Justification for Echelon Foot: Descriptor; Dorsi Flexion ... · The Echelon Foot provides dorsi...
Transcript of Justification for Echelon Foot: Descriptor; Dorsi Flexion ... · The Echelon Foot provides dorsi...

Justification for Echelon Foot: Descriptor; Self Aligning Feature, with Adjustable HydraulicPlantar & Dorsi Flexion Control
Patient Name: Above Knee: Below Knee:
Prosthetist: Facility:
Date:
Dear Medical Professional/Insurance Adjuster
As no particular code exists for the specific function of the Echelon Foot, a code ofL-5999 withthe above descriptor must be used. Please read the information which describes the major benefitof the Echelon Foot for an amputee.
The Echelon Foot provides dorsi flexion and plantar flexion including a feature of automaticalignment to terrain. It is designed to facilitate walking on level or uneven ground, up and downinclines, ascending or descending stairs and sitting down at ease. The Echelon's continuousadjustment to terrain helps give the amputee better distribution of forces at the interface from theprosthesis to the body. Through increasing knee stability and safety for the amputee the risk offalls is significantly reduced and confidence is increased as a result. The Echelon and it's uniqueability to self align distinguish it from all other conventional ankle-foot systems.
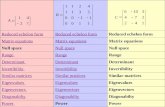
When the user walks on level terrain the Echelon Foot remains in a dorsi flexed position after"toe off'. This enables the user a greater ground clearance during swing phase, minimizing therisk of catching the toe and potentially falling. At heel strike the foot moves into plantar flexionto initiate a stable safe base for loading of the prosthesis. When the amputee walks up or downinclines the hydraulic fluid adjusts the foot to match to the gradient. In stair ascent Echelonmoves up to 9 degrees (seefig J) during the first step. Similarly when descending stairs thehydraulic ankle allows dorsi flexion during the first step which permits the user to place theentire prosthetic foot on the subsequent downward step further enhancing safety and comfort.
I, j~.§~
r\,_~.1 '3'JJ.J t=~ i Ij !
I '~!\ I Hydraulic AnkleI"
<;) \1,~ __I?) 0
Fig L Echelon model of the self-aligning with plantar/dorsi flexion motion
How this is achieved:
Apart from prosthetic socket fit, the alignment of prosthesis (e.g. the geometrical positioning ofthe prosthesis relative to the body) has a profound effect on the function that the prosthesisprovides and the long-term rehabilitation outcomes for amputees. The main drawback withcurrent prostheses is that all the prosthetic foot designs are based upon an ankle-foot mechanismthat continually force the ankle-foot towards a fixed position established by the prosthetist duringfitting in a clinic on level terrain. This means the alignment of the foot relative to the body

creates a condition where the forces transmitted through the prosthetic socket interface are biasedto achieving one specific position during weight bearing. With such ankle-foot mechanisms it ispossible to align the foot of the prosthesis to provide satisfactory function, but on level groundwalking at a fixed speed only. In contrast the relatively simple task of standing and walking onuneven inclined surfaces may present a painful and significant physical challenge for amputeesince the ankle-foot cannot realign itselfto match the altered inclination of the foot with thesurface. As a consequence the forces generated at the socket interface on the limb are no longeroptimally matched and this may lead to increased pain. In such cases a conventional prostheticlimb can hinder locomotion, balance, confidence, stability and most importantly safety. Theadded stress to the residual limb can exacerbate common complications such as neuroma, edemaand ulceration. Compensatory mechanisms adopted to account for the loss of balance andstability created by the poor interface between interface foot and ground can result in aprolonged and continuous physiological burden upon lower back, residual joints and muscles.These factors diminish the quality of life and confidence when using the prosthesis and pose agreater risk to safety. The Echelon Foot addresses the issue through utilizing hydraulic fluid tomimic the way muscle adapts during stance phase and the variable anterior-posterior tilt will selfalign automatically on contact to compensate for the changes of the surface terrain.
The physiological ramifications of the conventional ankle-foot system can expose the amputee toincreased risk of stumbling or falls which are further compounded by the fact that many currentprosthetic feet do not adopt a dorsi flexed position or comply with uneven ground (seefig 2). Theloss of this natural mechanism results in a loss of confidence in walking and amputees may adoptpathological gait deviations (e.g. vaulting and circumduction are common examples). Thusreducing the level of rehabilitation and restoration to normal activities of daily living.
DF = Dorsi Flexion, PF = Plantar Flexion
DF Echelon; ground clearance during swing phase PF DF Fixed Ankle-Foot PF Fig.2
Sincerely,