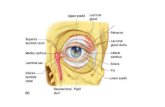
Lacrimal system ii,03.08.2016, a.r.rajalakshmi
-
Upload
srikanth-k -
Category
Healthcare
-
view
66 -
download
2
Transcript of Lacrimal system ii,03.08.2016, a.r.rajalakshmi

Lacrimal System II
Dr AR Rajalakshmi

Tear Film
Functions of the tear film :• provide a smooth optical surface at the air–cornea
interface• serve as a medium for removal of debris• contains a vast number of antimicrobial agents,
protect the ocular surface• lubricates the cornea–eyelid interface & prevents
desiccation of the ocular surface.

Pre-corneal tear film
Trilaminar structure


Spread of the tear film : • Normal blink reflex. • Contact between the external ocular surface
and the eyelids. • Normal corneal epithelium.

Lipid LayerComposition• The anterior layer of the
tear film• contains polar
(phospholipids)and nonpolar lipids (waxes, cholesterol esters and triglycerides )
• Lid movement during blinking is important in releasing lipids from glands
Functions• retard evaporation
• maintain a hydrophobic barrier (lipid strip) that prevents tear overflow by increasing surface tension
• prevent damage to eyelid margin skin by tears
Deficiency results in evaporative dry eye

Aqueous Layer
• 95% by the main lacrimal glands and rest by the accessory lacrimal glands of Krause and Wolfring
• Basic & Reflex Secretion of tears.
• Composition • Water, electrolytes,
dissolved mucins and proteins.
• Growth factors
Functions • supply oxygen to the
avascular corneal epithelium• Antibacterial activity due to
proteins such as IgA, lysozyme and lactoferrin.
• Wash away debris and noxious stimuli & facilitate the transport of leukocytes after injury.
• smooth minute irregularities of the anterior corneal surface

Mucin LayerComposition • Mucins are high molecular
weight glycoproteins that may be transmembrane or secretory in type.
• Secretory mucins are produced mainly by conjunctival goblet cells & lacrimal glands.
• The superficial epithelial cells of the cornea and conjunctiva produce transmembrane mucins that form their glycocalyx
Functions • To permit wetting by converting
the corneal epithelium from a hydrophobic to a hydrophilic surface.
• Lubrication. • Deficiency of the mucous layer
may be a feature of both aqueous deficiency and evaporative states. Goblet cell loss occurs with cicatrizing conjunctivitis, vitamin A deficiency, chemical burns and toxicity from medications.

Tear Dysfunction
• change in the amount of tear-film constituents• change in the composition of tear film• uneven dispersion of the tear film because of corneal
surface irregularities• ineffective distribution of the tear film caused by
eyelid–globe incongruity

Dry eye has been defined as • “a multifactorial disease of the tears and
ocular surface that results in symptoms of discomfort, visual disturbance, and tear-film instability with potential damage to the ocular surface” (Dry Eye Workshop, 2007)

Mechanism of Dry eye disease
DRY EYE DISEASE
TEAR INSTABILITY
TEAR HYPEROSMOLARITY
INFLAMMATION
OCULAR SURFACE DAMAGE

Classification


CLINICAL FEATURES
Symptoms :• feelings of dryness, grittiness and burning that
worsen over the course of the day• Stringy discharge• Transient blurring of vision• Redness and crusting of the lids

Signs :• Posterior (seborrhoeic)
blepharitis

Conjunctiva:• Redness. • Staining with fluorescein and rose Bengal • Keratinization. • Conjunctivochalasis- a common response to, and
exacerbating factor for, the chronic irritation of dry eye

Tear film
Mucous Debri in tear film
Thin marginal tear meniscus

Cornea Punctate erosions
Punctate erosions, filaments
Filamentary keratopathy
Mucous plaque

Complications-vision-threatening • Epithelial breakdown• Corneal melting • Corneal perforation • Bacterial keratitis

INVESTIGATIONS
• Stability of the tear film as related to its break-up time (BUT).
• Tear production (Schirmer, fluorescein clearance and tear osmolarity).
• Ocular surface disease (corneal stains and impression cytology).

Tear film break-up time

Schirmer test
• no. 41 Whatman filter paper• Schirmer I without
anaesthesia• Schirmer II with anaesthesia• Less than 10 mm of wetting
after 5 minutes without anaesthesia or less than 6 mm with anaesthesia is considered abnormal.

Ocular surface staining
• Fluorescein stains corneal and conjunctival epithelium where there is sufficient damage to allow the dye to enter the tissues

Rose Bengal• Stains dead or devitalized epithelial cells that
have a lost or altered mucous layer

• Lissamine green similar to Rose Bengal• Interpalpebral staining of the cornea and
conjunctiva is common in aqueous tear deficiency

• Other investigations :• Fluorescein clearance test -Delayed clearance • Tear film osmolarity • Tear constituent measurement • Tear meniscometry • Impression cytology

TREATMENT
• International Dry Eye Workshop (DEWS) 2007• control of symptoms and the prevention of
surface damage • Treatment options depend on the level of
severity of disease graded from 1 to 4.• The DEWS guidelines can also be applied in a
graded approach, proceeding to the next level if the preceding measures are inadequate.

Level 1 • Education and environmental/dietary modifications • Systemic medication review• Artificial tear substitutes • Eyelid therapy
Level 2• Non-preserved tear substitutes • Anti-inflammatory agents • Tetracyclines • Punctal plugs. • Secretagogues • Moisture chamber spectacles and spectacle side shields
Level 4 • Systemic anti-inflammatory agents. • Surgery - Eyelid surgery, such as tarsorrhaphy. - Salivary gland autotransplantation. - Mucous membrane or amniotic membrane transplantation for corneal complications
Level 3 • Serum eye drops. Autologous or umbilical cord serum. • Contact lenses. • Permanent punctal occlusion

Tear substitutes
• based on replacement of the aqueous phase of the tear film
• Drops and gels • Ointments• Artificial tear inserts• Eyelid sprays• Mucolytic agents

Punctal occlusion • Punctal occlusion
reduces drainage and preserves natural tears and prolongs the effect of artificial tears.
• Moderate to severe KCS who have not responded to frequent instillation of topical agents.
• Temporary – Collagen plugs
• Reversible prolonged occlusion can be achieved with silicone or long-acting (2–6 months) collagen plugs
• Permanent

Anti-inflammatory agents • Topical steroids
– effective supplementary treatment for acute exacerbations. • Omega fatty acid supplements (e.g. omega-3 fish oil, flax seed
oil)– facilitate the reduction of topical medication.
• Oral tetracyclines – may control associated blepharitis– reduce tear levels of inflammatory mediators.
• Topical ciclosporin (usually 0.05%) – reduces T-cell mediated inflammation of lacrimal tissue– increase in the number of goblet cells – reversal of squamous metaplasia of the conjunctiva.

Miscellaneous options
• Optimization of environmental humidity – Reduction of room temperature to minimize
evaporation of tears & Room humidifiers • Botulinum toxin injection • Oral cholinergic agonists • Submandibular gland transplantation • Serum eye drops

• Name 2 investigations for dry eye• Draw the layers of Tear film• Functions of tear film

Reference & Further study:• Parson’s Disease’s of the eye 21st ed• Kanski Clinical Ophthalmology 8th ed• AAO BCSC 2015-16 Vol 8 External Diseases &
Cornea