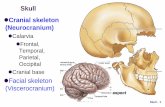
A. Divisions of the skeletal system B. Skull 1. Sutures 2. Fontanels
Label the Skeleton BR 1. Download notes and bone lists 2 ......Incomplete development Skull Many...
Transcript of Label the Skeleton BR 1. Download notes and bone lists 2 ......Incomplete development Skull Many...

Label the Skeleton BR
1. Download notes
and bone lists
2. Intro to bones
3. ID work with
models
carpals
clavicle
fibula
humerus
ilium (of coxal bone)
ischium (of coxal bone)
mandible
metacarpals
metatarsals
patella
phalanges
radius
ribs
scapula
skull
tarsals
tibia
ulna
vertebrae (lumbar)

Skeletal System
Functions:
1. Support and
protection
• Bones,
ligaments,
cartilage
2. Body movement
3. Blood cell
formation
4. Storage of inorganic
salts

Figure 7.2
Flat bone
(frontal bone)
Irregular bone
(vertebra)
Long bone (femur)
Short bone
(tarsal bone)
Bones are classified by shape:
• Long bones
• Short bones
• Flat bones
• Irregular bones

Figure 7.3a
Proximal
epiphysis
Metaphysis
Diaphysis
Metaphysis
Distal
epiphysis
(a) Humerus, anterior view
Articular cartilage
Spongy bone
Articular cartilage
Epiphyseal line
Compact bone
Spongy bone
Medullary cavity
(contains yellow bone
marrow in adult)
Endosteum
Periosteum
Perforating fibers
Nutrient artery
through nutrient foramen
Long Bone – Gross Anatomy• Diaphysis (shaft of bone)
• Compact bone – solid; gives bone its strength
• Medullary cavity
• Cavity in diaphysis – resists bending
• Contains yellow bone marrow
• Epiphysis
• Proximal and distal
• Spongy bone – withstands compressive forces
• Red bone marrow
• Metaphysis (growth plate)
• Contains epiphyseal disk/line
• Periosteum
• Covering of bone
• Important in repair
• Endosteum
• Lines medullary cavity
• Articular cartilage
• Hyaline
• Covers epiphysis

Overview of the Skeletal System
Types of boneCompact bone
• also called dense or cortical bone
• relatively dense connective bone tissue
• appears white, smooth, and solid
• 80% of bone mass
Spongy bone
• also called cancellous or trabecular bone
• located internal to compact bone
• appears porous
• 20% of bone mass

Cartilage• Hyaline cartilage
• attaches ribs to the sternum
• covers the ends of some bones
• cartilage within growth plates
• model for formation of most bones
• Fibrocartilage• weight-bearing cartilage that
withstands compression
• forms intervertebral discs
• forms pubic symphysis
• forms cartilage pads of the knees
Ligaments• Anchor bone to bone
Tendons• Anchor muscle to bone
Connective tissue keeps the skeletal system together…..

Axial vs. Appendicular Skeleton
• pectoral girdle and upper limbs
• pelvic girdle and lower limbs
• skull, hyoid, vertebral column, thoracic cage

Key Bone Terms
Sinus
• a cavity within a bone or other tissue, especially one in the bones of the face or skull connecting with the nasal cavities
Suture
• a seamlike immovable junction between two bones, such as those of the skull

Key Bone Terms
Foramen
• an opening, hole, or passage, especially in a bone
Fossa
• a shallow depression or hollow
Canal
• a tubular duct serving to convey liquid or air
Condyles
• a rounded protuberance at the end of some bones, forming an articulation with another bone

Key Bone Terms
Crest
• a ridge along the surface of a bone
Protuberance
• Anatomical landmark that appears as a blunt projection, eminence, or swelling
Process
• a natural appendage or outgrowth on or in an organism, such as a protuberance on a bone

Key Bone Terms
Meatus
• a passage or opening leading to the interior of the body

Key Bone TermsNotch
• indentation, indenture. a concave cut into a surface or edge
Tuberosity
• a large prominence on a bone usually serving for the attachment of muscles or ligaments

Download Bone list from moodle
Using the diagram book, Anatomy Revealed, and the models – start to learn the bones and bone markings –ID Test 3/17/19http://anatomy.mheducation.com/html/apr.html?animal=human&login=1551189998374
Complete Long Bone coloring by end of the block

Osteon BR
1. Formation of Bone
2. Skull and vertebral
column notes
3. Continue working
on ID and begin
organization lab
HW – Ch. 7 (5-10)
questions and labeling
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rZ
y_GMWV87g

Intramembranous Bones• Bones of the skull
• Begin to form in first few weeks of life and grow into adulthood
• Develop from layers of connective tissue differentiating
• Formed by osteoblasts (bone stem cells) which become osteocytes (mature bone cells)


Endochronal Bone Development• Most bones of the skeleton
• Begin as hyaline cartilage
• Ossification centers
– region of bone formation
– forms from the inside out
• Epiphyseal disk
– band of hyaline cartilage between ossification centers
– The direction of growth is
toward the diaphysis (shaft of
long bone).
– The newly forming spongy
bone (below the growth plate)
is not clearly organized as the
older spongy bone in the
epiphysis above the growth plate.


Endochronal Bone DevelopmentDamaged epiphyseal disk• long bone growth ceasesHomeostasis of osteoclasts (cells
that breakdown osteocytes) & osteoblasts
• reabsorption and replacementBone Cancer• abnormal increase in
osteoclastic activity

Symptoms:
•Joint and bone swelling.
•Pain.
•A hard lump felt on the
surface of a bone, often
painful when pressure is
applied.
•Fever.
•Unexplained weight
loss.
•Inability to move freely.
•Frequent bone fracture.

Fractures – All are either Complete or IncompletePartial/Incomplete• Descriptive of all breaks;
break does not completely separate the bone
Complete• Descriptive of all breaks;
break completely separates the bone

Fractures – All are either closed or open
Simple/Closed
• Complete or incomplete
• Contained within the soft tissues
• No communication with the skin or mucous membranes
Compound/Open
• Complete or incomplete
• Communicates with the outside surfaces
• Associated with bone marrow infections

Healing of a Fractured Bone1. Blood clot from fractured blood vessels form
and a hematoma results
2. Hematoma invaded by phagocytic cells
3. Osteoblasts and spongy (woven) bone formation
4. Build up of fibrocartilage
5. Cartilaginous callus (internal) forms
6. Bony callus (external) replaces fibrocartilage
7. Osteoclasts remove extra bone that forms while repairing (remodeling)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dJ-ENmMX09c



Functions of BoneSkeletal System
Support and Protection
• shape and form
• underlying tissue protection

Functions of BoneBody Movement• LeversBlood Cell Formation• hematopoiesisStorage of Inorganic
Salts• quantity of calcium
phosphate initiates osteoblasts and osteoclasts
• osteoporosis

Cranial BonesFrontal• anterior; superior to eyes
Parietal• posterior to frontal• bulge on head
Occipital• posterior and base of
cranium
Temporal• lateral and base

Cranial Bones
Sphenoid and ethmoid• create sinuses
• sinusitis

Functions of the CraniumEnclose and protect
the brain
Paranasal sinuses
• reduce weight
• increase intensity of voice through resonance

Jaw BonesMaxillary bone
• upper jaw
Mandible
• Movable
Cleft Palate

Infantile Skeleton development -SkullIncomplete development
Many fontanels (“soft spots”)• Permit movement between bones • Allow skull to be compressed during birth• Allow for continued brain growth• Eventually fuse - suturesProportions are quite different from those in
an adult skull• small face• prominent forehead• large orbits

Typical Vertebrae
• Drum shaped body
• Body and bony arch surround spinal cord
• Notches provide the foramen for spinal nerves

3 Types of VertebraeCervical• first 7Thoracic• middle 12Lumbar• last 5Scoliosis


Cervical Vertebrae
Bony axis of neck
Atlas• 1st vertebrae
• supports and balances head
Axis• 2nd vertebrae
• provides pivot of head

Thoracic Vertebrae
• Larger than cervical
• Facets articulate with the ribs

Lumbar VertebraeLarge and strongSupport most body
weightSacrum• 5 fused vertebrae
Coccyx (tailbone)• 4 fused vertebrae• lowest part of vertebral
column

Infantile Skeleton development –Vertebral Column
Spinal curvatures well developed –Primary curvatures
• Thoracic
• Sacral
Cervical curvature
• Develops as baby learns to lift his/her head
Lumbar curvature
• Develops during learning to sit and walk

Disorders
Spina Bifida
• Vertebrae do not completely develop
• Genetic – quad screen test

Spina Bifida

Disorders
Herniated Disk
• Elastic portion of disk degenerates
• Back pain; loss of muscular function

Continue working on ID from bone list on the models in the classroom.
Begin Organization Lab (won’t be due until the end of class on Friday)

Bone Labeling BR
1. Notes of
Organization
2. Work on lab and ID
HW – Finish CH. 7
HW questions for
Monday

Thoracic Cage
Shaped like an inverted cone
Ribs
Thoracic vertebrae
Sternum
• Manubrium, body, xiphoid process
Costal Cartilage
• attach ribs to sternum
Why articulate with cartilage instead of bone?

Functions of the Thoracic Cage
• Support pectoral girdle and arms
• Protect organs
–Heart and lungs
• Aid in breathing

Ribs• 12 pairs
– first seven are true
– last five are false
• Curves around chest and slope downward
• Articulate with transverse process on vertebrae

Sternum
Breast bone
Articulates with the clavicle
Red marrow
• produces RBC
Sternal puncture
• thin compact bone so easy to obtain marrow for diagnosis

Pectoral Girdle • Incomplete ring
• 2 Clavicles (collar bone)
– slender, elongated
– hold shoulders in place
– attachment site for muscles of the arm, chest, back
• 2 Scapula (shoulder blade)
– broad, triangular bones
– articulates with humerus

Upper LimbHumerus
• articulates with radius & ulna
Radius
• elbow to wrist
• articulates with humerus, ulna, wrist
Ulna
• overlaps humerus
• articulates laterally with radius
Hand
• carpals, metacarpals, phalanges

Pelvic GirdlePelvis
• sacrum, coccyx, girdle
2 Coxal bones (3 fused bones)
• Ilium (hipbone)
• Ischium (“butt” bone tuberosity
• Pubis
• Fused at the symphysis pubi

Lower Limb• Femur
– knee to hip
– longest bone in the body
• Tibia
– shinbone
• Fibula
– lateral to tibia
– bears no weight
• Foot
– Tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges
– calcaneus

Male v. Female Skeleton Male
• larger
• hip bones more narrow
• more bone mass
Female
• wider hip bones
• angle at symphysis pubis is greater
• less bone mass

Continue working on ID from bone list on the models in the classroom.
Begin Organization Lab (won’t be due until the end of class on Friday)
Learn the lower limb
“Quiz” at 10:35
pollev.com/kbrelsf872

Label the Skull BR
** Turn in lab
1. Notes on
movements
2. Work on ID -
particularly the
skull
HW – xsword – Wed
Quiz – Wed
ID Practical – 3/14

Types of JointsFibrous (immovable)
• Sutures
• Between skull bones
Cartilaginous (slightly movable)
• symphysis pubis
• between vertebrae
• Between ribs and sternum
• Connected with disks offibrocartilage
Synovial (movable)
• Most common
• Synovial fluid

Types of Joints - Synovial
Covered with hyaline cartilage
Bursae
• Fluid filled sacs b/w skin and processes

Types of Joints - Synovial
Ball and socket
• Shoulder and hip
• Highly movable joint
• Allow movement in all directions
Condyloid
• Metacarpals and phalanges
• Metatarsals and phalanges

Types of Joints - SynovialGliding (sliding)• Wrist and ankle• Allows bones to slide in all
directions
Hinge• Elbow• Knee• Allows bones to
move back and forth

Types of Joints - SynovialPivot
• Radius and ulna
Saddle
• Thumb

Arthroscopy

Arthritis• Inflamed, swollen joints
Osteoarthritis
• Most common; old age
• Articular cartilage wears down

ArthritisRheumatoid
• Autoimmune disorder
• Cartilage replaced by bone
• Very disfiguring

ArthritisInfectious/Acute
• Bacterial infection
• Lyme disease
Gouty
• Result of uric acid being deposited b/c kidneys are not properly filtering
• Deposited in great toe first

Gouty Arthritis

Additional DisordersRickets
• Soft bone condition in children
• Lack of calcium and/or vitamin D
Osteomyelitis
• Acute or chronic bone infection
• Commonly caused by bacteria (at times – fungi)

Flexion - Extension• decrease - increase angleAbduction - Adduction• away - toward midlineRotation• around an axisPronation - Supination• palm down -palm upElevation - Depression• raising - lowering

Continue working on ID from bone list on the models in the classroom.
Learn the skull
“Quiz” at 11:50
pollev.com/kindrabrelsf872

Label the Upper Limb
BR
1. Joint movements
lab
2. Work on ID
3. Upper limb, coxal
bone, and sacrum at
10:35
HW – study
ID Practical – 3/13


Label the Long Bone BR
1. Review xword
2. Review Game
3. Quiz
4. Bone ID review
• Practice practical
5. Naming muscles
HW – Ch. 8 (1-14)
ID Practical – 3/13