Last time: looked at proton-proton chain to convert ...cmcasey/ast307_fa16/lec13.pdf · Mass and...
Transcript of Last time: looked at proton-proton chain to convert ...cmcasey/ast307_fa16/lec13.pdf · Mass and...

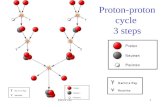
Last time: looked at proton-proton chain to convert Hydrogen into Helium, releases energy.

Last time: looked at proton-proton chain to convert Hydrogen into Helium, releases energy.
Fusion rate ~ Temperature i.e. the hotter it is, the more the core will fuse.

Last time: looked at proton-proton chain to convert Hydrogen into Helium, releases energy.
Fusion rate ~ Temperature i.e. the hotter it is, the more the core will fuse.
Even hotter temperatures: you can start fusing heavier elements. This is NOT happening in the sun now.

Last time: looked at proton-proton chain to convert Hydrogen into Helium, releases energy.
Fusion rate ~ Temperature i.e. the hotter it is, the more the core will fuse.
Even hotter temperatures: you can start fusing heavier elements. This is NOT happening in the sun now.
E = mc2

Stars exist in a state of hydrostatic equilibrium for most of their lives.
This balances the inward force of gravity with the outward pressure of very hot gasses.

Thinking about hydrostatic equilibrium (gravity vs. pressure):
Fusion rate ~ Temperature i.e. the hotter it is, the more the core will fuse.
What would happen if the core temperature of the sun dropped a little bit? DISCUSS.

Stars exist in a state of hydrostatic equilibrium for most of their lives.
This balances the inward force of gravity with the outward pressure of very hot gasses.
Decline in core temperature causes fusion rate to drop, so core contracts and heats up.
Rise in core temperature causes fusion rate to rise, so core expands and cools down.

What happens to the sun as it burns through its hydrogen?
The sun started out with some Helium when it was born, ~10% of the sun by mass, and that helium was spread throughout the sun.
R�
When the sun was born.
fract
iona
l co
mpo
sitio
n
Distance from the Sun’s center.
1
0
0.5
hydrogen
helium

What happens to the sun as it burns through its hydrogen?
The core of the sun is where fusion happens and suddenly most of the core is actually
made up of helium, as the hydrogen is consumed, still most of the sun is still made of
hydrogen, but towards the outter layers.
R�
After 5 billion years
fract
iona
l co
mpo
sitio
n
Distance from the Sun’s center.
1
0
0.5
hydrogen
helium

What happens to the sun as it burns through its hydrogen?
The core of the sun is where fusion happens and suddenly most of the core is actually
made up of helium, as the hydrogen is consumed, still most of the sun is still made of
hydrogen, but towards the outter layers.
R�
After 10 billion years.
fract
iona
l co
mpo
sitio
n
Distance from the Sun’s center.
1
0
0.5
hydrogen
helium

When the sun is burning hydrogen via fusion as usual, it is a main sequence star.
main sequence
The temperature of the star determines the rate
of nuclear fusion.
colder stars, slower burners
hotter stars, much faster
burners
If we have mass constraints on stars
(giving their hydrogen mass = nuclear fusion
fuel) and their luminosity, we can
estimate their lifetimes.

main sequence
Mass and Lifetimes of Main Sequence Stars
2⇥ 104 L�
4⇥ 10�3 L� 0.1M�
10M�
How do we measure mass again?
How do we measure luminosity again?

main sequence
Mass and Lifetimes of Main Sequence Stars
2⇥ 104 L�
4⇥ 10�3 L� 0.1M�
10M�
How do we measure mass again?
How do we measure luminosity again?
F =L
4⇡r2

main sequence
Mass and Lifetimes of Main Sequence Stars
2⇥ 104 L�
4⇥ 10�3 L� 0.1M�
10M�
How do we measure mass again?
How do we measure luminosity again?
F =L
4⇡r2

main sequence
Mass and Lifetimes of Main Sequence Stars
2⇥ 104 L�
4⇥ 10�3 L� 0.1M�
10M�
Life expectancy of the sun: 10 billion years.
Life expectancy of blue, massive star:10M�
Life expectancy of red dwarf star:0.1M�

main sequence
Mass and Lifetimes of Main Sequence Stars
2⇥ 104 L�
4⇥ 10�3 L� 0.1M�
10M�
Life expectancy of the sun: 10 billion years.
Life expectancy of blue, massive star:10M�
Life expectancy of red dwarf star:0.1M�
Burning fuel 104 times faster, 10 times more fuel, lifetime is 1/1000 that of the sun.

main sequence
Mass and Lifetimes of Main Sequence Stars
2⇥ 104 L�
4⇥ 10�3 L� 0.1M�
10M�
Life expectancy of the sun: 10 billion years.
Life expectancy of blue, massive star:10M�
Life expectancy of red dwarf star:0.1M�
Burning fuel 104 times faster, 10 times more fuel, lifetime is 1/1000 that of the sun.10 million years

main sequence
Mass and Lifetimes of Main Sequence Stars
2⇥ 104 L�
4⇥ 10�3 L� 0.1M�
10M�
Life expectancy of the sun: 10 billion years.
Life expectancy of blue, massive star:10M�
Life expectancy of red dwarf star:0.1M�
Burning fuel 104 times faster, 10 times more fuel, lifetime is 1/1000 that of the sun.
Burning fuel 103 times slower, 1/10th the fuel, lifetime is 100 that of the sun.
10 million years

main sequence
Mass and Lifetimes of Main Sequence Stars
2⇥ 104 L�
4⇥ 10�3 L� 0.1M�
10M�
Life expectancy of the sun: 10 billion years.
Life expectancy of blue, massive star:10M�
Life expectancy of red dwarf star:0.1M�
Burning fuel 104 times faster, 10 times more fuel, lifetime is 1/1000 that of the sun.
Burning fuel 103 times slower, 1/10th the fuel, lifetime is 100 that of the sun.
10 million years
1 trillion years

Eventually, the sun runs out of its fuel, like all stars.
What happens then??

Eventually, the sun runs out of its fuel, like all stars.
What happens then??

Stars Part 3: life & death.

Stars Part 3: life & death.

Where a star sits on the HR diagram is determined by
- its mass,- its age. main sequence
giants
supergiants
white dwarfs
Stars on the main sequence are burning
through their main supply of hydrogen via the p-p
chain (and when really massive, the
CNO cycle).
We learned how to compute lifetimes of stars on the main
sequence knowing their masses and luminosities.

Where a star sits on the HR diagram is determined by
- its mass,- its age. main sequence
giants
supergiants
white dwarfs
Stars on the main sequence are burning
through their main supply of hydrogen via the p-p
chain (and when really massive, the
CNO cycle).
We learned how to compute lifetimes of stars on the main
sequence knowing their masses and luminosities.
How does a star get there? And what happens when that fuel runs out?

Early life! How are stars born?

Collapse of molecular gas clouds…
Conservation of Angular Momentum propels gas into fast rotating disks from which solar systems form.

Collapse of molecular gas clouds…
Conservation of Angular Momentum propels gas into fast rotating disks from which solar systems form.




Along with the “core” which becomes a star, a disk forms…

What do star-forming clouds look like?





As a star is born, it accretes mass from its disk and heats up.
Fusion has started, and the star is adding mass…

Young stars which are still accreting material are called T-Tauri Stars.
Because mass is piling on, they sometimes have explosive outbursts.

Young stars which are still accreting material are called T-Tauri Stars.
Because mass is piling on, they sometimes have explosive outbursts.

Eventually the dust and debris in the protoplanetary disk is cleared out, potentially leaving planets & other debris behind. The star is no longer adding mass and has landed on the main sequence, where it will sit for
most of its lifetime, until it runs out of fuel…

The birth of stars.
Why do young stars form disks?
(a) once there is an overdense region of matter it has a run-away effect and everything collapses down into a
disk due to gravity. (b) the angular momentum of the original star forming
cloud builds with time forming a disk (c) the angular momentum of the star forming cloud is
constant with time and so as things collapse they start to spin and through friction form a disk,
(d) trick question; not all stars have disks when they form.

The birth of stars.
Why do young stars form disks?
(a) once there is an overdense region of matter it has a run-away effect and everything collapses down into a
disk due to gravity. (b) the angular momentum of the original star forming
cloud builds with time forming a disk (c) the angular momentum of the star forming cloud is
constant with time and so as things collapse they start to spin and through friction form a disk,
(d) trick question; not all stars have disks when they form.

The birth of stars.