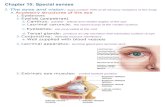
Lacrimal apparatus Consists of lacrimal gland and several ducts Ducts drain lacrimal secretions into...
-
Upload
shannon-may -
Category
Documents
-
view
282 -
download
0
Transcript of Lacrimal apparatus Consists of lacrimal gland and several ducts Ducts drain lacrimal secretions into...


Lacrimal apparatus• Consists of lacrimal gland and several ducts
• Ducts drain lacrimal secretions into nasal cavity
• Gland continually release dilute salt solution (ie; tears) to anterior (front) surface through ducts…

Tears (lacrimal secretion) flush across eyeball into…
Lacrimal canals
Lacrimal sac
Nasolacrimal duct
Nasal cavity
• Lysozyme enzymes destroy bacteria• Cleans and protects eyeball
•When there is an increase in lacrimal secretion, tears fill eyelids and nasal cavities causing congestion

3 Tunics (Coats)
1. Outer• Fibrous• Aqueous humor (fluid)
2. Middle• vascular
3. Inner• Sensory• Vitreous humor (fluid)

Outer Tunic
• Scelera• White part of the eye
• Cornea• light enters• a lot of nerve endings…especially pain• most exposed• can be transplanted one individual to another without
rejections because there is no blood flow, therefore, no connection to the immune system where rejections occur.• Aqueous fluid between cornea and lens supplies nutrients and
oxygen

Middle Tunic
• Choroid• Prevents light scattering• Merges in to “ciliary bodies” that the lens (used for focusing) attaches by “ciliary zonule” ligament
• Iris• Colored part of the eye• Regulates amount of light entering eye to see clearly
• Pupil• dark = dialate… light = constriction

Inner Tunic (p.277 activity fig 8.5)
• Retina• Contains photoreceptors (rods & cones) that receive
information by responding to light• Has vitreous humor
• Gel-like fluid inside the eyeball• Holds retina flat against choroid coat giving the eye it’s spherical shape
• Fovea centralis is the point on the retina where the light rays focus• Produces the sharpest vision• Optic disc is the place where the nerve fiber leave retina and
become optic nerves• Causes a blind spot because there are no photoreceptors here

1. Electrical impulse from the photoreceptors by:a. Bipolar cellsb. Ganglion cells
2. Leaving retina via optic nerve3. When impulses are transmitted to optic cortex4. Vision results

• RODS• Most dense at edge of retina• Allows us to see gray tones• Peripheral vision
• CONES• Most dense in the center of retina• Allow us to see color
• Blue + red = purple• All 3 = white• Interpretation of color happens in the brain NOT in the retina





















![[PPT]Osteon (Haversian) System - Lone Star College – Start … · Web viewLacrimal Apparatus Lacrimal gland Canaliculi Lacrimal sac Conjunctiva Cornea Anterior cavity w/ Aqueous](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5ae7f9f47f8b9acc268f6a98/pptosteon-haversian-system-lone-star-college-start-viewlacrimal-apparatus.jpg)