H
H H
H
H3C
H H
H
H3C
H3C H
H
H3C
H3C CH3
CH3
alkene relative rate (krel)
1
61
5400
920,000
σ➞∏donation

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Halogen Addi'on Modifica'on: Aqueous Solu'ons Give Halohydrins
42
• if the solvent for the reaction is changed to water, halohydrins are formed
• since water is much more concentrated, it will add to halonium ion intermediate faster than the halide
bromohydrin

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Forma'on of Halohydrins is Regioselec've
43
H3C H
Br Br
H3C H
Br
OH2HH3C
H3CH3C
HH
Br
OH
HH3C H
Br H3CH3C
HH
Br
HOOH2
• product is most substituted alcohol; least substituted halide
• most substituted carbon is most partially positively charged in transition state = strongest electrophile = water most attracted to that carbon

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
i>Clicker Ques'on
44
What is the major organic product obtained after the following sequence of reactions?
A
B
C
D
E. none of the above
Nucleophile adds to the most substituted carbon of the halonium ion.

CHM 223 • Organic Chemistry IFall 2012, Des Plaines • Prof. Chad Landrie
Sec)ons 8.7-‐8.8
Oxida)on of Alkenes: Epoxida)on, Ozonolysis and
Dihydroxyla)on

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Expoxides
46
• three-membered rings containing an oxygen atom• common intermediates in organic synthesis

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Epoxida'on: Pa=ern
47
H3C
O
OHacetic acid
H3C
O
Operoxyacetic acid
OH
• peroxyacids are source of electrophilic oxygen atoms• addition of a single oxygen atom across double bond• similar to formation of bromonium ion intermediate• don’t worry about mechanism; for curious see textbook page 259

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Epoxida'on: Examples
48
• any peroxyacid will work• more substituted double bonds react faster• because only adding one atom across double bond, must be syn addition

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Ozonolysis: Pa=ern
49
ozone
• ozone adds across double bonds to give ozonides• ozonides react further with reducing agents to provide
carbonyl compounds• we will not discuss mechanism for this reaction
C O CO

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Ozonolyis: Condi'ons
50
reducing agents;reduce ozonide intermediate
pattern = alkene is cut in half and replaced by an oxygen atom at each end
carbonyl product depends on substitution of alkene

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Prepara'on of Diols: Dihydroxyla'on
51
We will not learn the mechanism, just the pattern.

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Prepara'on of Diols: Dihydroxyla'on
52
Dihydroxylation is syn addition of vicinal hydroxyl (-OH) groups. This reaction can be stereospecific then.

CHM 223 • Organic Chemistry IFall 2012, Des Plaines • Prof. Chad Landrie
Synthesis

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Retrosynthe'c Analysis
54
How could you prepare 1-methylcyclohexene from methylcyclohexane?
CH3 ? CH3
Step One: Devise a retrosynthesis. Work backwards from the target molecule. For each step backward, you should ask, “How can I prepare the target functional group?”
CH3 CH3Br
CH3
dehydrohalogenation radical bromination

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Synthe'c Route
55
How could you prepare 1-methylcyclohexene from methylcyclohexane?
CH3 ? CH3
Step Two: Write the synthesis out in the forward direction including all necessary reagents and conditions.
CH3 Br2, CHCl3
light, 60 ºC
CH3Br
NaOCH2CH3
DMSO, 55 ºC
CH3

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
Complimentary Retrosyntheses
56
?CH3 H3C OH
?CH3 CH3
OH
H3C OH
CH3OH
CH3 H3C Br CH3
1. H2SO42. H2O/heat
1. B2H6
2. NaOH
/H2O2

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
i>Clicker Ques'on
57
OHBr
Br
OHBr
OH
OHBr
OH
OHBr Br
OH
B.
C.
D.
Br2, CHCl3
light, 60 ºCBr
NaOCH2CH3
DMSO, 55 ºC
Br2
H2O/THF
OHBr
Which retrosynthetic analysis provides the best route for the synthesis of 2-bromocyclopentanol?
A.

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
i>Clicker Ques'on
58
Devise a retrosynthesis for the synthetic target below.
?
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl OH
Cl O
A.
B.
C.
D.
1. B2H6, diglyme2. H2O2, NaOH
OH
SOCl2K2CO3

© 2012, Dr. Chad L. LandrieOrganic Chemistry 1 (CHM 223)
Slide Lecture 21: November 6
i>Clicker Ques'on
59
HO
HO
H
OH
OBr
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Which starting material could be used to prepare the molecule below? Write out your synthesis. Don’t guess.

CHM 223 • Organic Chemistry IFall 2012, Des Plaines • Prof. Chad Landrie
Next Lecture. . .9.1 -‐ 9.9