Laptop Troubleshooting Handout Part1
-
Upload
queenie-obligado -
Category
Documents
-
view
156 -
download
2
Transcript of Laptop Troubleshooting Handout Part1

OUTLINE:

I.II.
Common & Proper Tools Needed Basic Electronics
III. Parts Familiarization & Function IV. Desktop & Laptop/Notebook Comparison V. Laptop/Notebook Advantages & Disadvantages VI. How To Remove, Replace & Upgrade Laptops/Notebooks Parts VII. How To Assemble & Re-assemble Laptop/Notebook VIII. Troubleshooting Laptop/Notebook Problems & Solutions IX. Tips, Tricks & Techniques X. Preventive Maintenance XI. BIOS XII. FAQ

I. COMMON & PROPER TOOLS NEEDED:
TOOLS NEEDED FOR LAPTOP/NOTEBOOK DIS-ASSEMBLY, RE-ASSEMBLY, PARTS UPGRADE, PARTS REPLACEMENT, TROUBLESHOOT AND REPAIR
- Wrist grounding strap and conductive mat for preventing electrostatic discharge - Small Philips screw driver - Philips screw driver - Flat head screwdriver - Plastic flat head screw driver - Hex screw driver - Tweezers - Guitar Pick (Heavy) - Screws container - Ballpen - Notepad - Documentation
OTHER TOOLS: FOR CLEANING, TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR - Analog/Digital Multimeter - Desoldering Pump - Soldering Iron - Paintbrush - Soldering Stand - Toothbrush - Soldering Paste - Paperclip - Soldering Lead - Eraser
SET OF FLAT HEAD SCREW DRIVER
SET OF HEX SCREW
SET OF TWEEZER
SET OF PHILIP SCREW

LONGNOSE, CUTTER & PLIER
GUITAR PICK (HEAVY)
PLASTIC CONTAINER FOR SCREW
TOOTHBRUSH
PAINTBRUSH
ALL IN ONE PACKAGE
DIGITAL & ANALOG MULTIMETER
ERASER
SOLDERING SET
PAPER CLIP

SOFTWARE & UTILITIES MUST HAVE
II.
Start-up or bootable disk Operating system Anti-virus Anti-spyware Application software System diagnostic utility Data back-up utility Driver back-up utility
BASIC ELECTRONICS:
VOM Multimeter
Data recovery utility Hardware utility Hard drive partition utility System monitoring utility Registry utility Dead pixel utility Updated hardware drivers collections
is used to measure electrical resistance, direct current (DC) voltage, or alternating current (AC) voltage and Resistance (Ω).

CAUTION!
- Always check your selector switch before testing components & electrical sources. - Set to specific type of voltage range (AC or DC) and always set to a much higher voltage than
the actual voltage output. - Always check your positive (+) & negative (-) probe when testing DC voltage.
AC Voltage Test = no polarity ( AVR output, wall outlet, UPS output, power cable connected to wall outlet etc.)
DC Voltage Test = with polarity (laptop battery, CMOS battery, desktop power supply connector pins, AC adaptor connector etc.)
Continuity test = no polarity & not connected to circuit (power cable, switch, fuse, wire, speaker, power jack connector, transformer etc.)
Resistance test (Ω ohms) = with polarity ( diode, transistor, electrolytic capacitor etc.)
POWER CONNECTOR OF AN AC ADAPTOR
Voltage output measured near to voltage specs.
Commonly Used Connector
End (Tip) to End (Tip) Test
Not Commonly Used
means the AC Adapter is good. - No deflection means the wire is open (bad) - With deflection means the wire is good

X1
With deflection means the fuse is good No deflection means the fuse is bad (wire is open)
No deflection at all in any of the two contact terminal means the Power Jack is bad (Open)
With deflection in any one of the two contact terminal means the Power Jack is good

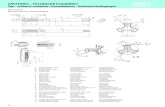
III. PARTS FAMILIARIZATION & FUNCTION
FRONT VIEW
RIGHT PANEL
LEFT PANEL

REAR PANEL
BOTTOM VIEW

LOCK KEYS The keyboard has 3 lock keys w/c you can toggle on & off.
TOUCHPAD
The built-in touchpad is a pointing device that senses movement on its surface. This means the cursor responds as you move your finger on the surface of the touchpad. The central location on the palmrest provides optimal comfort and support.
NOTE: If you are using an external USB mouse, you can press Fn-F7 to disable the touchpad.
PARTS OF THE LCD SCREEN DISPLAY 1. LCD bezel/rear cover 2. LCD hinge/bracket with antenna 3. LCD cable 4. Wi-Fi antenna 5. LCD inverter/LED card 6. LCD panel 7. Backlight (CCFL) 8. Frame 9. Digitizer 10.Transparent
PARTS OF THE SYSTEM UNIT 1. Keyboard bezel middle cover 2. Keyboard bezel upper case 3. Optical drive (UltraBay Plus CD/DVD) 4. UltraBay Plus guide rail 5. Microphone cable 6. Communications daughter card (CDC)
1 = Left Click Button 2 = 4-Way Scroll Key Button 3 = Right Click Button

7. Bluetooth/modem 8. I/O bracket 9. Mini PCI access door 10. Main battery (Li-ion) 11. Backup (CMOS) battery 12. DIMM access door 13. Speakers 14. Lower case 15. Bluetooth antenna 16. DDR SODIMM 17. 802.11a/b Wi-Fi wireless card 18. Motherboard 19. CPU (Pentium M processor) 20. Hard disk guide rails 21. PC Card/CardBus slot 22. CPU heatsink/fan 23. Hard disk drive with tray 24. Hard disk drive access cover 25. Keyboard 26. TrackPoint cap 27. Hinge cap a. Communications daughter card (CDC) plate b. Modem cable c. Motherboard chipset heatsink d. Video chipset heatsink
Simple diagram that will help you to understand how a Laptop/Notebook display assembly works and how an image appears on the screen.
VIDEO CABLE
A video signal from the motherboard goes to the LCD screen through the video cable. The video cable connects to the motherboard (or video card) through the connector 1. The video cable connects to the LCD screen through the connector 2. The video cable (in most cases) is also responsible for supplying a necessary voltage for the FL inverter board. The video cable connects to the FL inverter board at the point 3.

FL INVERTER BOARD
This board is responsible for converting low voltage DC power (point 3) to high voltage AC (point 4), necessary to light up the backlight bulb.
CCFL (backlight bulb) – Cold Cathode Flourescent Lamp
When the backlight bulb lights up, you can see an images on the LCD screen.
LID CLOSE SWITCH
The lid close switch is a small button that locates close to the display hinges. On some newer models there is no button, because the switch is magnetic. You can set up your laptop to go to a hibernation mode or to a standby mode when the LCD is closed. It’s done through power management software. These modes are triggered when the display is closed and the lid close switch is pressed down.

COMPLETE HARDWARE PARTS OF A LAPTOP/NOTEBOOK

LCD SCREEN VIDEO FLEX CABLE

LAPTOP LI-ION BATTERY
HIGH CAPACITY EXTERNAL UNIVERSAL LI-ION BATTERY PACK
AC ADAPTOR
It provides power to the system and recharges the batteries when they are low. It comes with a detachable power cord. It encloses 2-pin or 3-pin plug type. Because in its universal, it can receive a range of AC voltage from 100 – 240 volts.

UNIVERSAL POWER ADAPTER
EXPRESS CARD ADAPTERS
PC CARD OR CARDBUS
LAPTOP/NOTEBOOK COOLING PAD

DOCKING STATION & PORT REPLICATOR

IV. DESKTOP AND LAPTOP/NOTEBOOK COMPARISON
CRT
DESKTOP
DESKTOP SYSTEM UNIT
LCD
DESKTOP MONITOR
DESKTOP KEYBOARD
DESKTOP PROCESSOR
LAPTOP
LAPTOP SYSTEM UNIT
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
LAPTOP KEYBOARD
LAPTOP PROCESSOR

DESKTOP MOTHERBOARD
3.5” IDE 40 PINS
DESKTOP HARDISK
DDR2 240 PINS DIMM
DDR1 184 PINS DIMM
DESKTOP MEMORY
DESKTOP PCI LAN CARD
DESKTOP VIDEO CARD
LAPTOP MOTHERBOARD
2.5” IDE 44 PINS
LAPTOP HARDISK
200 PINS SODIMM PINS
214 PINS MICRO SODIMM
LAPTOP MEMORY
INTERNAL WIRELESS CARD WIMAX PC CARD (WIFI CARD) WIRELESS LAN PCMCIA
CARD
LAPTOP LAN CARD
LAPTOP VIDEO CARD

PCI INTERNAL MODEM
DESKTOP MODEM LAPTOP MODEM
INTERNAL MICRO PCI MODEM
PCMCIA MODEM
DESKTOP CD-ROM DRIVE
DESKTOP BTX POWER SUPPLY
DESKTOP CPU HEATSINK FAN (HSF)
DESKTOP OPTICAL MOUSE
DESKTOP VGA CABLE
LAPTOP CD-ROM DRIVE
AC ADAPTOR
LI-ION BATTERY PACK
LAPTOP POWER SUPPLY
LAPTOP CPU HSF
LAPTOP TOUCHPAD
FLEX TYPE
RIBBON TYPE
LAPTOP VGA CABLE

PCI SLOT
DESKTOP CMOS BATTERY
DESKTOP PCI SLOT
PCI EXPRESS SLOT
LAPTOP CMOS BATTERY
LAPTOP MICRO PCI SLOT

V.
Portability Flexibility
LAPTOP/NOTEBOOK ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES
ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES Speed Little bit expensive
Light in weight Low-Energy Consumption Built-in UPS Integrated Design
Limited Hardware Upgrade or not easily upgraded Greater Risk of being loss & stolen Greater Risk of being damage Not ergo for extensive typing Limited hardware availability Repair cost are expensive Not easy to isolate or swap parts for troubleshooting
Upgradeable Laptop System Components
Component Upgradeable NotesMotherboard
CPU
Memory
Video adapter/chipset
Video display
Keyboard/pointing device
Hard disk
Removable-media drives (floppy, CD/DVD, CD-
RW/DVD+-RW)USB, IEEE 1394
(FireWire/i.LINK), serial (RS-232), parallel (IEEE 1284), SCSI, and so on
10/100/1000Mbps Ethernet LAN
Wireless 802.11a/b/g (Wi-Fi), Bluetooth
No
Yes
Yes
No1
No2
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Nonstandard form factors prevent internal upgrades.Installing a faster CPU of the same type and model is usually possible; however, there can be limitations due to voltage, thermal, and/or BIOS support issues, and clock speed increases will normally be small.Normally, only one or two SIMM/DIMM sockets are available. You may need to remove lower-capacity existing modules to upgrade.Video is integrated into a non-upgradeable motherboard.Nonstandard form factors and connections prevent internal upgrades.Nonstandard form factors and connections prevent internal upgrades.Older systems might not have BIOS support for drives larger than 8.4GB. Many systems are limited to 9.5mm- or 12.5mm-thick drives. Drive trays or caddies are often required for installation.
Install these internally via modular bays or use external USB or IEEE 1394 (FireWire/i.LINK) drives.
Install these via PC Card/CardBus or ExpressCard adapters.
Install this via a PC Card or CardBus adapters.
Install these via PC Card, CardBus, Mini PCI (internal) cards, or mobile daughter cards (MDCs). Internal cards may require preinstalled antennas.
1. It is normally possible to connect an external display and use it in lieu of or in addition to the existing internal display.2. It is normally possible to connect an external keyboard and/or pointing device to use in lieu of or in addition to the existing internal devices.