Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
-
Upload
faninfajrifauzi -
Category
Documents
-
view
230 -
download
0
Transcript of Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
1/21
KULIAH SISTEMKARDIOVASKULAR
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
2/21
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
A. ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
B. THE HEART
C. THE ARTERIAL PULSE
D. BLOOD PRESSURE
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
3/21
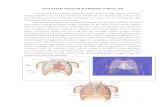
A. ANATOMY AND
PHYSIOLOGY1. SUFACE PROJECTION OF THE HEART AND
GREAT VESSELS
Right Ventricle :
( + ) the pulmonary artery A Wedgelike structure
behind and to the left f the sternum
Inferior border : below the junctional of the sternumand the Xiphoid Process
Meets The pulmonary artery : 3rdleft costal cartilage
close to the sternum
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
4/21
Left Ventricle : Lying to the left of and behind to the right ventricle
Forms the left border of the heart and produces the apical
impulse ( 5thinterspace, 7-9 cm from the midsternal )
Right Atrium :
Forms the right border of the heart
Not usually identifiable on physical examination
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
5/21
Left Atrium :
Mostly posterior and cannot be examined directly
The Aorta :
Curves upward from the left ventricle to the level of thesternal angle arches backward down
The superior Vena Cava :
on the right, empties into the right atrium
The Inferior Vena Cava :
Base :the right and the left 2nd interspace close to thesternum
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
6/21
2. CARDIAC VALVES
Tricuspid left atrioventricular valvemitral right atrioventricular valve
Aortic and Pulmonic semilunar valve
As the heart valve close normal heart sounds
3. CARDIAC CYCLE
Systole the period of ventricular contraction
Diastole the period of ventricular contraction
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
7/21
4. HEART SOUND
S1 2 COMPONENTS :
Mitral sound : much louder, can be heard best at thecardiac apex
Tricuspid sound : softer, heard best at the louder left sternalborder
S2 2 OMPONENTS :
The Aortic valve closure ( A2 )
The pulmonic value closure ( p2 )
S3 Rapid ventricular filling as blood flows early indiastole rom left atrim to left ventricle
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
8/21
S4 ATRIAL CONTRACTION
EARLY SYSTOLIC EJECTION SOUND ( EJ )
Accompanied the opening of the aortic valve
OPENING SNAP ( OS ) The mitral valve opens ( in
mitral stenosis )
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
9/21
5. HEART MURMURS
LONGER DURTION
ATRIBUTED TO TURBULENT BLOOD FLOW
MAY INDICATE SERIOUS DISEASE THE MEANING OF MURMUR MUST BE ABLE TO
TIME THEM IN THE CARDIAC CYCLE ANDIDENTIFY WHERE THEY CAN BE HEARD BEST
6. RELATION OF AUSCULTATORY FINDINGS TO THECHEST WALL SOUND AND MURMUR THATORINATE IN :
The Mitral valve at and around the cardiac apex
The Tricuspid valve the lower left sternal border
The Pulmonic valve the 2ndand 3rdleft interspace close tothe sternum
The Aortic valve may be heard anywhere from the right2ndinterspace to the apex
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
10/21
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
11/21
If ( - ) ask patient to exhale fully and stop breathing for
a few second
If ( + ) make finer assessments with fingertips and then
withone finger ( location, diameter, amplitude and duration
)
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
12/21
THE LEFT STERNAL BORDER IN THE 3RD, 4TH AND
INTERSPACE ( RIGHT VENTRICULAR AREA )
The patient should rest supine at 30o
Place the tips of your curved finger in the 3rd, 4th,and 5th
interspace and try to feel the systolic impuls of the right
ventricle
Improves your observation asking the patient to breath
out and then briefly stop breathing
Location, amplitude and duration
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
13/21
THE EPIGASTRIC ( SUB XIPHOPID ) AREA
Useful when examine a person with an increased
anteroposterior diameter of the chest
2. PERCUSSION
IN MOST CASES, PALPITATION HAS REPLACEDPERCUSION IN THE ESTIMATION OF THE
CARDIAC SIZE
PERSUS FROM RESONANCE TOWARD CARDIAC
DULLNESS IN THE 3RD
, 4TH
, 5TH
AND POSSIBLY6THINTERSPACES ( THE LEFT ON THE CHEST )
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
14/21
3.AUSCULTATION
LOCATION : 2ndinterspace close to the sternum ( right aortic, lelt
pulmonic )
Along the left sternal border in each interspace from 2nd
through 5th
interspaces ( tricuspid ) The apex ( mitral ) if the heart is enlargedor displaced, you
should alter your pattern accordinely
SEQUENCE :BASE APEX OR APEX BASE
STETOSCOPE : THE DIAPRAGHM S1 AND S2 ;MURMUR OF AORTIC AND MITRAL REGURTATION
THE BELL S3 AND S4 ; MURMUR OF MITRAL
STENOSIS
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
15/21
POSITION :
Supine entire precordium
Roll partly ontothe left side the apical impulse ( bell )
Sit up, lean forward, exhale completely and stop breathing
along the left sternal border and at the apex ( diaphraem ).
Pausing periodically so the patient may breath .
WHAT TO LISTEN FOR ?
S1 intensity, spliting ?
S2 intensity, spliting ?
Extra sound in systole ( ejection sound or systole click )
Extra sound in diastole ( S3, S4, or opening snap )
Systolic murmurs
Diastolic murmurs
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
16/21
C. ARTERIAL PRESSURE
HEART RATE
The Radial Pulse
The pads of your index and middle fingers a maximalpulsation is detected
Rhythm is regular and the rate seems normal 15 seconds
and multiply by 4
The Rate is unusual , fast or slow 60 seconds
The rhythm is irregular the rate should be evaluated by
cardiac auscultation
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
17/21
D. BLOOD PRESSURE CHOICE OF SPHYGMOMANOMETER
Choose a cuff of appropriate size
The inflatable bladder of the cuff :
- Width about 40 % of limbs circumference
- Length about 80 % of limbs circumference
Aneroid or Mercury Type
An aneroid instrument often becomes inaccurate with
repeated use so it should be recalibrated periodically
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
18/21
TECHNIQUE
- Avoid smoking or ingesting caffeine for 30 minutes
- Rest for at least 5 minutes
- The room should be quiet and comfortably warm
- The arm selected should be resting and free of
clothing
- Free of : a. Arteriovenous fistules for dyalisis
b. Scarring from Brachia Artery
cutdown
c. Lymphedema
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
19/21
- The Brachial Artery should at the heart level
( 4th interspace at its junction with the sternum )
- The patients arm so that it is slightly flexed at the
elbow
- The inflatable bladder over The Brachial Artery
- The lower border of the cuff should be about 2,5
cm above The Antecubital Crease
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
20/21
1. Feel The Radial Artery with the fingers of one hands
rapidly inflate the cuff until the radial pulse disappears
2. Read this pressure on the manometer and add 30
mmHg to it
3. Deflate the cuff promptly and completely and wait 15
30 minutes
4. Place the bell of a stethoscope lightly over The
Brachial Artery
5. Inflate The Cuff rapidly again to the level just determined
and then deflate it slowly at a rate of about 2-3 mmHgg /
seconds
-
8/12/2019 Kuliah Sistem Kardio Vaskular
21/21
6. Note the level at which you hear the sounds of at least twoconsecutive beats ( Systolic Pressure )
7. Continue to pressure slowly until the sounds become
muffled and then disappear ( Diastolic Pressure )
8. To confirm the disappearance of sounds, listen as thepresure falls another 10-20 mmHg then deflate the cuff
rapidly
9. Wait 2 or more minutes and repeat and take the
average. If the first two readings differ by more than
5 mmHg, take the additional readings