L2 BICHAT 2019-2020 - Accueil · Web viewCollar bone 4) Sternum Breast bone 5) Rib Ribcage 6)...
Transcript of L2 BICHAT 2019-2020 - Accueil · Web viewCollar bone 4) Sternum Breast bone 5) Rib Ribcage 6)...

UE9 AnglaisED 211/02/2020 de 8h30 à 10h30Ronéotypeur : Léo Lévy
ED d’Anglais n°2
Ronéo 4 1 sur 11

Cet ED comprend la fin du 1er manuel « medical english curriculum » commencé à la séance précédente, ainsi que le début du 2ème manuel. Cette première partie porte sur le premier manuel violet
Tissues, Gap Filling p12:
• The cells in a tissue are not identical, but they* work TOGETHER to accomplish specific functions.
• Connective tissue (= tissus conjonctif) is the tough, often fibrous tissue that binds the body's structures to-gether. It* is present in almost every ORGAN, forming a large part of skin, tendons, and muscles.
Vocabulary p13-14 :
• To make a reference (by a specific name) : TO REFFER TO• A portion, piece, or segment that is representative of a whole; a specimen : SAMPLE => blood, urine,
stool.• The region of the digestive and respiratory tracts extending from the back of the mouth (nasopharynx) to
just below the larynx, including the pharynx, the larynx, and related structures : THROAT• The internal structure composed of bone and cartilage that protects and supports the soft organs, tissues,
and other parts of the body : SKELETON• A disk-shaped, biconcave cell in the blood that contains hemoglobin, lacks a nucleus, and transports oxy-
gen and carbon dioxide to and from the tissues. : RED BLOOD CELL / ERYTHROCYTE
Complete the sentence p15 :
The functions of epithelium and connective tissue are to provide structure and support, to bind cells toge-ther, and to perform functions like secretion and absorption.
True or False p15 :
1) In total, there are 4 types of tissue in the body : FALSE
4+1 basic types : Epithelium, Connective tissue, Muscle tissue, Nervous tissue, Vascular ; but a lot of subtypes : Muscles => smooth, skeletal and cardiac.
2) Skeletal muscle is under voluntary nervous control, whereas smooth and cardiac muscles contract without nervous control : FALSE
Autonomic nervous system (ANS) controls/regulates smooth and cardiac muscles (fight or flight reaction)
Skeletal muscles Cardiac / Smooth muscles
- Voluntary nervous system- The information goes from the Central nervous
system (CNS) to the Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
- Involuntary nervous system- ANS => Sympathetic, Parasympathetic - Regulation action
Ronéo 4 2 sur 11

Vocabulary p16:
A small, pear-shaped muscular sac, located under the right lobe of the liver, in which bile secreted by the liver is stored until needed by the body for digestion : GALLBLADDER (= Vésicule biliaire)
Written comprehension p17:
What are organs ? What are they made up of ?
- Several types of tissues- Specific function- Specific location, stationary position in the body
Which cells control the amount of light that enters the eye ?
The Iris controls the amount of light that enters the eye.
Light crosses the lens and is projected to the fauvea which contains photoreceptor cells (cones => color vi-sion, rods => black and white vision). After that, the optic nerve conducts the impulse to the occipital lobe.
True or False p17:
1) A synonym for the heart is the « Myocardium » : FALSE
Myocardium is a tissue of the heart, which is made of three layers from the outside to the inside :
- Pericardium, outer lining (serous membrane)- Myocardium : « heart muscle proper »- Endocardium, inner lining
The heart contains also connective tissue, nervous tissue, vascular tissue, and valvular tissue
2) Blood contains several different types of cells, with different functions, and should therefore be considered as an organ : FALSE
Blood doesn’t have a stationary position in the body, so therefore isn’t an organ.
3) The light-sensitive cells in the pupil control the amount of light that enters the eye : FALSE
It is the cells in the iris, that is indeed a muscle, which controls the amount of light that enters the eye. The image is projected on the retina which contains ganglion cells responsible of detecting the amount of light, and they trigger the autonomic nervous system (ANS). The oculomotor nerve contains the sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers that regulate the movements of the muscles in the pupil.
There are two types of muscles : - circular muscles = sphincter pupillae (parasympathetic NS)- Radial fibers (sympathetic NS)
Ronéo 4 3 sur 11

Gap filling p18 :
- The muscular, membranous tube for the passage of food from the pharynx to the stomach : (O)Esophagus
Synonym for trachea = Windpipe
- A pair of organs in the dorsal region of the abdominal cavity, functioning to maintain proper water and electrolyte balance, regulate acid-base concentration, and filter the blood of metabolic wastes, which are then excreted as urine : Kidney
- A large, reddish-brown, glandular organ located in the upper right portion of the abdominal cavity that se-cretes bile and is active in the formation of certain blood proteins and in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins : Liver
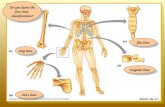
Match the descriptions on the right with the appropriate anatomical structure on the left, p2 :
Ronéo 4 4 sur 11

Grammar, p20 :
Three ways of expressing « Permettre » in english
1. PERMETTRE A QN. DE FAIRE Quelque CHOSE= ALLOW SOMEONE TO DO SG.
Lungs allow people to breath.
2. IMPERSONAL STRUCTURE: SG. MAKES IT POSSIBLE TO
Ex. Ribosomes make it possible to synthesize proteins.
3. PASSIVE: CAN/CANNOT + BE + PAST PARTICIPLE
Ex. Cells can be seen with microscopes.
Traduction p20 :
1. Historiquement l’invention du microscope a permis aux scientifiques de découvrir non seulement que la cellule était l’unité fondamentale de la vie, mais aussi que beaucoup de maladies étaient provoquées par des microbes comme les bactéries :
Historically, the invention of the microscope allowed scientists to discover not only that the cell was the basic (fundamental) unit of life, but also that many illnesses (deseases) were caused by microbes like bacteria.
2. Le microscope électronique permet d’observer des structures comme les ribosomes, que les microscopes optiques ne permettent pas de distinguer :
The electron microscope makes it possible to see structures such as ribosomes which cannot be distin-guished with light microscopes.
Ronéo 4 5 sur 11

La deuxième partie va porter sur le deuxième manuel orange.
The skeletal system p2 :
Medical Term
Everyday English
1) Cranium Skull
2) Mandible Lower jaw
3) Clavicle Collar bone
4) Sternum Breast bone
5) Rib Ribcage
6) Vertebra,ae Vertebral column, backbone, spine
7) Humerus
8) Ulna,ae
9) Radius,i
10) Pelvis Hip bone
11) Femur Thighbone
12) Patella Kneecap
13) Tibia,ae Shinbone
14) Fibula,ae Calfbone
Gap Filling p1-2 :
- This system includes not only the stomach, small intestine, and LARGE intestine (=Colon), which move and absorb food, but also associated organs such as the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder, which produce digestive enzymes, remove toxins, and store substances necessary for digestion.
Ronéo 4 6 sur 11

- The digestive system even directly stimulates the heart through nerve impulses and chemicals released into the bloodstream. The heart responds by pumping more BLOOD . The brain responds by perceiving less hunger, more fullness, and less interest in vigorous activity.
Vocabulary p 2-3 :
- A pathological condition of a part, an organ, or a system of an organism resulting from various causes, such as infection, genetic defect, or environmental stress, and characterized by an identifiable group of signs or symptoms : DISEASE (synonym : illness, sickness, condition, pathology)
- A useless or worthless by-product 2. The undigested residue of food eliminated from the body; excre-ment : WASTE
Waste eliminated via a bowel movement => Stools, FecesWaste eliminated via the urinary tract / Kidney => Urine
- To reserve or put away for future use : TO STORE- A point of articulation between two or more bones, especially such a connection that allows motion :
JOINT- The flow of blood through the circulatory system of an organism : BLOODSTREAM
Written Comprehension p3 :
1. How is food broken down in the digestive tract ?
The food is broken down mechanically into smaller pieces in the mouth via chewing and through the whole digestive tract via muscular peristalsis. It is then digested by enzymes secreted by glandular organs such as the liver, gallbladder, or pancreas.
2. How does the brain react during digestion ?
Baroreceptors in the wall of the stomach perceive the distension. These baroreceptors are linked to the va-gus nerve, which conducts the impulse to the hypothalamus that perceives satiety.At the same time, leptin hormone is produced in order to reduce the feeling of hunger.
3. How does the cardiovascular system react ?
Parasympathetic => VasodilationSympathetic => Vasoconstriction
True or False p3 :
1. The digestive system needs more blood during digestion because its work increases : TRUE
Smooth muscles need more oxygen to produce movement. The absorption of nutrients requires also more blood flow.
Hormones need blood flow to circulate : Gastrin is needed to induce the secretion of gastric juice, Secretin does the same to induce the secretion of pancreatic enzymes, and CCK permits the secretion of bile.
2. Organs can belong to more than one organ system : TRUE
Ronéo 4 7 sur 11

- Pancreas => Digestive system and endocrine system- Stomach => Digestive system and endocrine system- Bone (marrow) => Hematopoietic system and musculoskeletal system
Gap Filling p6 :
One of the best-known transmitters is the hormone epinephrine (adrenaline). When a person is suddenly STRESSED or frightened, the brain instantly sends a message to the adrenal glands (= suprarenal gland) , which quickly release epinephrine. Within moments, this chemical has the entire body on alert, a response sometimes called the "fight-or-flight" response.
Vocabulary p 7-8 :
- Two small, dissimilarly shaped endocrine glands, one located above each kidney, consisting of the cortex, which secretes several steroid hormones, and the medulla, which secretes epinephrine : ADRENAL GLANDS
- To grow gradually less or smaller in number, amount, or intensity, diminish : DECREASE
Synonym : drop, fall, lessen, dwindle, plumet, wane
- A sensation of dryness in the mouth and throat related to a need or desire to drink. The desire to drink : THIRST, being THIRSTY
Written comprehension p9 :
- What systems is the communication necessary for homeostasis carried out by? How many major categories of chemical transmitters are there ? (What are they ?)
Homeostasis is maintained with the help of the endocrine system that produces hormones that help organ systems to communicate, and the autonomic nervous system (ANS) that communicates via neurotransmit-ters.
- What bodily processes does dehydration trigger ?
2 types of receptors :
• Baroreceptors : perceive blood pressure in the wall of arteries • Osmoreceptors : detect the concentration of ions in the blood
Ronéo 4 8 sur 11

These receptors communicate with the hypothalamus, and the hypothalamus communicates with the pitui-tary gland which produces vasopressin or antidiuretic hormone. These hormones trigger the kidneys to retain water, and also induces vasoconstriction to increase blood pressure.
True or false p9 :
- Vasoconstriction and vasodilation are examples of homeostasis : FALSE (incomplete)
It can be pathological : Raynaud’s disease, nicotine…
La prof n’a pas eu le temps de finir le manuel, la suite sera traitée dans la prochaine ronéo.
Dédicaces :Ronéo 4 9 sur 11

Ronéo 4 10 sur 11

Bon cette fois c’est Dan le chef ronéo donc j’peux pas trop mettre de photo de lui. Ducoup j’me suis rabattu sur les 2 autres lascars :
Ronéo 4 11 sur 11