Learning Graphs and Learning Science with Sensors
description
Transcript of Learning Graphs and Learning Science with Sensors

Learning Graphs and Learning Science with Sensors
In Learning Corners in Grades 5 and 6Ed van den Berg ([email protected]), Frank Schweickert, Gerda Manneveld
€SenseSensors• Temperature• Light intensity • Sound level
Actuators• Buzzer• LED
AMSTEL InstituteUniversity of Amsterdam
EuroSense activities in English:http://www.pollen-europa.nl (see “EuroSense”)
sensors
and
senses
Sources: Hardware and software:http://www.cma.science.uva.nl
D i s ta nc e - T i me di a gr a m
0
0 . 5
1
1. 5
2
2 . 5
3
3 . 5
4
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35
T ime ( s ec on ds )
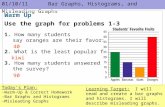
Grade Direction Standing still
Time Speed
5 41% 75% 55% 41%6 81% 100% 90% 77%
Laying the groundwork for concepts and variables by sensory experience
Sound level versus Time
Interview with Iris (12): Intv: How would you use sensor and graph to
determine the winner in a fast clapping contest? I: Let everybody clap in separate room, all for the
same time, and see how many claps everyone has.
Int: What do you count? I: How many curves there are, per second,
…..look at the time, ….count all the lines, …..everybody 10s
Int: Is it enough if you just count for one second? I: You count the first second how many, then
how many in the 2nd second, then the third, etc. and then you compute the average.
OBJECTIVES Children learn to interpret graphs and tell stories
with graphs:
link what you see, hear, and feel with numbers and graphs
relate more and less intense, and fast and slow change
link graphs with events use a graph as a tool in a new situation
RESEARCH QUESTIONS Can children communicate with distance-time
graphs? Can children use graphs as a tool in a new situation?
METHOD
PretestDistance sensor activity 27 children grade 5Temperature activity 13 children grade 6
Posttest recording audio/videoPost interview + graphs
Results posttest: Distance – Time Diagram